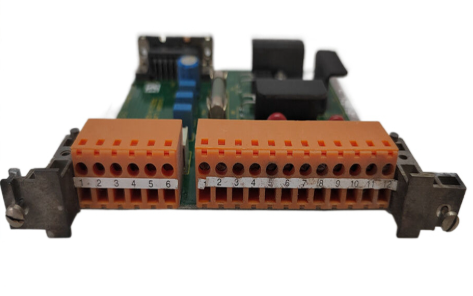
AB 1785-L20C15 ControlNet PLC-5 Programmable Controllers
AB 1785-L20C15 ControlNet PLC-5 Programmable Controllers
Installation Process
Pre-preparation: Check the processor package and make sure the accessories are complete, including the processor, battery, and related documents. Prepare the tools and equipment needed for installation, such as I/O chassis, power supply, screwdriver, etc., and record the Ethernet hardware address.
Installation operation: Pay attention to the model and operation specification when installing the battery to prevent electrostatic discharge. Set the I/O chassis back panel switches, configuration plugs and keystrip to select the DH+ station address, serial interface, and ControlNet network address. When plugging the processor into the I/O chassis, be sure to operate it without power to avoid electrical arcing. When connecting remote I/O, DH+, and ControlNet networks, follow cable length and connection specifications and use appropriate terminating resistors.
System planning and use
ControlNet I/O Principle: The ControlNet system enables high-speed, repeatable, and deterministic I/O transfer, supporting the coexistence of control and message information on the same physical medium. Data transfers are scheduled and unscheduled, with scheduled data transfers being continuous and asynchronous for ladder logic program scans, and unscheduled data transfers being used in scenarios where determinism is not required.
Connections and Mapping: introduces the various connection types, such as exclusive owner, input-only, listen-only, and redundant owner connections, as well as the rules for combining them.I/O Mapping involves the creation and maintenance of I/O mapping tables, designating storage locations for the different types of I/O data transfers, as well as reserving space for non-ControlNet I/O.
Optimisation strategy: The use of the I/O image table can be optimised by reasonably arranging the position of the I/O modules, such as placing the less used module types on the left side, and placing the modules that do not need the space of the I/O image table on the right side. There are two methods of optimising complementary without slot and optimising complementary with slot, which are often used in combination in practical applications.
Software Configuration and Programming
Software tools: RSNetWorx for ControlNet software is used to define network parameters and monitor the status of I/O mapping entries; RSLogix 5 software is used to input user programme files, configure modules, etc.; RSLinx software provides the network interface and polls network devices.
Project Operation: When uploading and downloading software projects, ensure that the ControlNet configuration information in the RSLogix 5 project file and the RSNetWorx project file is consistent. Once downloaded, you can use the RSNetWorx software to perform verification activities such as verifying keeper signatures and scanner signatures.
Command usage: ControlNet supports various commands, such as the Message (MSG) command for sending message commands within the network, which can be used for multi-hop communication; the ControlNet I/O Transfer (CIO) command for non-discrete I/O data transfer; and the Immediate Data Input (IDI) and Immediate Data Output (IDO) commands, etc., which have their own scenarios and methods of usage. There are also Immediate Data Input (IDI) and Immediate Data Output (IDO) instructions.
Monitoring and Troubleshooting
Status monitoring: The general operation status of the processor can be understood through the various status indicators on the processor, such as BATT, PROC, FORCE, COMM, etc.; the ControlNet status indicator reflects the operation status of the ControlNet network; and the DH+/RIO status indicators are used to monitor the status of the data highway and the remote I/Os.
Troubleshooting: The common fault codes and their meanings are introduced, for example, 200 indicates that the ControlNet scheduling output data is lost and it is necessary to check whether there is any electrical noise in the network. Corrective action is provided for each fault code.
Technical Specifications and References
Processor specifications: covers the electrical, environmental, mechanical, and communication parameters of the processor, such as backplane current, operating temperature, network update time, etc. It also introduces the available ink cartridges, batteries, memory modules, and so on.
Status File and Instruction Set: The contents stored in each word of the processor status file are described in detail, including arithmetic flags, processor status and flags, and fault codes. The instruction set of ControlNet is introduced, including I/O transfer instructions, message instructions, immediate data I/O instructions, etc., as well as the execution time and memory requirements of the instructions.
Performance Advantages
Efficient and Reliable Communication Performance
High-speed deterministic transmission: ControlNet network is designed for high-speed, repeatable and deterministic I/O transmission, ensuring stable coexistence of control and message information on the same physical medium. In industrial production scenarios, for time-sensitive control commands and real-time data acquisition, it can ensure the timeliness and accuracy of data transmission and avoid production failures caused by delayed or unstable data transmission. In automotive production lines, a large amount of sensor data and equipment control commands are transmitted through the ControlNet network, and its deterministic transmission characteristics ensure the accurate operation of the production line.
Multiple communication methods: A variety of communication methods are supported, including Scheduled Data-Transfer Operations (continuous and asynchronous in ladder logic programme scanning) and Unscheduled Data-Transfer Operations (for scenarios with non-deterministic requirements). This flexible communication mechanism allows the controller to choose the most appropriate communication method for different application requirements, which not only meets the needs of real-time control, but also handles non-deterministic messaging such as programming devices and human-machine interface (HMI) devices, and improves the overall communication efficiency of the system.
Powerful data processing capabilities
Efficient data transfer mechanism: Both discrete I/O data transfer and non-discrete I/O data transfer can be performed in an efficient manner. Discrete I/O data transfers can be configured in the I/O map table for deterministic and repeatable operations; non-discrete I/O data transfers can be configured in the I/O map table or updated using the ControlNet I/O Transfer (CIO) instruction, and have the same priority as discrete I/O data transfers, which effectively improves the speed and efficiency of data processing. This effectively improves the speed and efficiency of data processing. The controller's non-discrete I/O data transfer capability meets the high demand for real-time processing of large amounts of analogue data in chemical production processes.
Supports multi-processor control: multiple ControlNet PLC-5 processors can update the I/O adapters at the same time, and any processor can control the adapters on the network, send CIO commands, and carry out peer-to-peer communication, which realises distributed control and cooperative work of the system, enhances the overall data processing capability and control flexibility of the system, and is suitable for multi-node control of large-scale complex industrial systems. It is suitable for multi-node control of large and complex industrial systems.
Flexible Configuration
Flexible I/O mapping: I/O mapping is highly flexible, users can map I/O data into I/O image table or DIF/DOF file according to the actual demand, and the mapping position and size of input and output data can be adjusted according to the specific situation. This flexibility enables the controller to adapt to different I/O device layouts and data processing requirements, improving the adaptability and scalability of the system configuration. In industrial automation projects of different sizes, the I/O mapping can be flexibly adjusted according to the number and type of I/O devices to meet the specific needs of the project.
Optimized I/O Configuration: A variety of methods are provided to optimize I/O configuration, such as optimizing the use of I/O image table, which can make full use of I/O resources and reduce the waste of resources by adjusting the location of modules and choosing appropriate addressing modes. In practical applications, according to the I/O demand and resources of the system, you can choose to optimise the slotless complementary or optimise the slotted complementary method to improve the efficiency of I/O resources.
Easy Diagnosis and Maintenance
Comprehensive Fault Diagnosis: Equipped with a perfect fault diagnosis mechanism, it can quickly and accurately determine the system's operation status and fault types through the various status indicators (such as BATT, PROC, FORCE, COMM, etc.) on the processor, as well as the ControlNet status indicator and the DH+/RIO status indicator. Combined with detailed fault codes (such as those stored in S:12 in the processor status file), it can provide in-depth understanding of the cause of the fault, and provide strong support for troubleshooting and repair. When a system failure occurs, technicians can quickly locate the point of failure and shorten troubleshooting time based on the indicator status and fault codes.
Convenient monitoring and maintenance: The configuration and status of the ControlNet network can be comprehensively monitored with software tools such as RSNetWorx for ControlNet, RSLogix5, and RSLinx, which can be used to define network parameters and monitor the status of I/O map entries; RSLogix5 can be used to monitor ControlNet diagnostic files and manage user programme files; RSLinx can be used to poll network devices and monitor station diagnostic information. The coordinated use of these software tools facilitates the daily maintenance and management of the system, and improves the reliability and stability of the system.
- ABB
- General Electric
- EMERSON
- Honeywell
- HIMA
- ALSTOM
- Rolls-Royce
- MOTOROLA
- Rockwell
- Siemens
- Woodward
- YOKOGAWA
- FOXBORO
- KOLLMORGEN
- MOOG
- KB
- YAMAHA
- BENDER
- TEKTRONIX
- Westinghouse
- AMAT
- AB
- XYCOM
- Yaskawa
- B&R
- Schneider
- Kongsberg
- NI
- WATLOW
- ProSoft
- SEW
- ADVANCED
- Reliance
- TRICONEX
- METSO
- MAN
- Advantest
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bently
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- Beijer
- Moxa
- Rexroth
- Johnson
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- Application field
- XP POWER
- CTI
- TRICON
- STOBER
- Thinklogical
- Horner Automation
- Meggitt
- Fanuc
- Baldor
- SHINKAWA
- Other Brands