The "Top Ten Advances in China's Life Sciences" in 2021 was announced
On January 10, the Life Science Society of the China Association for Science and Technology jointly announced to the society the results of the "Top Ten Progress in China's Life Sciences" in 2021.
Based on the principle of "fairness, fairness and openness", the selection of "Top Ten Progress in China's Life Sciences" in 2021 will continue the way of classifying and evaluating project achievements by knowledge innovation and technological innovation, organizing member societies to recommend them, and selecting them by senior experts in the fields of life science, biotechnology and clinical medicine. After review by the Presidium of the Association of Life Sciences of the China Association for Science and Technology, the results of 8 knowledge innovation and 2 technology innovation projects were finally determined as the "Top Ten Progress in China's Life Sciences" in 2021.
The selected projects in this year's "Top Ten Advances in Life Sciences in China" have the characteristics of outstanding originality and great social significance. The specific results are as follows (in no particular order).
1. Artificial synthesis from carbon dioxide to starch
Starch is the most important component of grain and also an important industrial raw material. The Tianjin Institute of Industrial Biotechnology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, together with the Dalian Institute of Chemical Compounds and other units, extracted the chemical essence of natural photosynthesis, designed and created an unnatural pathway from carbon dioxide to starch synthesis from the ground up, and solved scientific problems such as ab initio calculation of pathway metabolic flow, design and assembly of key enzyme elements, and precise regulation of biochemical pathways. The 11-step reaction coupled with biocatalysis and chemical catalysis overturns the complex biochemical process of natural photosynthesis to fix carbon dioxide to synthesize starch, and realizes the artificial total synthesis of carbon dioxide to starch for the first time in the world, with energy efficiency and rate exceeding corn and other crops, breaking through the limitations of natural photosynthesis, and opening a window for the workshop manufacturing of starch. It also provides a new idea for the synthesis of complex molecules from carbon dioxide. It has been strongly echoed internationally and is considered a landmark breakthrough that will have a transformative impact in the next generation of bio-manufacturing and agricultural production.
The results are in the journal Science (2021,373 (6562):1523-1527).

2. Genetic innovation mechanism of vertebrate evolution from aquatic to terrestrial
The transition from aquatic to terrestrial vertebrates more than 400 million years ago was a major event in the evolution of terrestrial vertebrates, including humans, but little has been known about the genetic innovation mechanism of this major event for a long time.
The team of Wang Wen and Wang Kun from the School of Ecology and Environment of Northwestern Polytechnical University, in collaboration with He Shunping from the Institute of Hydrobiology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and Zhang Guojie from the Kunming Institute of Zoology, found that the ancestors of bony fish had evolved a preliminary genetic basis related to terrestrial adaptability, which was further strengthened in the meal-finned fish represented by lungfish, and finally perfected and successfully landed on land. According to Science, the results reveal "hidden genetic secrets of aquatic to terrestrial evolution in live fish". Professor Per Alhberg, a member of the Swedish Academy of Sciences, wrote that the results overcome the challenges of fossil research to study soft tissue organs and physiological problems, Neil Shubin, a member of the American Academy of Sciences and an internationally renowned vertebrate landing research expert, wrote that the results "provide key cognitive and long-expected data" for understanding the study of vertebrates from aquatic to terrestrial life.
Two research papers on this result were published as cover stories in the journal Cell, 2021,184 (5):1362-1376; 1377-1391).
Major genetic innovations in aquatic to terrestrial evolution of vertebrates
3. Mechanism of the novel coronavirus escaping host natural immunity and antiviral drugs
The outbreak of the novel coronavirus pneumonia has lasted for two years, and the continuous emergence of mutant strains poses an urgent need for the development of broad-spectrum drugs. The "transcriptional replication complex" consists of viral replicase, which is responsible for the whole process of viral transcription and replication. It is highly conserved in each mutant strain and is the core target of developing broad-spectrum drugs.
The research group of Academician Rao Zihe and Professor Lou Zhiyong of Tsinghua University has discovered and reconstructed the complete composition of the novel coronavirus transcription and replication machine for the first time in the world. On this basis, the key enzyme molecules of viral mRNA "cap" maturation were identified for the first time, which answered the unresolved questions in coronavirus research for nearly 30 years. Moreover, the molecule is highly conserved in various mutant strains and has no homologues in human beings, providing a new target for the development of novel and safe broad-spectrum antiviral drugs. At the same time, they also found for the first time that the virus "removes" the right base and antiviral drugs in a "trans-traceback" way, clarifying the molecular mechanism of the adverse effect of drugs such as Redesivir, and providing a key scientific basis for optimizing antiviral drugs targeting polymerase.
These findings are published in the journal Cell, 184(1):184-193; Cell, 184(13):3474-3485).
mRNA capping status and replication correction status of the novel coronavirus transcriptional replication complex
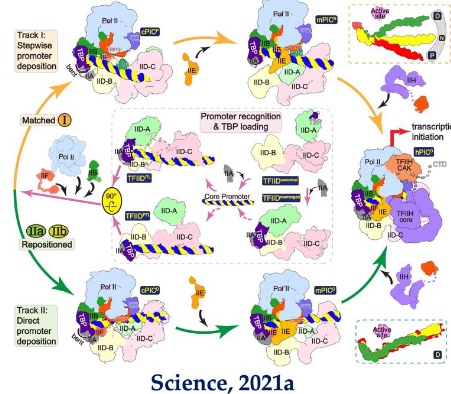
4. Transcription initiation super complex assembly mechanism
The transcriptional initiation supercomplex is the core of the transcriptional step in the central law, which is of great significance for understanding the regulation of gene expression and related physiological and pathological processes, and has been the core and frontier of international life science research.
The team of Xu Yanhui at Fudan University analyzed the three-dimensional structure of the transcription initiation complex PIC and its transcription initiation super complex composed of Mediator (Mediator), systematically demonstrated the whole process of the transcription machine to recognize and complete the assembly of different types of promoters, and revealed why transcription occurs on the promoters of almost all genes. Overturning the traditional understanding of promoter recognition and transcription initiation complex assembly, we elucidate the mechanism of Mediator promoting PIC assembly and transcriptional activation.
These results are published in two long papers in the journal Science 372, eaba8490; Science 372, eabg0635), one of which was selected for the cover article in the journal Science, titled "How Transcription Begins."
5. A new model of high efficiency and low toxicity therapy to improve the curative effect of middle and advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma
Nasopharyngeal cancer is a tumor with "Chinese characteristics", accounting for half of the new cases in the world. Small residual tumors in the whole body after radiotherapy are the root cause of treatment failure, and due to the poor physical condition of patients after radiotherapy, it is difficult to tolerate the previous high-intensity traditional chemotherapy (the completion rate is only about 40%-50%), which becomes the bottleneck restricting the improvement of curative effect.
Ma Jun's research team at the Cancer Prevention and Control Center of Sun Yat-sen University proposed a metronomic chemotherapy mode of small-dose, long-term oral cytotoxic drug capecitabine, which can continuously inhibit tumor through anti-angiogenesis, killing tumor stem cells and other mechanisms, while improving body tolerance. A multi-center, prospective clinical study led by Professor Jun Ma found that the use of "capecitabine beat chemotherapy" after radiotherapy can significantly reduce the risk of failure by 45%, and the incidence of serious side effects is reduced by three-fifths, and the completion rate is 74%. At the same time, the oral use of capecitabine is convenient and easy to promote to the grassroots.
Thus, the study broke the bottleneck of the efficacy of traditional chemotherapy and established a new standard for the treatment of nasopharyngeal cancer that is internationally leading, efficient, low toxic and simple.
A new therapeutic model with high efficiency and low toxicity of capecitabine beat chemotherapy
6. Rapid de novo domestication of allotetraploid wild rice
The current cultivated rice is the result of thousands of years of artificial domestication from the ancestral diploid wild rice, accompanied by a decrease in genetic diversity and the loss of excellent genes. The team led by Jiayo Li and his collaborators at the Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, proposed for the first time a new strategy for rapid de nivation of allotetraploid wild rice, which provides a new feasible path for coping with future food crises and opens up a new breeding direction. Using this strategy as the blueprint, the project selected a tetraploid tall culm wild rice resource, established an efficient tissue culture regeneration, genetic transformation and gene editing system, assembled a high-quality reference genome, and successfully created a new tetraploid rice material with different types of improved grain setting, awn, plant height, grain length, stalk thickness, growth period, etc., breaking through all technical bottlenecks. It is proved that rapid de novo domestication strategy of allotetraploid wild rice is highly feasible. The successful cultivation of new tetraploid rice crops in the future is expected to bring a subversive revolution to world food production.
7. Cross-species recognition and molecular mechanism of coronaviruses
In the last 20 years, humanity has suffered three major outbreaks caused by coronaviruses. Most coronavirus-infecting humans originate from animals, and we have found that the transmission of viruses from person to person is often delayed, and the threshold of disease prevention and control needs to move forward in "time".
A team of Academician Gao Fu of the Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences has established efficient methods to evaluate the cross-species recognition ability of coronaviruses, and used these methods to assess the potential risk of cross-species transmission of bat-derived coronaviruses RaTG13 and pangolin-derived coronaviruses GD/1/2019 and GX/P2V/2017. The molecular mechanism of cross-species recognition was also clarified. The study found that the above three coronaviruses have the potential risk of cross-species transmission, suggesting that we should continue to monitor animal-derived coronaviruses to prevent new coronaviruses from causing outbreaks, and at the same time provide a molecular basis for understanding virus evolution.
The results have been published in the journal Cell (2021, 184(13):3438-3451.e10) and the Journal of the European Molecular Biology Organization (EMBO J, 2021, 41(1):e109962).
8. Uncover the mystery of long-distance bird migration
Bird migration is one of the most watched natural wonders. The formation process, maintenance mechanism and future trend of migration routes under climate change, as well as the genetic basis of migration strategies, have been the focus and difficulty of academic research.

A team from the Institute of Zoology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), Zhan Xiangjiang, spent 12 years integrating years of satellite tracking data and population genomic information to establish a continent-scale migration research system for Arctic peregrinus Falco peregrinus. The researchers elucidated the role of climate change in the formation, maintenance and future trends of bird migration routes, and found that a gene associated with memory ability, ADCY8, was positively selected in populations of peregrine falcons that migrated over longer distances, suggesting that long-term memory may be an important basis for long-distance migration in birds. The study fully integrates new research methods such as remote sensing satellite tracking, genomics, and neurobiology, demonstrating the key role of interdisciplinary innovative research in answering major scientific questions.
The work was published as a cover article in the journal Nature (2021,591 (7849):259-264) and was named one of 12 annual reviews by Nature Ecological Evolution.
The cover of Nature magazine and the Arctic Peregrine falcon migration route
9, interference single molecule positioning microscope
The physiological processes of cells are carried out by nanoscale biomolecules, so a deeper understanding of life activities requires imaging techniques with nanoresolution. The technical research team composed of Academician Xu Tao Group and Ji Wei Group of Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, has been focusing on the research of breaking through the resolution of optical microscopic imaging. The pre-developed ROSE microscope has improved the lateral (X-Y) resolution to the nanometer level (Nature Methods, 2019). Based on the innovative principle of interference localization, ROSE-Z microscope was developed, which further broke through the axial (Z) resolution and could resolve the nanoscale subcellular structure, providing a powerful tool for life science research. The research shows that the optical microscope has entered the era of nanometer resolution, and Chinese scientists have the ability of interdisciplinary technological innovation in this field, and the new super-resolution imaging equipment with independent intellectual property rights is in the leading position in the world.
The results are published in the journal Nature Methods (2021, 18:369-373).
The hollow structure of cell microtubules was analyzed by interferometric single molecule localization microscopy
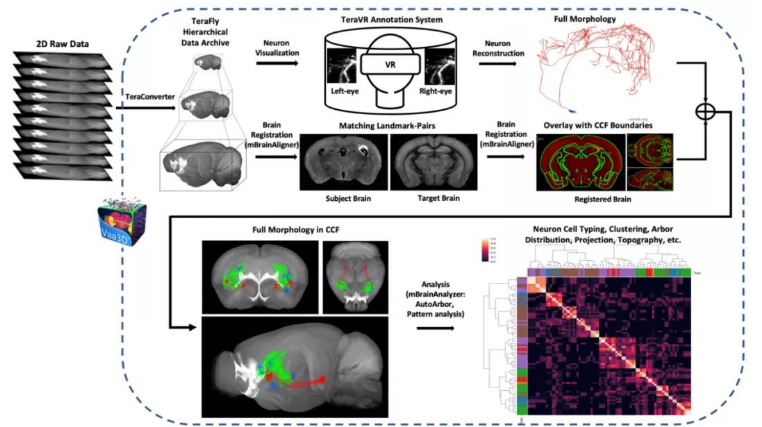
10. Whole brain single neuron diversity research and informatics big data platform
Single-neuron precision whole-brain mapping is crucial to understanding the brain. The team of Peng Hanchuan, Gu Zhongze and Xie Wei from the Institute of Brain Science and Intelligent Technology of Southeast University established the world's first complete whole brain single neuron resolution big data and informatics platform and applied it to the whole mouse brain research, and carried out high-throughput neuron reconstruction, whole brain mapping and intelligent data mining for the whole brain three-dimensional image data of neurons. Based on this platform, we produced the largest single cell neuron morphological dataset in the world, revealing for the first time the long-term projection rule and the diversity of neuron morphological subclasses on the basis of molecular level. It continues to play an important role in the study of brain cell classification and function, brain connectivity circuits, whole-brain large-scale simulation, brain-like computing, and new artificial intelligence algorithms and systems based on biological brains. This achievement realizes the first PB-level hyperscale brain big data platform combined with hardware and software and the first complete single cell morphology data production pipeline, which quantitatively proves that complete single cell anatomy analysis is crucial for the identification of nerve cell types.
The main research results were published in Nature (598:174-181;). And "Nature Methods" (19:111-118).
Complete neuronal morphological imaging, reconstruction, registration, analysis platform and process in the whole brain
According to reports, since 2015, the Association of Life Science Societies of China Association for Science and Technology has carried out the annual "Top Ten Progress in China's life sciences" selection work, aiming to promote life science research and technological innovation, and fully demonstrate and publicize major scientific and technological achievements in the field of life science in China. At present, the selection activity has been carried out for 7 consecutive years. After the selection results are announced every year, the selected project experts are invited to write and publish popular science books, and exchange meetings and popular science reports for teenagers are held to reveal new mysteries of life science to the public, provide new ideas for the development of new life science technologies, new medical breakthroughs and the development of bioeconomy, and greatly improve the social influence of life science and related technologies.
- ABB
- General Electric
- EMERSON
- Honeywell
- HIMA
- ALSTOM
- Rolls-Royce
- MOTOROLA
- Rockwell
- Siemens
- Woodward
- YOKOGAWA
- FOXBORO
- KOLLMORGEN
- MOOG
- KB
- YAMAHA
- BENDER
- TEKTRONIX
- Westinghouse
- AMAT
- AB
- XYCOM
- Yaskawa
- B&R
- Schneider
- Kongsberg
- NI
- WATLOW
- ProSoft
- SEW
- ADVANCED
- Reliance
- TRICONEX
- METSO
- MAN
- Advantest
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bently
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- Beijer
- Moxa
- Rexroth
- Johnson
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- Application field
- XP POWER
- CTI
- TRICON
- STOBER
- Thinklogical
- Horner Automation
- Meggitt
- Fanuc
- Baldor
- SHINKAWA
- Other Brands




































































































































