The "Top Ten Advances in China's Life Sciences" in 2021 was announced
These findings are published in the journal Cell, 184(1):184-193; Cell, 184(13):3474-3485).
mRNA capping status and replication correction status of the novel coronavirus transcriptional replication complex
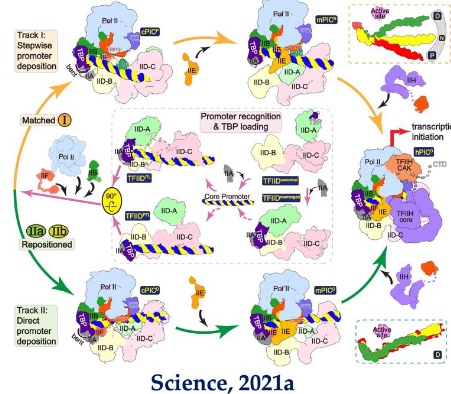
4. Transcription initiation super complex assembly mechanism
The transcriptional initiation supercomplex is the core of the transcriptional step in the central law, which is of great significance for understanding the regulation of gene expression and related physiological and pathological processes, and has been the core and frontier of international life science research.
The team of Xu Yanhui at Fudan University analyzed the three-dimensional structure of the transcription initiation complex PIC and its transcription initiation super complex composed of Mediator (Mediator), systematically demonstrated the whole process of the transcription machine to recognize and complete the assembly of different types of promoters, and revealed why transcription occurs on the promoters of almost all genes. Overturning the traditional understanding of promoter recognition and transcription initiation complex assembly, we elucidate the mechanism of Mediator promoting PIC assembly and transcriptional activation.
These results are published in two long papers in the journal Science 372, eaba8490; Science 372, eabg0635), one of which was selected for the cover article in the journal Science, titled "How Transcription Begins."
5. A new model of high efficiency and low toxicity therapy to improve the curative effect of middle and advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma
Nasopharyngeal cancer is a tumor with "Chinese characteristics", accounting for half of the new cases in the world. Small residual tumors in the whole body after radiotherapy are the root cause of treatment failure, and due to the poor physical condition of patients after radiotherapy, it is difficult to tolerate the previous high-intensity traditional chemotherapy (the completion rate is only about 40%-50%), which becomes the bottleneck restricting the improvement of curative effect.
Ma Jun's research team at the Cancer Prevention and Control Center of Sun Yat-sen University proposed a metronomic chemotherapy mode of small-dose, long-term oral cytotoxic drug capecitabine, which can continuously inhibit tumor through anti-angiogenesis, killing tumor stem cells and other mechanisms, while improving body tolerance. A multi-center, prospective clinical study led by Professor Jun Ma found that the use of "capecitabine beat chemotherapy" after radiotherapy can significantly reduce the risk of failure by 45%, and the incidence of serious side effects is reduced by three-fifths, and the completion rate is 74%. At the same time, the oral use of capecitabine is convenient and easy to promote to the grassroots.
Thus, the study broke the bottleneck of the efficacy of traditional chemotherapy and established a new standard for the treatment of nasopharyngeal cancer that is internationally leading, efficient, low toxic and simple.
A new therapeutic model with high efficiency and low toxicity of capecitabine beat chemotherapy
6. Rapid de novo domestication of allotetraploid wild rice
The current cultivated rice is the result of thousands of years of artificial domestication from the ancestral diploid wild rice, accompanied by a decrease in genetic diversity and the loss of excellent genes. The team led by Jiayo Li and his collaborators at the Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, proposed for the first time a new strategy for rapid de nivation of allotetraploid wild rice, which provides a new feasible path for coping with future food crises and opens up a new breeding direction. Using this strategy as the blueprint, the project selected a tetraploid tall culm wild rice resource, established an efficient tissue culture regeneration, genetic transformation and gene editing system, assembled a high-quality reference genome, and successfully created a new tetraploid rice material with different types of improved grain setting, awn, plant height, grain length, stalk thickness, growth period, etc., breaking through all technical bottlenecks. It is proved that rapid de novo domestication strategy of allotetraploid wild rice is highly feasible. The successful cultivation of new tetraploid rice crops in the future is expected to bring a subversive revolution to world food production.
7. Cross-species recognition and molecular mechanism of coronaviruses
In the last 20 years, humanity has suffered three major outbreaks caused by coronaviruses. Most coronavirus-infecting humans originate from animals, and we have found that the transmission of viruses from person to person is often delayed, and the threshold of disease prevention and control needs to move forward in "time".
A team of Academician Gao Fu of the Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences has established efficient methods to evaluate the cross-species recognition ability of coronaviruses, and used these methods to assess the potential risk of cross-species transmission of bat-derived coronaviruses RaTG13 and pangolin-derived coronaviruses GD/1/2019 and GX/P2V/2017. The molecular mechanism of cross-species recognition was also clarified. The study found that the above three coronaviruses have the potential risk of cross-species transmission, suggesting that we should continue to monitor animal-derived coronaviruses to prevent new coronaviruses from causing outbreaks, and at the same time provide a molecular basis for understanding virus evolution.
- ABB
- General Electric
- EMERSON
- Honeywell
- HIMA
- ALSTOM
- Rolls-Royce
- MOTOROLA
- Rockwell
- Siemens
- Woodward
- YOKOGAWA
- FOXBORO
- KOLLMORGEN
- MOOG
- KB
- YAMAHA
- BENDER
- TEKTRONIX
- Westinghouse
- AMAT
- AB
- XYCOM
- Yaskawa
- B&R
- Schneider
- Kongsberg
- NI
- WATLOW
- ProSoft
- SEW
- ADVANCED
- Reliance
- TRICONEX
- METSO
- MAN
- Advantest
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bently
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- Beijer
- Moxa
- Rexroth
- Johnson
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- Application field
- XP POWER
- CTI
- TRICON
- STOBER
- Thinklogical
- Horner Automation
- Meggitt
- Fanuc
- Baldor
- SHINKAWA
- Other Brands




































































































































