SIEMENS S7-300 PLC Beginner's Practice: From Hardware Installation to Program Debugging
SIEMENS S7-300 PLC Beginner's Practice: From Hardware Installation to Program Debugging
The Siemens SIMATIC S7-300 series programmable logic controller (PLC) is a classic product in the field of industrial automation, widely used in mechanical control, process automation, and production line scheduling. For technicians who are new to the field of industrial control, mastering a complete set of PLC system construction, configuration, and debugging processes is the key first step towards automation practice. This article will be based on the "S7-300 Beginner's Guide" and use the example of "conveyor belt control" to systematically explain the entire process from hardware installation, electrical wiring, software configuration to program debugging, providing readers with a clear and replicable learning path.
Project Overview: A Classic Beginner's Example
This example aims to achieve the start stop and direction control of the conveyor motor, using CPU 312C (order number 6ES7312-5BE03-0AB0) as the control core. This CPU integrates 10 digital inputs and 6 digital outputs, and has a built-in MPI communication interface, suitable for small and medium-sized automation tasks. The project aims to help learners understand the basic components of PLC systems through practical operations, including power modules CPU、 Signal module (integrated in this example), input device (button), output device (motor), and programming debugging tool.
It takes about 1 hour to complete this example, provided that you have basic Windows operating skills and electrical knowledge. The entire process strictly follows safety regulations and emphasizes the importance of being operated by "qualified professionals". All operations must be carried out under power-off
Hardware preparation and installation: Building the physical foundation of the system
1. Component List and Safety Warning
At present, the following core components need to be prepared for implementation:
S7-300 Startup Kit: Includes installation rails, CPU 312C, SIMATIC Micro Memory Card (MMC), terminal block, and PC Adapter USB.
Additional components: power module (such as 6ES7307-1EA00-0AA0), 24V momentary contact switch (4 pieces), motor (optional), installation cables and tools.
Safety first: The guidelines emphasize electrical safety multiple times. All wiring and installation must be carried out in the event of a power outage. Before powering on, ensure that the CPU is in STOP mode and comply with safety standards such as IEC 204.
2. Mechanical installation and grounding
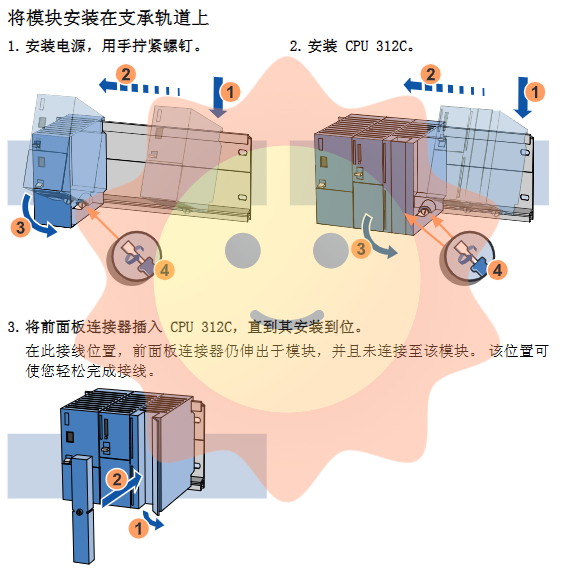
Installation begins with fixing the S7-300 mounting rail. The guide rail should be securely installed with M5 screws and ensure at least 40mm of space above and below to meet heat dissipation and maintenance requirements. The key step is protective grounding: a yellow green grounding cable with a cross-sectional area of not less than 10 mm ² must be used to reliably connect the guide rail to the system's grounding terminal to ensure that all modules have a unified reference potential and resist interference and electric shock risks.
Subsequently, install the power module and CPU 312C in sequence. The module is mounted on the guide rail through a U-shaped hook on the back, and then fixed with screws. The front panel connector should be inserted into the "pre wired" position before wiring is completed to facilitate wire connection.
3. Electrical wiring: Building control circuits
Wiring is the bridge that connects the logical and physical world. This project requires the construction of two circuits:
Input circuit: Connect one end of the four momentary contact switches (corresponding to "start", "stop", "clockwise", "counterclockwise") to the DI (digital input) terminal of the CPU (such as 10.0 to 10.3), and connect the other end to a 24V DC power supply. The switch status will be visually displayed through LED.
Output circuit: Connect the DO (digital output) terminals of the CPU (such as Q0.0 and Q0.1) to the control terminal of the motor driver or relay to drive the motor in both forward and reverse directions. If a real motor is not used, the status can be observed through the LED on the output terminal.
All wires should be equipped with insulation sleeves using crimping tools to ensure a secure connection and good insulation. After completion, push the front panel connector to the final position and close the front cover.
Software environment setup: STEP 7 Lite and communication configuration
After the hardware is ready, it is necessary to set up a programming and communication environment on the PC.
1. Software installation
STEP 7 Lite V3.0: This is an entry-level configuration and programming software provided by Siemens, which can be downloaded and installed for free from the official website. It includes functions such as project management, hardware configuration, ladder diagram programming, and online monitoring.
PC Adapter USB Driver: This adapter is used to connect the USB port of the PC to the MPI interface of the CPU, and is a key communication bridge for programming and debugging. Please install the CD or official website driver correctly.
2. Interface settings
After installation, the PG/PC interface needs to be set up in the Windows Control Panel or STEP 7 Lite. Select 'PC Adapter (MPI)' as the access path and configure it as a USB interface in the properties. This step ensures the establishment of a stable MPI communication connection between the PC and CPU 312C.
STEP 7 Lite Project Configuration: Mapping Hardware in Software
In automation engineering, hardware configuration is a crucial step, which is the process of defining actual physical modules and their parameters in programming software.
1. Create project and hardware configuration
After opening STEP 7 Lite, first create a new S7-300 site. The software interface will display virtual installation rails. Subsequently, based on the actual hardware, drag and drop from the hardware directory in sequence:
Power module (such as PS 307 5A)
CPU 312C (requires accurate selection of order number and firmware version)
The software will automatically assign I/O addresses (such as I0.0-I0.3, Q0.0-Q0.5) to the module, which is the basis for subsequent programming addressing.
2. CPU parameter settings
Double click on the CPU in the rack to enter the property settings. An important security parameter is' retention memory '. To prevent uncontrolled restart of the device after power failure, it is recommended to set the number of retention storage bits (such as M memory) to 0 in this example. This means that after a power outage, all intermediate states will be lost and the system must be restarted.
3. Establish online connection and download configuration
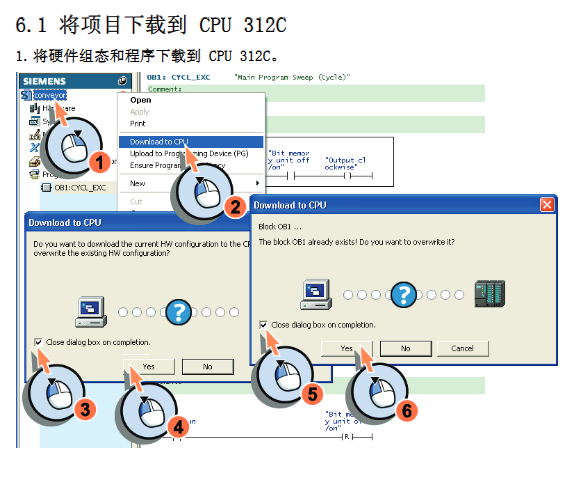
After connecting the hardware via PC Adapter USB, click on "Establish Online Connection" in STEP 7 Lite. After successful connection, the status bar will display the running status of the CPU (such as STOP).
Before downloading, it is best to perform a "memory reset" on the CPU to clear the original configuration and program. Subsequently, download the edited hardware configuration to the CPU. After downloading, you can use the "online and offline comparison" function to ensure that the configuration in the software is completely consistent with the actual configuration in the CPU, which is the basis for the correct execution of the program.
Ladder diagram programming and debugging: implementing control logic
1. Understanding of program structure
The control logic is written in the organizational block OB1, which is the main program for CPU loop execution. This example program uses ladder diagram (LAD) language, which is intuitive and easy to read. The program consists of multiple "networks", each containing contacts (representing input conditions) and coils (representing output actions), connected through logical relationships such as "and" or ".
2. Program logic analysis
For conveyor belt control, the program needs to implement:
Start stop circuit: Press the "Start" button (I0.0), the motor runs (Q0.0) and locks itself; Press the 'Stop' button (I0.1) to stop the motor.
Direction interlock: The "clockwise" (I0.2) and "counterclockwise" (I0.3) buttons interlock to ensure that only one direction signal is valid at the same time, driving different output points (such as Q0.3 and Q0.5) respectively.
3. Download and test run
Download the complete project (including hardware configuration and program) to the CPU. Then turn the mode selection switch on the CPU to the RUN position, and the RUN LED will light up.
Subsequently, functional testing will be conducted:
Press the green "start" button and observe that the corresponding input LED lights up, while the motor operation output LED lights up.
Press the "clockwise" button, the motor direction output LED changes, simulating direction switching.
Press the red 'stop' button to turn off all output LEDs.
The entire process intuitively demonstrates the complete PLC control flow of "input (button) → program logic processing → output (motor control)".
Fault diagnosis and resource extension
1. Basic diagnosis
If the system is abnormal, you can troubleshoot from the following points:
Power supply: Check if the 24V DC power LED is lit.
Communication: Check the LED status of the PC Adapter USB and confirm that the MPI connection is normal.
CPU status: The SF (system fault) LED lights up, usually indicating a configuration error or hardware failure. Details can be viewed through the online diagnostic function of STEP 7 Lite.
I/O status: Force or monitor input/output points in software to determine whether it is an external wiring issue or an internal logic issue.
2. In depth learning resources
After completing the introductory practice, you can deepen your learning through the following resources:
Accompanying documents: online help for STEP 7 Lite (F1), electronic manual for "STEP 7 Lite Beginner's Guide".
Core manual: "S7-300, CPU 31xC and CPU 31x: Installation" explains installation and debugging details; The "Technical Specifications for CPU 31xC and CPU 31x" provide detailed performance parameters.
Network resources: Siemens Automation official website, technical support forum, and online knowledge base, providing a large number of application examples, FAQs, and firmware updates.
- ABB
- General Electric
- EMERSON
- Honeywell
- HIMA
- ALSTOM
- Rolls-Royce
- MOTOROLA
- Rockwell
- Siemens
- Woodward
- YOKOGAWA
- FOXBORO
- KOLLMORGEN
- MOOG
- KB
- YAMAHA
- BENDER
- TEKTRONIX
- Westinghouse
- AMAT
- AB
- XYCOM
- Yaskawa
- B&R
- Schneider
- Kongsberg
- NI
- WATLOW
- ProSoft
- SEW
- ADVANCED
- Reliance
- TRICONEX
- METSO
- MAN
- Advantest
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bently
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- Beijer
- Moxa
- Rexroth
- Johnson
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- Application field
- XP POWER
- CTI
- TRICON
- STOBER
- Thinklogical
- Horner Automation
- Meggitt
- Fanuc
- Baldor
- SHINKAWA
- Other Brands
- UniOP