Motorola MVME162 Embedded Controller
Motorola MVME162 Embedded Controller
Motorola MVME162 is a high-performance VME module embedded controller based on MC68040/MC68LC040 microprocessor, widely used in industrial automation, communication control, experimental systems, OEM embedded development and other fields. Its modular design, rich I/O interfaces, and flexible configuration options make it an ideal core component for complex embedded systems. This article will comprehensively analyze MVME162 from the aspects of hardware architecture, configuration methods, functional characteristics, and system integration.
Product Overview and Model Classification
MVME162 adopts a double-layer VME board structure, equipped with MC68040 (including floating-point coprocessor) or MC68LC040 microprocessor, with a main frequency of 25 MHz. According to different configurations, the controller offers multiple models, covering different memory capacities, interface options, and VME bus support, to meet diverse application needs.
Main models and configuration examples:
MVME162-001:MC68LC040,1MB DRAM,512KB SRAM
MVME162-023:MC68040,4MB DRAM,SCSI,Ethernet,512KB SRAM
MVME162-043:MC68040,8MB DRAM,SCSI,Ethernet,512KB SRAM
All models support up to four Industry Pack (IP) module extensions, with two serial interfaces (EIA-232D/EIA-530) and optional SCSI and Ethernet interfaces.
Detailed explanation of hardware architecture
1. Processor and local bus
MVME162 is equipped with Motorola MC68040 series processors, built-in instruction and data caches, and supports 32-bit synchronous local bus. The bus adopts a priority arbitration mechanism, and the priority from high to low is: 82596CA LAN controller, NCR 53C710 SCSI controller, VME bus MPU。 This design ensures the real-time requirements of high bandwidth peripherals.
2. Memory system
DRAM: Supports 1MB, 4MB, or 8MB capacity, optional parity protection, supports interleaved access to improve performance.
SRAM: 512KB static RAM with battery backup, capable of maintaining data for up to 200 days after power failure.
Flash/EPROM: Onboard 1MB Flash memory, supports booting from Flash or EPROM via J22 jumper selection.
BBRAM and Real Time Clock: Using MK48T08 chip, integrating 8KB non-volatile RAM and real-time clock for system configuration storage and time recording.
3. VME bus interface
Optional VMEchip2 dedicated chip for implementing VME bus interface, supporting:
Master/Slave mode transmission, supporting A16/A24/A32 addresses and D8/D16/D32 data widths
DMA controller, supporting block transfer (BLT) and multi block transfer (MBLT)
System controller functions, including bus arbitration and interrupt handling
No VME bus version available for embedded standalone applications
4. I/O interface expansion
Serial interface: Two serial ports are provided through the Zilog Z85230 controller, supporting asynchronous and synchronous protocols, with a baud rate of up to 38.4 KB/s.
SCSI interface: using NCR 53C710 controller, supporting DMA transfer, suitable for storage devices such as hard drives and tape drives.
Ethernet interface: Intel 82596CA controller implements 10 Mbps Ethernet communication, with MAC address fixed in BBRAM.
Industry Pack interface: Supports up to four IP modules through IPIC chips, providing flexible functional expansion capabilities.
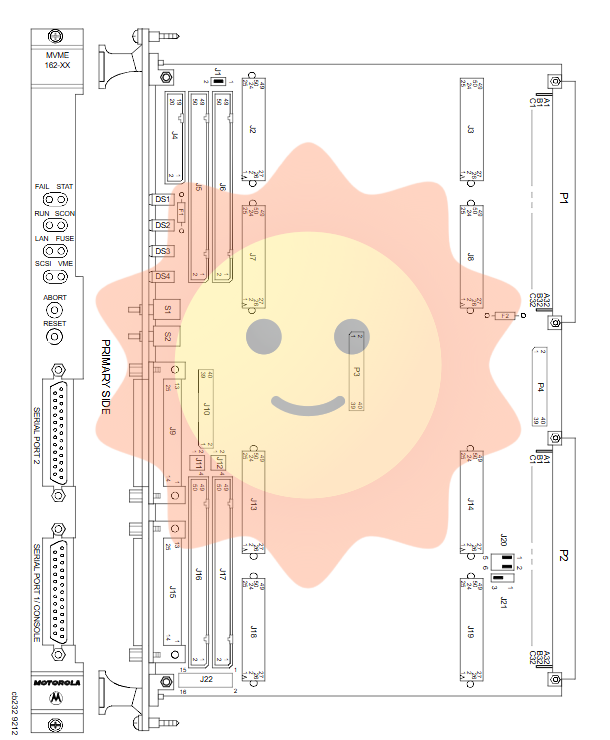
System configuration and installation
1. Hardware configuration jumper
MVME162 provides multiple sets of jumpers for system configuration:
J1: System Controller Selection
J11/J12: Serial port synchronous clock selection
J20: SRAM backup power selection (VMEbus+5VSTDBY or onboard battery)
J21: EPROM Capacity Selection
J22: Universal readable jumper, used for starting source selection, etc
2. Installation steps
SIM module installation: The physical interface of serial port 2 is configured as EIA-232-D or EIA-530 through a pluggable SIM module (SIM05-SIM08).
IP module installation: Up to four IP modules can be installed, and signals are led out through the front and rear panel connectors.
Board installation: It needs to be inserted into the P1/P2 connector of the VME chassis. If used as a system controller, it needs to be placed in Slot 1.
Transition module connection: Connect the serial port through the MVME712 series transition module SCSI、 External interfaces such as Ethernet.
3. Power supply and heat dissipation requirements
Power requirements:+5V (typical 3.5A), ± 12V (100mA each)
Working temperature: 0 ° C to 70 ° C (forced air cooling)
Heat dissipation suggestion: It is recommended that the airflow rate be ≥ 10 CFM to avoid adjacent installation of high-power boards
Software and Debugging Support
1. Firmware and monitoring program
Onboard 162Bug debugging and monitoring firmware, providing:
Memory viewing and modification
Breakpoint setting and program tracking
Assembly/disassembly function
System self-test and I/O debugging support
2. Memory Mapping and Register Programming
MVME162 adopts memory mapped I/O, and all peripheral registers are mapped to a unified address space. For example:
VMEchip2 LCSR:SFFF40000
MCchip control register: SFFF42000
Z85230 SCC register: SFFF45000-SFFF45800
3. Multi processor support
Support multiple MVME162 cards to work together in the same VME system, achieving communication and status synchronization between processors through global CSR.
Performance characteristic analysis
1. Memory access performance
DRAM access: At 25 MHz, non interleaved reads have 4-2-2-2 cycles, while interleaved reads can be increased to 4-1-1-1.
Flash/EPROM access: programmable for 3-10 clock cycles per byte.
DMA transfer: SCSI DMA supports a bandwidth of 44 MB/s, while Ethernet DMA supports a bandwidth of 20 MB/s.
2. Real time and reliability
Watchdog timer: Both MCchip and VMEchip2 integrate a watchdog, which can trigger a system reset or local reset upon timeout.
Local bus timeout: Programmable timeout period (8 µ s to 256 µ s) to prevent bus suspension.
Battery backup system: SRAM and real-time clock are backed up by lithium batteries, with data retention time exceeding 2 years.
3. Scalability and compatibility
Support VMEbus Rev. C1 standard
Compatible with Industry Pack Rev 1.0 specification
Provide a complete driver and debugging toolchain
Application scenarios and system integration suggestions
MVME162 is suitable for the following fields:
Industrial control: real-time data acquisition, motion control, process monitoring
Communication system: protocol conversion, gateway devices, base station control
Experimental testing: Hardware in the loop simulation, data recording, instrument control
Embedded development: customized hardware platform, prototype verification
System integration precautions:
If using the EIA-530 interface, avoid mixing it with the MVME712 transition module as it does not support balanced signals.
In a multiprocessor system, it is necessary to allocate VME interrupts and bus bandwidth reasonably.
In high temperature environments, it is necessary to ensure that the heat dissipation ducts are unobstructed, and low-power IP modules are preferred.
To obtain FCC Class A certification, all external cables must be shielded and grounded.

- ABB
- General Electric
- EMERSON
- Honeywell
- HIMA
- ALSTOM
- Rolls-Royce
- MOTOROLA
- Rockwell
- Siemens
- Woodward
- YOKOGAWA
- FOXBORO
- KOLLMORGEN
- MOOG
- KB
- YAMAHA
- BENDER
- TEKTRONIX
- Westinghouse
- AMAT
- AB
- XYCOM
- Yaskawa
- B&R
- Schneider
- Kongsberg
- NI
- WATLOW
- ProSoft
- SEW
- ADVANCED
- Reliance
- TRICONEX
- METSO
- MAN
- Advantest
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bently
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- Beijer
- Moxa
- Rexroth
- Johnson
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- Application field
- XP POWER
- CTI
- TRICON
- STOBER
- Thinklogical
- Horner Automation
- Meggitt
- Fanuc
- Baldor
- SHINKAWA
- Other Brands





































































































































