Reliance Electric AutoMax Programming Executive V3.5
Reliance Electric AutoMax ® Programming Executor V3.5: Deep Analysis of the Core Software Platform for Distributed Control Systems
In the field of industrial automation and process control, a powerful, reliable, and easy-to-use programming and configuration software platform is the key to unleashing the potential of hardware systems. The AutoMax launched by Reliance Electric ® Distributed control systems, with their modularity, strong real-time performance, and networking capabilities, have been applied in numerous industrial scenarios. As its core programming and project management tool, AutoMax Programming Executive Version 3.5, provides users with a software that runs on Microsoft Windows ™ A complete environment for offline engineering design and online system operation in a graphical interface. This article aims to provide a comprehensive and in-depth technical analysis of the AutoMax programming actuator V3.5, offering a detailed application guide for automation engineers and technicians.
System Overview and Core Architecture
The AutoMax programming executor V3.5 marks a significant shift from early command-line or dedicated environments to modern graphical user interface (GUI) operations. It utilizes the 386 enhanced mode of Windows 3.1 (or higher) to provide engineers with an intuitive and efficient software engineering environment. The core design concept is to hierarchically and modularly manage a complete industrial control application project, mainly reflected in the four level structure of "Library → System → Section → Rack".
Library: The highest management level used to classify different project systems, with the default library being AMXLIB.
System: Represents a complete control application, such as a complete production line or a large process unit.
Region: Logical grouping of racks by function or physical location within the system for ease of management.
Rack: The most basic hardware unit, corresponding to a physical AutoMax chassis, including processors, I/O modules, communication modules, etc.
The software itself integrates four core applications, forming the backbone of offline engineering:
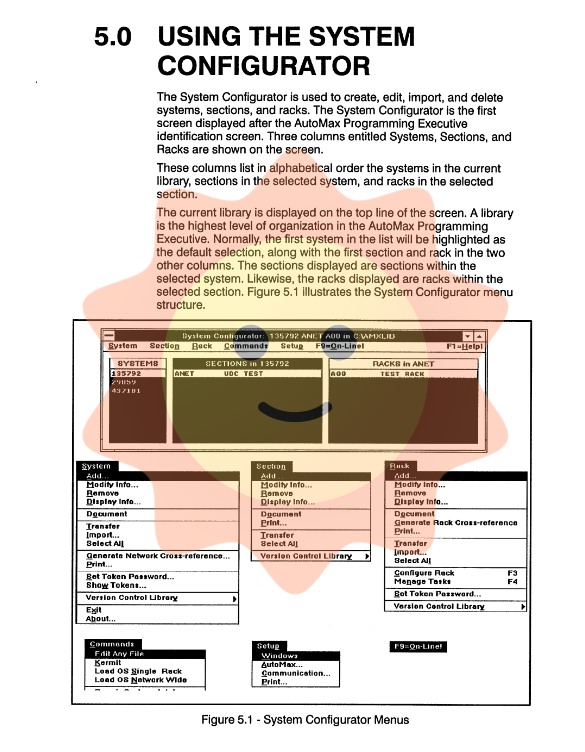
System Configurator: Used to create and manage the hierarchical structure mentioned above, and can import systems created in earlier versions (such as AutoMax V2) or ASD (AutoMax Software Designer) V8. x.
Rack Configurator: Graphically configure modules in physical racks, including local racks, remote I/O networks (supporting AutoMax and Shark remote racks, remote heads, digital tracks, etc.), and drive parameters (for UDC modules).
Variable Configurator: Maps meaningful variable names and descriptions to I/O points, network registers, and public memory locations, replacing the direct use of physical addresses in programming and greatly improving program readability and maintainability. It provides specific configuration forms for different types of modules (basic I/O, network interfaces, public memory).
Task Manager: Used to create, edit, compile, validate, and manage application tasks running on AutoMax processors or Universal Drive Controller (UDC) modules. Supports three programming languages: ladder logic (PC), control block language, and enhanced BASIC language.
Hardware and software environment requirements
To ensure stable software operation, V3.5 has clear requirements for the operating platform:
Computer: IBM compatible machine based on Intel 80386 or higher performance.
Memory: At least 2 MB RAM (4 MB is recommended for better performance).
Hard drive: At least 40 MB of free space.
Operating System: MS-DOS 5.0 or higher.
Graphics environment: Must run in 386 enhanced mode on Microsoft Windows 3.1 or later, and does not support real mode.
Peripheral devices: At least one idle serial port (COM1 or COM2) is required to connect to the AutoMax processor. A mouse is not necessary but strongly recommended as it can significantly improve operational efficiency in the Windows environment.
Network function: V3.5 supports the use of tokens, file locking, version control library (VCL), and other functions when workstations are connected to a local area network (LAN). This is crucial for multi engineer collaborative projects and can effectively prevent database file damage and task file change loss. VCL functionality requires Intersolv ™ Polytron Version Control System (PVCS) V5.0 or higher support.
Deep analysis of core functional modules
1. Rack and hardware configuration
The rack configurator is the core of building hardware images for control systems. Users can add supported modules from the module list, such as various processor modules (57C430A, 57C431, 57C435), digital/analog I/O modules, communication modules (network, remote I/O, Modbus, AB Link, etc.), and universal driver controller (UDC) modules.
Remote I/O configuration: By adding the 57C416 remote I/O interface module, the remote I/O network can be graphically expanded, remote racks or heads can be configured, and local heads, digital/analog tracks, etc. can be further attached to the remote heads to truly reflect the physical wiring structure.
General modules: For modules that are not directly supported or future hardware (marked as "external modules"), the software provides three types of general modules: GEN32, GEN32K, and GEN32KH, which allow users to allocate register space for variable mapping, ensuring system scalability and compatibility (subject to electrical and protocol requirements, see Appendix H of the manual for details).
Driver integration: For distributed power systems (DPS), UDC modules and their associated power module interfaces (PMI), analog/digital tracks, and other hardware can be configured, and detailed driver parameters can be directly set in the software, achieving seamless integration of driver control and logic control.
2. Variable Mapping and Data Management
Variable configuration is the bridge that connects hardware addresses with software logic. The variable configurator of V3.5 adopts a "form" format to customize the display of register structures for different modules.
Network variable configuration: This is the most complex part. For the 57C404 network interface module, in addition to basic settings and status register views, the core is the "Area 1-55 View". In this view, two names can be defined for each register/bit on the network:
Network global name: It uniquely identifies the data point throughout the entire network and is stored in a system level network database to prevent address conflicts and provide unified semantics.
Local name: The variable name used to access the data point within a specific rack.
The two can be linked. After linking, changing the network global name will be synchronized to all racks that use it through the network database, ensuring consistency in network data definition. This design ensures the rigor of global management while allowing flexibility in local programming.
3. Task programming and execution management
The task manager supports multitasking environments. Each AutoMax processor can run multiple tasks with different priorities and share data through common memory or network variables.
programming language
Ladder diagram logic: Using a dedicated PC editor, sequential logic programming is performed in traditional ladder diagram format, supporting standard elements such as contacts, coils, timers, counters, shift registers, and online monitoring and forcing.
Control Block Language: A function call set based on BASIC syntax, designed specifically for process control loops such as PID, integration, and hysteresis, suitable for AutoMax processors and UDC modules (with slightly different sentence sets supported).
Enhanced BASIC language: used for advanced programming such as complex algorithms, numerical processing, and human-machine interface (HMI) communication.
Compile and Download: BASIC and control block tasks need to be compiled into object code (. OBJ) and downloaded to the processor. The ladder diagram task is already in binary format (. PC) and can be downloaded directly.
Online operation: Through the "Online!" menu, engineers can connect to a running rack, perform loading configurations and tasks, start stop tasks, monitor and modify variable values (including tuning and forcing), real-time edit ladder programs (online editing), view processor and task error logs, and perform a series of key debugging and maintenance operations.
4. System security and documentation
Security level: The system provides multi-level access control based on key switch position (PROTECT/SETUP/PROGRAMM) and password, protecting configurations and tasks from unauthorized modifications.
Document integration: Systems, regions, racks, and tasks can all be associated with independent document files (. SDC,. CDC,. RDC,. TDC) for storing design specifications, maintenance notes, and other information, promoting knowledge management and project handover.
Cross reference report: It can generate detailed rack cross reference and network cross reference reports, listing the usage locations and hardware mapping relationships of all variables, and pointing out potential errors such as unconfigured variables, address conflicts, multitasking write conflicts, etc. It is a valuable tool for debugging and code review.
Compatibility and upgrade path
V3.5 fully considers users' existing investments and upgrade paths:
Backward compatibility: It is possible to convert AutoMax V1, V2 systems, and ASD V8. x systems to V3.5 database format through the "import" function, while preserving the original configuration, variables, and task source code as much as possible.
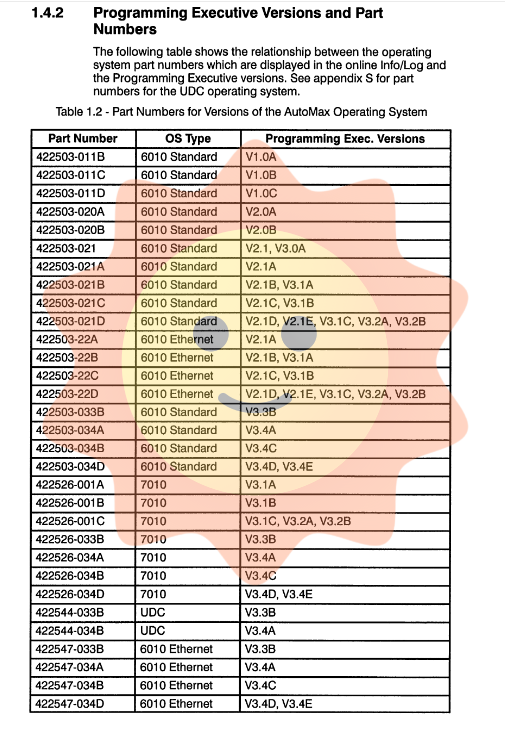
Operating system compatibility: There is a clear compatibility matrix between the programming executor version and the operating system version running on the rack processor. V3.5 actuators support operating systems from early V2.1B to the latest V3.5, but some advanced features may be limited by the version of the operating system in the rack.
Parallel installation: V3.5 can be installed on the same computer as previous versions of actuators (such as V2.x, V3.0A-V3.4E), and can be switched and used through different startup methods (icons or environment variables).
Key workflows in engineering practice
A typical AutoMax project development process is as follows:
Project Planning: Create a project structure (system, region, rack) in the System Configurator.
Hardware modeling: In the rack configurator, add all modules based on physical design, configure remote I/O network and drive parameters.
Data definition: In the variable configurator, allocate meaningful variable names and descriptions for all I/O points, network data exchange areas, and common memory, especially planning network global variables.
Application development: In the task manager, use appropriate programming languages to write control logic, algorithms, and human-machine interface programs, and perform compilation verification.
System integration and download: Load the operating system onto the rack processor and UDC module, and then download the generated rack configuration files, driver parameter files, and application task files to the target hardware.
Debugging and Monitoring: Utilize powerful online features to monitor variables, adjust parameters, and force I/O for system debugging in real-time.
Documentation and maintenance: Generate cross reference reports, improve documentation at all levels, and utilize transmission capabilities to backup or distribute project files to on-site debugging terminals.
- ABB
- General Electric
- EMERSON
- Honeywell
- HIMA
- ALSTOM
- Rolls-Royce
- MOTOROLA
- Rockwell
- Siemens
- Woodward
- YOKOGAWA
- FOXBORO
- KOLLMORGEN
- MOOG
- KB
- YAMAHA
- BENDER
- TEKTRONIX
- Westinghouse
- AMAT
- AB
- XYCOM
- Yaskawa
- B&R
- Schneider
- Kongsberg
- NI
- WATLOW
- ProSoft
- SEW
- ADVANCED
- Reliance
- TRICONEX
- METSO
- MAN
- Advantest
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bently
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- Beijer
- Moxa
- Rexroth
- Johnson
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- Application field
- XP POWER
- CTI
- TRICON
- STOBER
- Thinklogical
- Horner Automation
- Meggitt
- Fanuc
- Baldor
- SHINKAWA
- Other Brands





































































































































