SIMATIC MODNIM Module Deep Analysis: A Reliable Bridge for Industrial Modbus Communication
SIMATIC MODNIM Module: Core Technology Analysis of Industrial Modbus Network Integration
In industrial automation systems, reliable data communication is the lifeline of control networks. The SIMATIC TI505/TI500 MODNIM (Modbus Network Interface Module) launched by Siemens Industrial Automation is designed to meet this critical requirement, serving as a solid bridge between SIMATIC TI series programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and widely used Modbus industrial local area networks (LANs). This article will delve into the technical details, configuration methods, communication protocols, and application practices of this module, providing a comprehensive professional reference for automation engineers.
Module overview and core functions
The MODNIM module (model PPX: 505-5184/PPX: 500-5184) is essentially an intelligent communication adapter. Its core mission is to seamlessly integrate SIMATIC TI PLCs that comply with the TIWAY I protocol into a standard Modbus network, allowing a master computer (such as SCADA, HMI, or DCS) to communicate with up to 247 PLC nodes as slave stations. This master/slave architecture is the cornerstone of Modbus networks, where all communication is initiated by the master and responded to by the slave, ensuring network order and certainty.
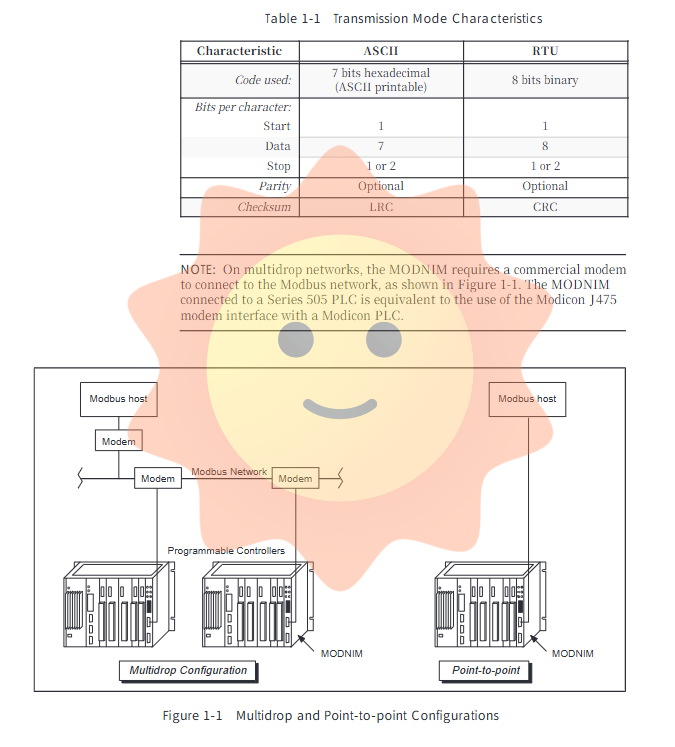
The module supports two well-known serial transmission modes: ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange) mode and RTU (Remote Terminal Unit) mode. ASCII mode uses human readable 7-bit character encoding, starting with a colon (:) and ending with a carriage return line break (CR/LF), and using LRC (Vertical Redundancy Check) for error detection. The RTU mode adopts a more compact and efficient 8-bit binary encoding, defines message frames through a silent interval of 3.5 characters transmission time, and uses CRC (cyclic redundancy check) to ensure data integrity. The two modes cannot be mixed, and all devices in the network must be unified.
Hardware installation and physical configuration
Installing the MODNIM module is the first step in system integration and requires rigorous operation to avoid electrostatic damage and mechanical failures.
Safety and anti-static treatment: Before contacting the module, it is necessary to ensure that personnel and the module are at the same grounding potential. It is recommended to operate on a conductive pad and wear a grounded wristband. Anti static containers or materials should be used for module transportation and storage.
DIP switch configuration: This is the core of module customization. The module is equipped with two sets of DIP switches:
Network Address Switch (8-bit): Used to set the unique address of the module in the Modbus network, with a valid range of 1-247 (binary 00000001 to 11110111). Address 0 is a broadcast address, and 248-255 are illegal addresses, which will cause the module to enter testing mode.
Network parameter switch (10 bits): used to configure communication physical layer parameters, including:
Data transmission rate (50 to 19200 bps)
Stop position (1 or 2)
Parity check (odd check, even check, or no check)
Transmission mode (ASCII or RTU)
RTS/CTS handshake signal (enabled or disabled, the latter commonly used for point-to-point modem free connections)
Y/C coil selection: determines whether the module reads coil data from the discrete output (Y) memory of the PLC or from the memory of the control relay (C).
Important note: The DIP switch setting is only read once when the module is powered on or reset. After any switch change, the reset button must be pressed for the new configuration to take effect, after which the module will be unable to communicate for several seconds.
Mechanical installation
TI505 series: After disconnecting the power supply of the I/O base, align the module with the slot, insert it smoothly until the edge connector is fully seated, and finally tighten the upper and lower screws of the front panel to secure and ground it.
TI500 series: Before installation, the provided keys can be used to key the dedicated slots to prevent accidental insertion of other I/O modules. The module is fixed by a locking buckle and will automatically lock when installed in place.
Status indication and diagnostic system
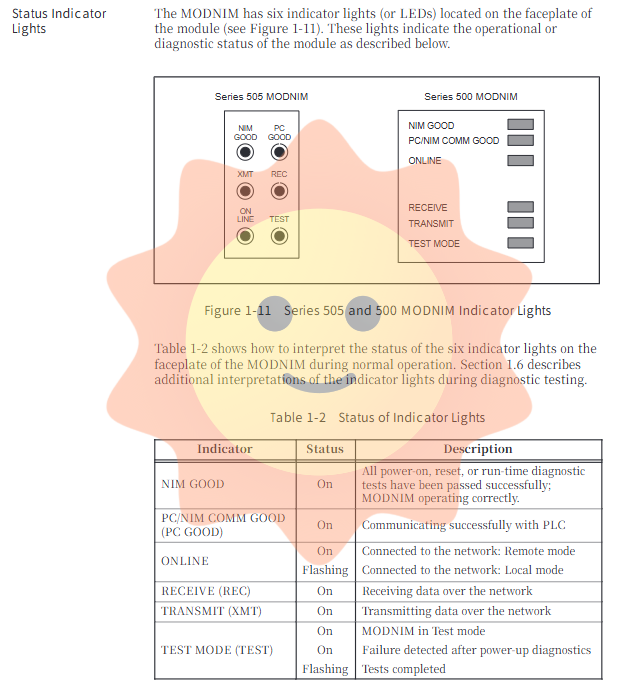
The front panel of the MODNIM module is equipped with a variety of indicator lights (LEDs) and function switches, forming an intuitive interface for status monitoring and diagnosis.
Indicator light (LED):
NIM GOOD: The module self-test passes and lights up when running normally.
PC/NIM COMM GOOD: It lights up when the module communicates successfully with the PLC.
ONLINE: The module is connected to the network. Constant light indicates being in "remote" mode (writable), while flashing indicates being in "local" mode (readable only).
ReceIVE (REC)/TRANSMIT (XMT): respectively indicate receiving or sending network data.
TEST MODE (TEST): The module lights up or flashes when it is in test mode or fails self-test.
Function switch/button:
Local/Remote switch: Switch module operation mode and control whether to allow write operations to be performed on the PLC.
Reset button: Initialize the module and trigger power on self-test.
Test button: Used in combination with the Reset button (press and hold Reset and press Test for 5 seconds) to initiate a comprehensive diagnostic test triggered by the user. At this time, the network cable needs to be disconnected and a loopback connector needs to be installed.
Three layer diagnostic testing:
Power on self-test: automatically executed every time power on or reset, checking the processor, RAM, and ROM.
Run time self-test: The backend continuously performs ROM integrity checks, PLC communication status monitoring, and prevents software deadlocks through watchdog timers.
User triggered self-test: Conduct comprehensive hardware testing, including communication ports. By observing the status of the LED after diagnosis (see Table 1-3), faults such as ROM/RAM faults, PLC communication failures, and port A/B faults can be quickly located.
Deep Mapping and Function Implementation of Modbus Protocol
The essence of the MODNIM module lies in its precise mapping between the Modbus protocol and the internal data structure of SIMATIC TI PLC.
Protocol frame structure: The module fully supports Modbus ASCII and RTU frame formats. ASCII frames start with ":" and contain address field, function code field, data field, LRC checksum, and CR/LF terminator. RTU frames are defined by time intervals and include addresses, function codes, data, and CRC checks.
Function code support and TIWAY mapping: The module supports a series of core function codes in the Modbus standard and translates them into corresponding TIWAY I network "primitive" commands. The key mappings include:
01/02 (Read coil/input status) → TIWAY primitive 20, TT type 7/8 (Y/C packaging) or 6 (X packaging).
03/04 (Read Hold/Input Register) → TIWAY Primitive 20, TT Type 1 (V Memory) or 9 (WX Word Input).
05/06 (write single coil/single register) → TIWAY primitive 30, TT type 4/5 (Y/C) or 1 (V memory).
15/16 (write multiple coils/registers) → TIWAY primitive 30, corresponding to the packaged data type.
Advanced features such as 08 (diagnosis), 11/12 (communication events), and 17 (reporting slave ID) are also fully supported.
Key difference in address mapping: Engineers must pay attention to a core difference: the memory addresses of SIMATIC TI PLCs are usually numbered from 1, while many Modbus PLCs (and protocol conventions) start from 0. If the host application does not adjust this offset, it may result in accessing the wrong data location. The address mapping of the module adopts absolute positional addressing, with a maximum supported address of 65535 (FFFF hex).
Data limit: Due to Modbus buffer limitations, there is an upper limit on the amount of data per request: coil/discrete input is 2000 points, registers are 125 (read) or 100 (write), and writing multiple coils is 800 points. Exceeding the limit request will trigger an exception code 03 response.
Advanced Diagnostic and Configuration Tool (MODASST)
Siemens provides powerful PC side auxiliary software MODASST with the module, greatly simplifying the configuration and debugging process.
Main functions:
Interactive configuration: Guide users to gradually set communication ports, baud rates, parity checks, stop bits, modes (ASCII/RTU), handshakes, Y/C mappings, and network addresses.
DIP switch diagram: Based on the set parameters, visually display the position of the DIP switch on the module.
Cable Pin Diagram: Provide the cable wiring diagram required to connect MODNIM to the host or modem.
Communication testing: Provides a "dialogue with module" function, allowing manual sending of formatted Modbus requests and viewing of raw responses, or automatic sending of test requests to verify communication.
Automatic parameter recognition: When the module parameters are unknown, the "Find Module Settings" function can automatically attempt all possible parameter combinations until communication is established and the current settings are reported.
Diagnostic execution: Integrated Modbus function code 08 (diagnostic), convenient for users to perform various diagnostic sub functions, such as loop testing, counter reset, event log query, etc.
Usage value: The MODASST program visualizes complex protocol details and hardware configurations, reducing the entry barrier and on-site debugging time for engineers. It is an indispensable tool to ensure the fast and accurate operation of MODNIM modules.
Error Handling and System Integration
A reliable system must include a comprehensive error handling mechanism. The MODNIM module reports an error to the main station through an exception response code:
01- Illegal Function: A function that is not supported by the module was requested.
02- Illegal data address: The requested data address exceeds the valid range of the PLC.
03- Illegal data value: The value in the requested data field is unacceptable (such as exceeding the quantity limit).
04- Associated device failure: PLC not responding or communication failure (PC GOOD light off).
06- Memory parity error: A parity check error occurred while reading PLC memory.
These exception codes have been carefully mapped with the internal TIWAY exception codes of SIMATIC TI PLC to ensure accurate transmission of error messages.
Application scenarios and system planning
The MODNIM module is suitable for various scenarios that require the integration of existing SIMATIC TI505/TI500 series PLCs into higher-level Modbus monitoring networks, such as factory process monitoring, building automation, data acquisition systems, etc. When planning, attention should be paid to:
Network topology: Supports multi-point and point-to-point connections. In multi-point networks, it is usually necessary to connect through a commercial modem.
Cable specifications: In industrial environments with high noise levels, it is recommended to use Siemens standard shielded communication cables or strictly follow the manual requirements (such as 26 AWG wire gauge, aluminum foil and braided double-layer shielding, specific connectors) to make homemade cables to ensure signal integrity.
Environmental specifications: The module design complies with strict industrial environmental standards, with an operating temperature of 0-60 ° C. It has good anti vibration, anti impact, and anti electromagnetic interference (EMC) capabilities, and has UL, CSA, FM and other safety certifications.
- ABB
- General Electric
- EMERSON
- Honeywell
- HIMA
- ALSTOM
- Rolls-Royce
- MOTOROLA
- Rockwell
- Siemens
- Woodward
- YOKOGAWA
- FOXBORO
- KOLLMORGEN
- MOOG
- KB
- YAMAHA
- BENDER
- TEKTRONIX
- Westinghouse
- AMAT
- AB
- XYCOM
- Yaskawa
- B&R
- Schneider
- Kongsberg
- NI
- WATLOW
- ProSoft
- SEW
- ADVANCED
- Reliance
- TRICONEX
- METSO
- MAN
- Advantest
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bently
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- Beijer
- Moxa
- Rexroth
- Johnson
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- Application field
- XP POWER
- CTI
- TRICON
- STOBER
- Thinklogical
- Horner Automation
- Meggitt
- Fanuc
- Baldor
- SHINKAWA
- Other Brands
- UniOP