SIEMENS SINUMERIK System 800 General Interface Technology Explanation and Configuration Guide
SINUMERIK System 800 General Interface Technology Explanation and Configuration Guide
The Siemens SINUMERIK System 800 is a high-performance CNC system widely used in machine tool control, and its powerful data exchange capability relies on a flexible and stable universal interface design. This article is based on the official Universal Interface Planning Guide, which systematically reviews its interface architecture, electrical characteristics, configuration methods, and actual connection cases, providing comprehensive technical references for equipment manufacturers, system integration, and maintenance personnel.
Overview of Interface System
SINUMERIK System 800 provides three main types of serial interfaces to meet the requirements of different transmission distances, environmental immunity and equipment compatibility:
V. 24 (RS232C) interface
Compliant with DIN 66020 and CCITT V.24/V.28 standards, using ± 12V voltage level, with a maximum transmission distance of 30 meters. The interface regards SINUMERIK as a data terminal equipment (DTE), equipped with complete control signal lines (DTR, RTS, DSR, CTS), supporting two transmission modes: line control and character control.
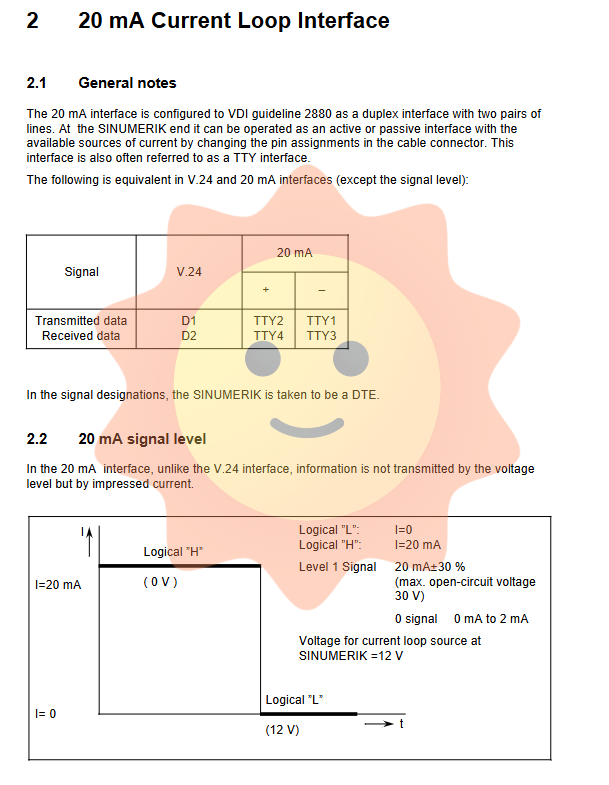
20mA current loop interface (TTY interface)
Using current signal transmission (about 20mA), it has strong anti-interference ability and a transmission distance of up to 1 kilometer. The interface supports duplex operation and can be configured as "active" (providing current) or "passive" (peripheral devices providing current) mode at the SINUMERIK end.
RS422 interface
Adopting differential signal transmission, it combines the integrity of V.24 control signals with the long-distance transmission capability of 20mA interface (up to 1 kilometer). The signal is converted through the AM26LS31 driver and AM26LS33 receiver, and supports level conversion cables to adapt from V.24 to RS422.
Interface Electrical and Pin Definition
1. Pin allocation for V.24/20mA universal interface (25 pin D-Sub socket)
Pin signal name, interface type, corresponding standard signal description
1 E1 (Protective Ground) Universal 101- Protective Ground
2 *TxD V.24 103 – Transmitted Data
3 *RxD V.24 104 – Received Data
4 RTS V.24 105 – Request to Send
5 CTS V.24 106 – Clear to Send
6 DSR V.24 107 – Data Set Ready
7 MEXT V.24 102- Signal Ground
10 TTY2 20mA data transmission+
11 T20mA 20mA transmission power supply
13 TTY4 20mA receiving data+
14 TTY3 20mA receiving data-
20 DTR V.24 108.2 – Data Terminal Ready
2. RS422 interface pin allocation (25 pin D-Sub socket)
In addition to having data and control signal lines corresponding to V.24 (such as TxD, RxD, RTS, CTS, etc.), the RS422 interface adopts differential pair transmission (such as TxD+/-, RxD+/-), significantly improving the ability to resist common mode interference.
Interface adaptation and setting data
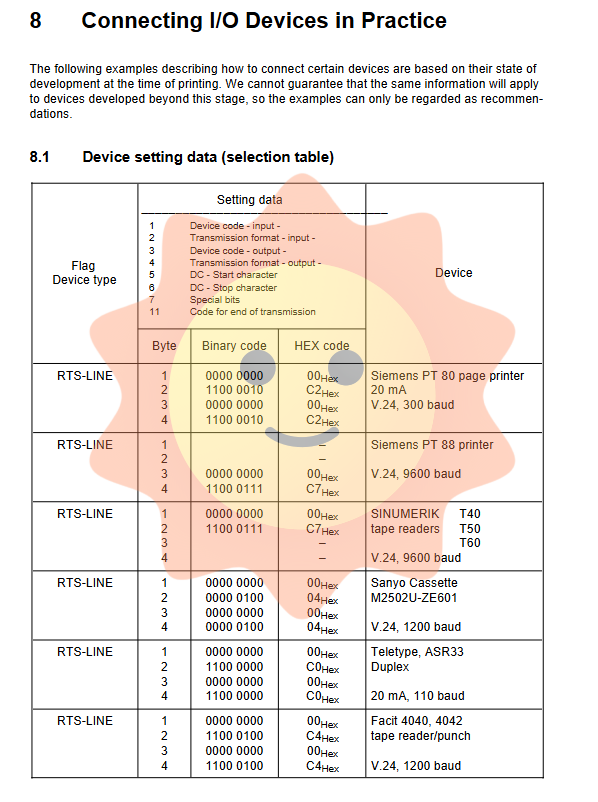
The system provides 8 bytes of Setting Data for each interface, configuring the working parameters for input/output directions separately:
Device Code: Identify the type of device control, such as wire controlled device (00H), Xon/Xoff character controlled device (01H), specific tape reader (02H), etc.
Transmission Format: including baud rate (110-9600 baud), number of stop bits (1, 1.5, 2), parity type (even/odd/none), etc.
Special character definitions: such as Xon/Xoff characters, replacement codes for missing characters in EIA codes (such as @,:,=, [, etc.), end of transmission characters (ETX), etc.
Special function bits: such as whether to enable DSR detection, whether to output leading and trailing codes, whether to enable time monitoring, etc.
Signal timing and transmission control
1. Line control equipment (such as PT80 printer, tape reader)
Data input: NC sets RTS=1 to start transmission, pause by lowering RTS; After receiving the end character (M02/M30/ETX), RTS=0 ends.
Data output: Start sending after NC detects CTS=1; The device pauses by lowering CTS; After the output is completed, DTR=0.
2. Character control devices (such as programming workstations, disk drives)
Control data flow through Xon (DC1)/Xoff (DC3) characters.
In most cases, there is no need to connect an RTS/CTS cable, only the DSR is used to detect the device's readiness status.
Interface layout of different controllers
Controller model, interface quantity, interface location and type description
SINUMERIK 805 1-2 panel front V.24/20mA, optional rear V.24 (can be converted to RS422)
SINUMERIK 810/820 1-2 front panel is V.24/20mA, optional rear panel V.24 (GA3 supports RS422 conversion)
SINUMERIK 840 1-2 control panel front V.24/20mA, optional operation panel rear V.24 (can be converted to RS422)
SINUMERIK 850 is equipped with up to 4 front and rear panels, as well as a central controller, all of which are equipped with V.24/20mA and some can be converted to RS422
SINUMERIK 880 has up to 4 interfaces similar to 850, distributed between the control panel and the central controller
Typical I/O device connection example
1. Printer (such as Siemens PT80)
Interface: V.24 or 20mA
Set data: device code 00H, baud rate 300, 2 stop bits, even parity check
Cable: 6FC9 340-8C (V.24) or 6FC9 340-8T (20mA)
2. Tape reader (such as SINUMERIK T40/T50)
Interface: V.24
Set data: device code 00H, baud rate 9600, 2 stop bits
Cable: 6FC9 340-8S
3. Disk drives (such as Siemens DSG 3.5)
Interface: V.24
Set data: device code 00H, baud rate 9600, 2 stop bits, Xon/Xoff control
Cable: 6FC9 344-2P
4. Programming workstation (such as SINUMERIK WS800)
Interface: V.24 or 20mA
Set data: device code 00H, baud rate 9600, 2 stop bits
Cable: 6FC9 344-1B (V.24) or 6FC9 344-1Q (20mA)
5. PLC programmer (such as SIMATIC PG 675/750)
Interface: 20mA or V.24
Set data: device code 04H, baud rate 9600, 2 stop bits, even parity check
Cable: 6FC9 340-8G (20mA) or 6FC9 344-4R (V.24)
Configuration precautions
Level and current cannot be mixed: V.24 transmitters and 20mA transmitters on the same interface must not be connected simultaneously.
DTE/DCE docking: If the peripheral device is also a DTE, the transmission and reception lines need to be crossed in the cable.
Cable length limit: V.24 does not exceed 30 meters, 20mA and RS422 can reach 1 kilometer.
Code conversion note: EIA code is missing some ISO characters, and alternative codes need to be defined in the settings data, otherwise it may cause read and write inconsistencies.
Time monitoring: By default, a 60 second timeout interrupt is enabled, which can be disabled by setting data.
- ABB
- General Electric
- EMERSON
- Honeywell
- HIMA
- ALSTOM
- Rolls-Royce
- MOTOROLA
- Rockwell
- Siemens
- Woodward
- YOKOGAWA
- FOXBORO
- KOLLMORGEN
- MOOG
- KB
- YAMAHA
- BENDER
- TEKTRONIX
- Westinghouse
- AMAT
- AB
- XYCOM
- Yaskawa
- B&R
- Schneider
- Kongsberg
- NI
- WATLOW
- ProSoft
- SEW
- ADVANCED
- Reliance
- TRICONEX
- METSO
- MAN
- Advantest
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bently
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- Beijer
- Moxa
- Rexroth
- Johnson
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- Application field
- XP POWER
- CTI
- TRICON
- STOBER
- Thinklogical
- Horner Automation
- Meggitt
- Fanuc
- Baldor
- SHINKAWA