Toshiba Discrete IGBTs: Core Architecture, Technological Evolution, and Application Details
Toshiba Discrete IGBTs: Core Architecture, Technological Evolution, and Application Details
In the rapid development of power electronics and industrial automation, insulated gate bipolar transistors serve as the core component of power switches, playing a bridge between low-voltage control signals and high-power loads. By combining the high input impedance advantage of MOSFETs with the high voltage driving capability of bipolar transistors, IGBT devices have demonstrated excellent performance in load control applications such as frequency converters, uninterruptible power supplies, and motor drives. This article will comprehensively analyze the technical essence of Toshiba's discrete IGBT product line, delve into its core planar structure, multi generation technology evolution trends, and specific selection strategies in different application scenarios.
Core architecture: n-pn-p four layer structure and conduction modulation
The excellent performance of Toshiba discrete IGBT is primarily attributed to its unique planar structure. Unlike traditional bipolar transistors, discrete IGBTs adopt a four layer structure, typically represented as n-pn-p. This structure includes a P+layer located on the collector side, which uses PNP transistors to achieve conduction modulation. The key advantage of this design is that it significantly reduces the collector emitter saturation voltage.
Low saturation voltage means that in the high current operating region, the conduction loss can be significantly reduced, thereby directly improving the thermal performance and overall energy efficiency of the device. In addition, the structure supports high input impedance, which allows for the use of voltage drive and simplifies the design of gate drive circuits. In order to further improve reliability, some Toshiba IGBT series adopt a built-in diode scheme, optimized for specific applications, effectively reducing the number of external components and optimizing the thermal path.
Technological Evolution: From High Speed Switching to Soft Switching and High Frequency Conversion
Toshiba's product plan clearly demonstrates the intergenerational iteration roadmap of power semiconductor technology, with each generation optimized for specific performance bottlenecks or application requirements.
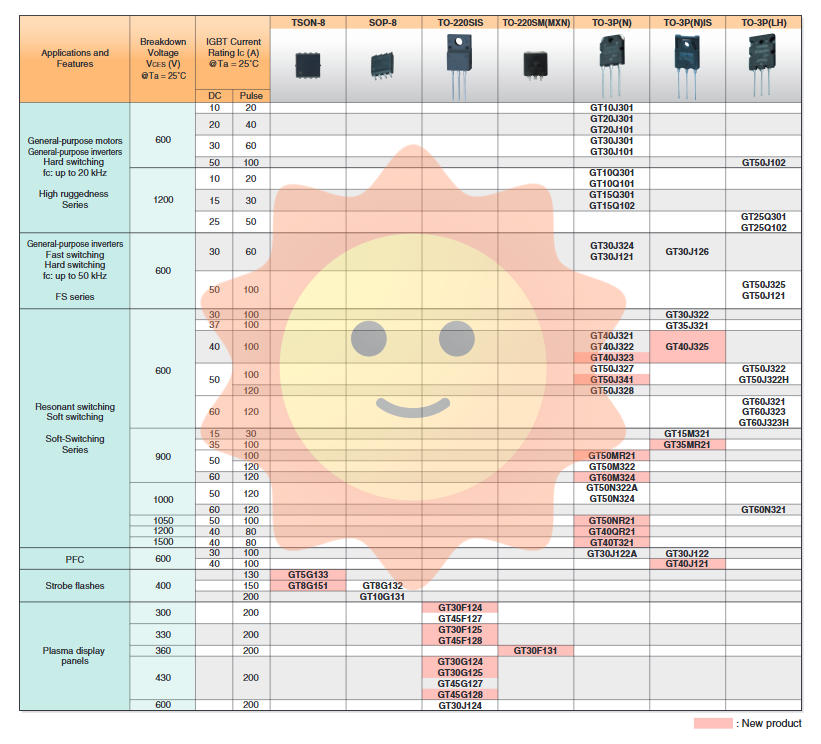
3rd generation (high robustness): This generation of products emphasizes high robustness and low collector emitter saturation voltage (VCE (sat)). Through optimized carrier injection technology and thinner wafer processes, this generation of products exhibits stronger durability in harsh industrial environments, able to withstand greater thermal stress and electrical shock. Typical models such as GT50N322 represent the technological achievements of this generation and are suitable for high reliability industrial applications.
4th/5th generation (soft switch -1200V and RC structure): Toshiba has launched soft switch technology for medium and low voltage (such as 1200V) frequency converters and induction heating (IH) cooking appliances. Soft switches improve energy efficiency by reducing switch losses and electromagnetic interference (EMI). In this generation, Toshiba developed the RC-IGBT (reverse conducting IGBT) series. This is a major breakthrough in soft switching technology. RC-IGBT integrates a freewheeling diode on the P+layer on the collector side. This design not only eliminates the need for external diodes, reduces system complexity and cost, but also improves overall thermal performance by reducing the thermal resistance of the diode path. The RC-IGBT series (such as GT35MR, GT50MR) is an ideal choice for applications with strict electromagnetic compatibility requirements, such as IH rice cookers, IH cookware, and microwave ovens.
6th generation (high-frequency switch): With the increasing demand for high-frequency inverters and power factor correction (PFC), the 6th generation products have shifted towards finer process geometries and thinner wafers. This optimization supports high-frequency switching, allowing the inverter to operate at higher switching frequencies, reducing the size of passive components and increasing power density. This generation of products achieves faster switching speeds while maintaining lower switching losses through carrier injection control technology.
7th/8th generation (plasma display and refinement): Plasma display panels (PDPs) have extremely high requirements for high current processing capability and precise conductivity characteristics. Toshiba's 7th and 8th generation IGBTs have been optimized specifically for this application. In addition to continuing the advantages of high-frequency switches, these devices use thinner wafers and finer process geometries to achieve extremely low conduction losses at high voltages. This is crucial for dealing with frequent hard switching in plasma drive circuits. Models of plasma display panels (such as GT30F124, GT45F128) are equipped with built-in fast recovery diodes (FRDs) that can protect devices during harsh commutation processes, ensuring the long-term reliability of the system.
Application scenarios and selection strategies: from industrial drive to consumer electronics
Toshiba's extensive product line of discrete IGBTs can cover a wide range of applications from heavy industry to precision consumer electronics.
General purpose inverters and motor drives (hard switch): For standard inverters and motor drives, Toshiba offers the FS (high-speed) series, such as the GT10J, GT20J, GT30J, and GT60J3xx series. These devices are designed for hard switching and support switching frequencies up to 20 to 50 kHz. Although hard switching characteristics can lead to high switching losses and EMI, they are essential in applications that require high bandwidth and fast dynamic response. Many models adopt isolation packaging (such as GT30J324, GT40J325) to provide additional electrical isolation and safety margin.
Soft switch applications: In uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), power factor correction circuits, and IH cooking appliances, Toshiba's RC-IGBT (reverse conducting) and FWD-IGBT (freely rotating diode) series dominate. These devices are specifically designed to provide soft switching characteristics by controlling the gate voltage to regulate the rising edge of the current, significantly reducing switching losses, minimizing EMI noise, and suppressing voltage spikes caused by large current variations. This feature is particularly important for induction heaters as it allows for more precise temperature control and reduces standby energy consumption. FWD-IGBT further reduces forward voltage drop and improves overall efficiency by integrating diodes inside the chip.
Flash: From early hard switch designs to the evolution of high-frequency/soft switches, the flash market has also benefited from Toshiba IGBT's technological advancements. Flashlights need to be able to switch large currents (such as 100A pulse currents) and withstand high voltages. Toshiba offers dedicated IGBTs such as GT5G, GT8G, and GT10G series. These devices not only have high current ratings, but are also optimized for low gate driving voltages (typically in the range of 2.5V to 4.0V), so that they can be directly driven by the logic levels inside the camera, simplifying circuit design. The 6th generation and later devices also exhibit excellent high-frequency switching characteristics, supporting more compact flash designs.
Plasma display panel: Plasma display panel (PDP) represents one of the most demanding fields in power semiconductor applications. Driving plasma requires hundreds of amperes of current and can withstand breakdown voltages of tens of thousands of volts. Toshiba has launched dedicated IGBT series for this application, such as the GT30F and GT45F series. These modules not only support continuous currents of up to 120A and pulsed currents of 200A (for specific models), but also achieve low conduction losses at voltages ranging from 300V to 400V. Many devices designed for PDP integrate built-in fast recovery diodes (FRDs), which are necessary for quickly restoring circuit functionality in the event of a hard short circuit or commutation fault in the plasma drive circuit.
Packaging and integration: adaptable to harsh environments
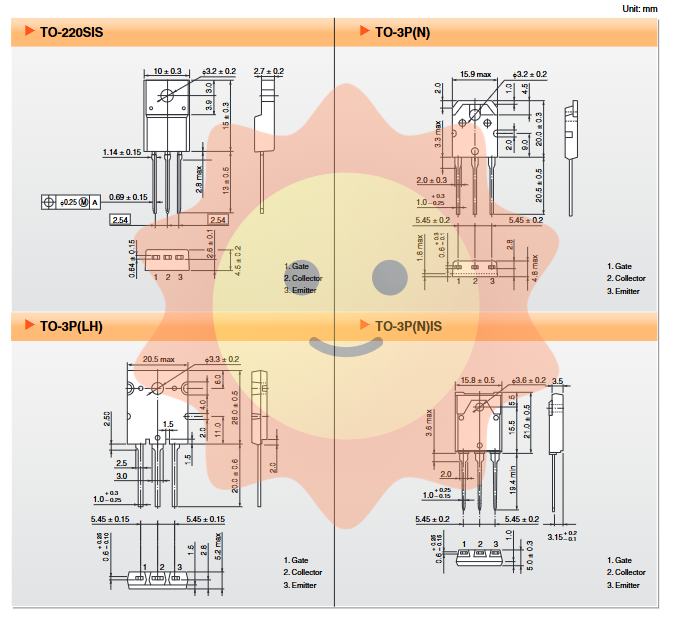
In order to meet different mechanical design and thermal management requirements, Toshiba has packaged its discrete IGBT in a variety of configurations, such as TO-220SIS, TO-3P (N), and TO-3P (LH).
TO-220SIS series: adopts a direct copper substrate, providing a low thermal resistance path from the device to the heat sink, which is very suitable for the rapid heat dissipation needs in high-power applications.
TO-3P (N) series: It is a semi insulated package that allows for more flexible heat sink design while maintaining electrical isolation, typically utilizing thermal interface materials.
TO-3P (LH) series: designed specifically for high thermal resistance applications, utilizing advanced thermal interface technology to ensure high reliability in compact spaces.
In addition, for specific markets such as flash in digital cameras, Toshiba also offers extremely small packages to meet the space limitations of compact camera modules.
Conclusion
In summary, Toshiba's discrete IGBT product line has established a technological benchmark in the field of power semiconductors with its n-pn-p four layer structure and RC-IGBT innovative design. From the high robustness of the third-generation products, to the soft switching RC-IGBT technology of the fourth/fifth generations, and to the high-frequency and high current solutions for plasma displays in the seventh/eighth generations, Toshiba continues to push the boundaries of IGBT performance. Whether it is industrial inverters that pursue ultimate energy efficiency or household appliances that require silent operation, Toshiba provides rigorously validated and technologically advanced solutions to ensure the stability, reliability, and long-term lifespan of the system in different application scenarios.
- ABB
- General Electric
- EMERSON
- Honeywell
- HIMA
- ALSTOM
- Rolls-Royce
- MOTOROLA
- Rockwell
- Siemens
- Woodward
- YOKOGAWA
- FOXBORO
- KOLLMORGEN
- MOOG
- KB
- YAMAHA
- BENDER
- TEKTRONIX
- Westinghouse
- AMAT
- AB
- XYCOM
- Yaskawa
- B&R
- Schneider
- Kongsberg
- NI
- WATLOW
- ProSoft
- SEW
- ADVANCED
- Reliance
- TRICONEX
- METSO
- MAN
- Advantest
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bently
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- Beijer
- Moxa
- Rexroth
- Johnson
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- Application field
- XP POWER
- CTI
- TRICON
- STOBER
- Thinklogical
- Horner Automation
- Meggitt
- Fanuc
- Baldor
- SHINKAWA
- Other Brands
- UniOP