KOLLMORGEN AKD ® Servo drive fault card
AKD ® Servo drive fault card
Basic Information
Scope of application: This fault card is applicable to Kollmorgen AKD series servo drives (hardware revision E), covering standard and AKD-T models (supporting BASIC program function). It provides a detailed list of fault/warning codes, causes, remedies, and drive responses, and is the core reference document for troubleshooting.
Version iteration: The document has undergone 13 revisions (A-M version), with the latest M version (November 2020) updating code descriptions such as F470 (feedback 3 fault) and F583/n583 (Hall effect sorting error). Historical versions have added key fault entries such as F314 (motor phase loss), F587 (full AC input phase loss), and F634 (failure of regenerator test).
Supporting tools: Fault information can be viewed through the driver panel display (single/dual 7-segment screen), LED indicator lights (screenless models), or WorkBench software. It supports reading the fault list through the DRV.FAULTRAS/DRV.Warning commands, which can be called by external controllers/HMIs to obtain information.
Basic explanation of faults and warnings
(1) Indicator type and display rules
Equipment configuration fault/warning indication display logic
The left side of the dual 7-segment display shows "F" (fault) or "n" (warning), and the right side displays a 3-digit code (such as F101, n107) to prioritize the highest priority fault. When there are multiple faults, they are displayed in turn
Single 7-segment display flashes in the order of "F/n+code" (such as "F" first, then "1", "0", "1"), following the same dual screen logic. The complete code needs to be identified through the flashing sequence
Only the LED indicator light flashing red indicates a fault, while flashing yellow indicates a warning. WorkBench needs to be connected to view the specific code
(2) Drive fault response type
Controlled shutdown: Slow down the motion to zero speed (parameter CS.VTHRESH/CS-TO defines threshold), then disable the power level, suitable for non emergency faults (such as F121 zero error, F438 position following error).
Immediately disable power level (coasting stop): Cut off the motor power directly and allow the motor to coast freely to a stop, suitable for hardware failures (such as F101 firmware incompatibility, F201 built-in RAM damage).
Dynamic braking: By short circuiting the motor phase to slow down the load, it is suitable for dangerous faults (such as F302 overspeed, F404 illegal Hall state), and attention should be paid to the mechanical stress during the braking process.
Extended response (AKD-C central power supply): In addition to the driver's own response, it will also disconnect the power fault relay, remove the global enable signal, and even cut off the logical voltage of the device string (such as F545 device string overcurrent).
Core fault classification and typical codes
(1) Hardware and firmware failures (F100-F299)
1. Firmware and FPGA related
F101 (firmware incompatible): The installed firmware does not match the hardware of the drive, and compatible firmware needs to be loaded (e.g. UCB1V2 label model requires firmware ≥ 4.0.0).
F103/F104 (FPGA damage): The resident/running FPGA detects a software malfunction, and restarting is ineffective. Technical support should be contacted, and it may be necessary to return to the factory for repair.
N101/n102 (FPGA version exception): The laboratory version FPGA or minor version does not match the firmware, and an official compatible FPGA version must be loaded.
2. Memory and hardware failures
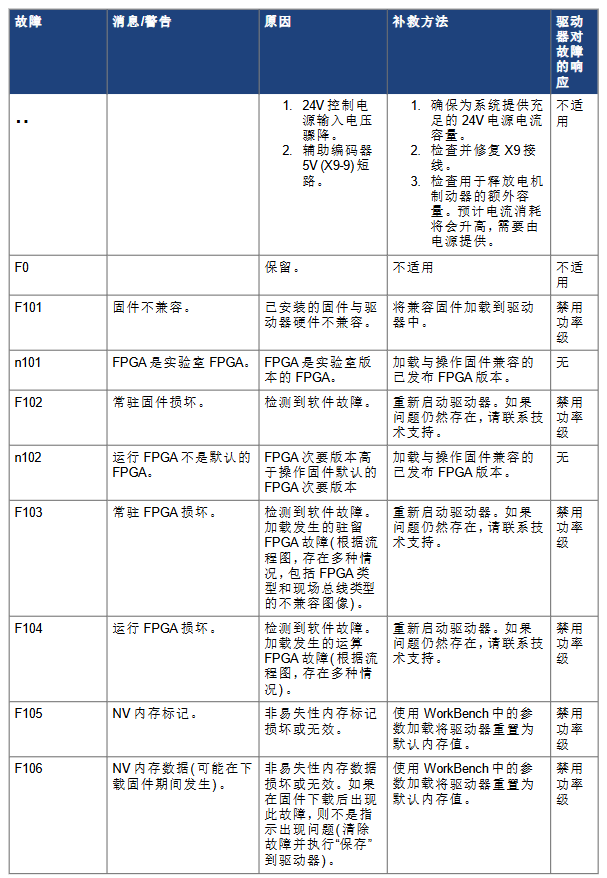
F105/F106 (NV memory error): Non volatile memory flag/data corruption, reset default parameters through WorkBench loading, F106 is normal after firmware download (fault needs to be cleared and parameters saved).
F201-F203 (RAM/code integrity failure): Internal/external RAM is damaged or FPGA register access is incorrect, restarting is ineffective and the driver needs to be replaced.
F234-F243 (temperature sensor malfunction): The sensor is at ultra-high temperature (F-level) or ultra-low temperature (F-level). Check the ventilation of the cabinet and clean the heat dissipation channel.
(2) Motor and feedback faults (F300-F499)
1. Motor related
F301/n301 (motor overheating): The motor temperature exceeds the threshold. Check the ambient temperature, radiator installation, reduce load or optimize the motion curve.
F302 (overspeed): If the motor speed exceeds VL.THRESH, it is necessary to increase the threshold or decrease the speed command, and dynamic braking will be triggered in emergency situations.
F304/n304 (motor current feedback): Exceeding the maximum motor power, check if the load is stuck and if the current limit is correct, and optimize the motion configuration by reducing acceleration.
F314 (motor phase loss): The motor phase wire is not connected correctly. Check the AKD motor connector wiring (if the U/V/W phase is loose), disable the power level, and repair it.
2. Feedback related
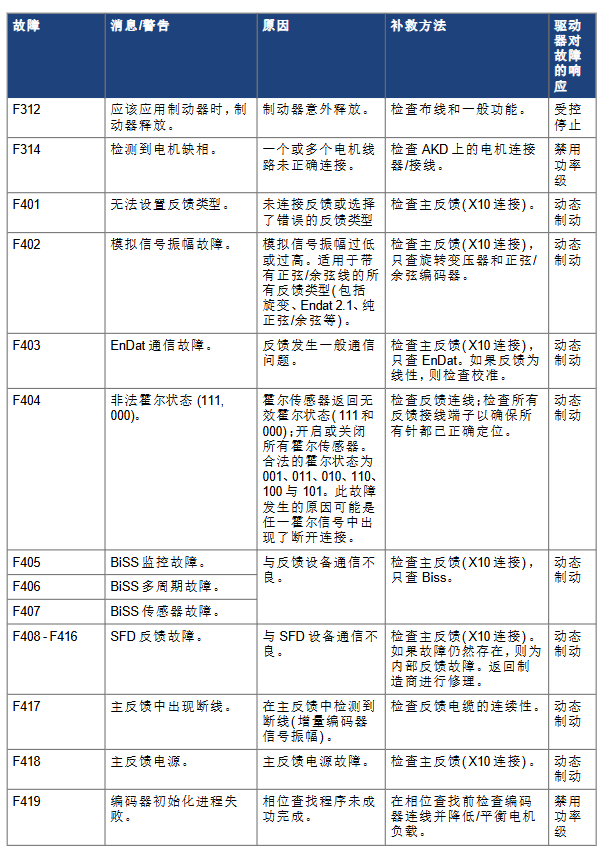
F401 (Invalid Feedback Type): Feedback type not connected or selected incorrectly. Check the wiring of the main feedback (X10 interface) and confirm that the feedback type (such as EnDat, BiSS, rotary transformer) is consistent with the parameter configuration.
F404 (Illegal Hall State): The Hall sensor returns 111/000 (the legal state is 001/010/011/100/101), check if the Hall wiring is broken or has poor contact, and trigger dynamic braking protection.
F438/n438 (position following error): The actual position exceeds the maximum allowable deviation. Check if the load has increased, if the feedback commutation setting is correct, and adjust the servo gain or position deviation threshold.
F470 (Feedback 3 Fault): The third level feedback (X9 interface) is not connected or communication is abnormal. Check FB3.FAULTRA for detailed information, repair the wiring or replace the feedback device.
(3) Power supply and power level faults (F500-F599)
1. Bus voltage related
F501/n501 (Bus Overvoltage): The bus voltage exceeds the threshold, often due to high regenerative energy of the load. It is necessary to reduce the load, optimize the deceleration curve, or increase the regenerative resistance capacity.
F502 (bus undervoltage): If the bus voltage is below the threshold, check if the input power supply is stable, check if the power supply wiring is loose or if there is a power supply fault, and trigger a controlled shutdown.
F503 (Bus capacitor overload): Connect the three-phase driver to a single-phase input or ultra single-phase load, confirm the power phase wiring (L1/L2/L3), and replace the matching power supply.
2. Power level and regeneration faults
F519 (short circuit in regeneration circuit): The regeneration resistor or IGBT is short circuited. It is necessary to disconnect the power supply and check the resistance wiring. Contact technical support to replace the power components.
F521/n521 (regeneration circuit over power): The power of the regeneration resistor is insufficient. Replace it with a larger capacity resistor or enable DC bus sharing, and disable power level protection equipment.
F525 (output overcurrent): If the current exceeds the peak value of the driver, check if the motor is short circuited and if there is a feedback fault. Urgently disable the power level to prevent hardware damage.
F531 (power level fault): Power level hardware fault, restart is ineffective and the driver needs to be replaced, which is a fatal fault.
(4) Fieldbus and communication failure (F600-F799)
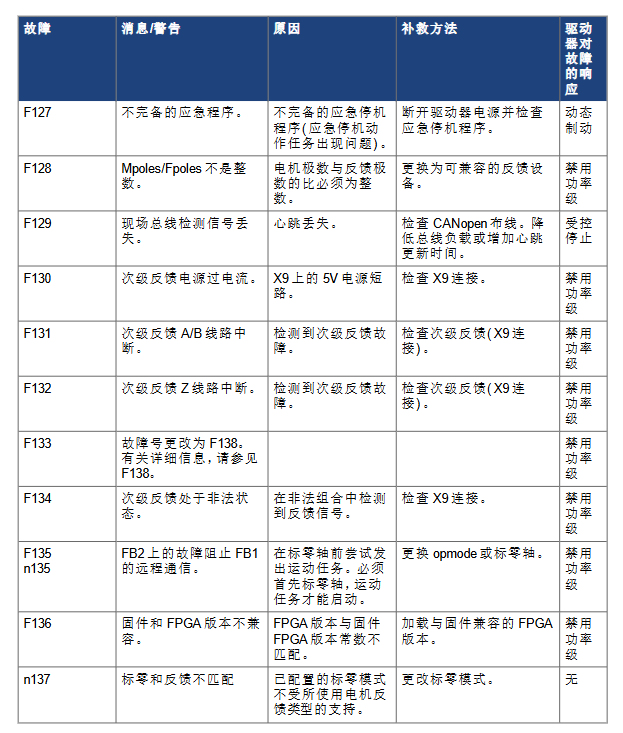
F602 (Safety Torque Off, STO): Trigger the STO function, confirm safety conditions, and then power on again, in accordance with functional safety specifications (such as EN ISO 13849).
F702/n702 (fieldbus communication disconnected): All fieldbus communication is lost. Check the X11 interface wiring (such as EtherCAT, CANopen), host settings, and trigger controlled shutdown.
F706/n706 (fieldbus set point loss): The host stops sending set points due to timeout. Check the stability of the bus connection, reduce the bus load, or adjust the timeout parameter.
(5) AKD-T exclusive fault (F800-F999)
AKD-T supports running BASIC programs, and many faults are related to program execution. The typical code is as follows:
F801 (divided by zero): There is a division by zero operation in the program, modify the code to avoid invalid calculations.
F802 (Stack Overflow): Insufficient program stack memory, optimize code structure, reduce nested calls.
F824/F825 (mode incompatible): DRV.OPMODE needs to be set to 2 (position mode), DRV.CMDSOURCE needs to be set to 5 (program command), adjust the parameters and restart the program.
F901 (Too Many Cams): The number of cams defined in the program exceeds the upper limit, reduce cam configuration or optimize motion logic.
Key fault troubleshooting process
Identification code: Obtain the fault code through panel display or WorkBench, confirm the code type (F/n) and priority.
Identify the cause: Based on the corresponding entries on the fault card, investigate the hardware wiring (such as feedback, power supply, motor phase lines), parameter configuration (such as feedback type, current limit), and environmental conditions (temperature, ventilation).
Execute remedial measures:
Wiring faults (such as F314 motor phase loss, F404 Hall wire breakage): Repair the wiring after power failure, and confirm the correctness of the connection before re enabling.
Parameter faults (such as F105 NV memory error, F501 bus overvoltage): Reset parameters or adjust thresholds through WorkBench, save and restart the drive.
Hardware failures (such as F201 RAM damage, F531 power level failure): If restarting is ineffective, please contact technical support and return to the factory for repair if necessary.
Clear the fault: Use the DRV.CLRFAULTS command or WorkBench button to clear the fault, confirm that the fault is eliminated, and then re enable the drive.
- ABB
- General Electric
- EMERSON
- Honeywell
- HIMA
- ALSTOM
- Rolls-Royce
- MOTOROLA
- Rockwell
- Siemens
- Woodward
- YOKOGAWA
- FOXBORO
- KOLLMORGEN
- MOOG
- KB
- YAMAHA
- BENDER
- TEKTRONIX
- Westinghouse
- AMAT
- AB
- XYCOM
- Yaskawa
- B&R
- Schneider
- Kongsberg
- NI
- WATLOW
- ProSoft
- SEW
- ADVANCED
- Reliance
- TRICONEX
- METSO
- MAN
- Advantest
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bently
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- Beijer
- Moxa
- Rexroth
- Johnson
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- Application field
- XP POWER
- CTI
- TRICON
- STOBER
- Thinklogical
- Horner Automation
- Meggitt
- Fanuc
- Baldor
- SHINKAWA
- Other Brands





































































































































