KOLLMORGEN S200 High Performance Compact Brushless Servo Drive
KOLLMORGEN S200 High Performance Compact Brushless Servo Drive
Introduction: Redefining Compact Servo Performance
In the field of industrial automation, the performance, volume, and reliability requirements for servo drives are becoming increasingly stringent. The S200 series high-performance compact brushless servo drive launched by Danaher Motion (now under Kollmorgen) is designed to address this challenge. This series of drivers integrates industry-leading servo technology into a full power range product family, covering both DC and AC input models, particularly in low-power applications, providing unprecedented high-performance, high robustness options without compromising on reliability or packaging size.
The S200 driver represents a significant advancement in fully digital industrial drive technology, with a speed bandwidth of up to 80 Hz. Combined with high-resolution (24 bit) feedback and a current bandwidth of up to 3-5 kHz, it achieves smooth motion control and fast start stop response, significantly optimizing machine performance. Its "intelligent feedback" technology combined with industry-leading high bandwidth eliminates the need for servo loop debugging in most applications, achieving fast and accurate "plug and play" debugging.
Product Overview and Core Features
The S200 series drivers are designed for demanding applications such as semiconductor manufacturing, electronic assembly, packaging, medical and woodworking equipment. Paired with Danaher Motion's AKM series servo motors, it can form a complete servo control solution.
The core features include:
Control Logic: Version 3.0 or higher. Units produced after November 2007 fully comply with the EU RoHS directive.
Standard control mode: The basic unit comes standard with torque or speed control.
Scalability: The factory can optionally add tabs that support SynqNet motion networks, or add preset indexes with CANopen communication.
Wide feedback compatibility: The tab has added interfaces with additional motor feedback devices such as Comcoder, 1 Vpp Sin Cos, EnDat 2.1, and EnDat 2.2 running in 2.1 compatibility mode, supporting single/multi turn absolute rotation or incremental/absolute linear encoders.
Flexible power input: Supports AC (120/240 VAC) or DC (20-90 VDC) power supply, with current ratings ranging from 1.5 ARMS continuous to 48 ARMS peak.
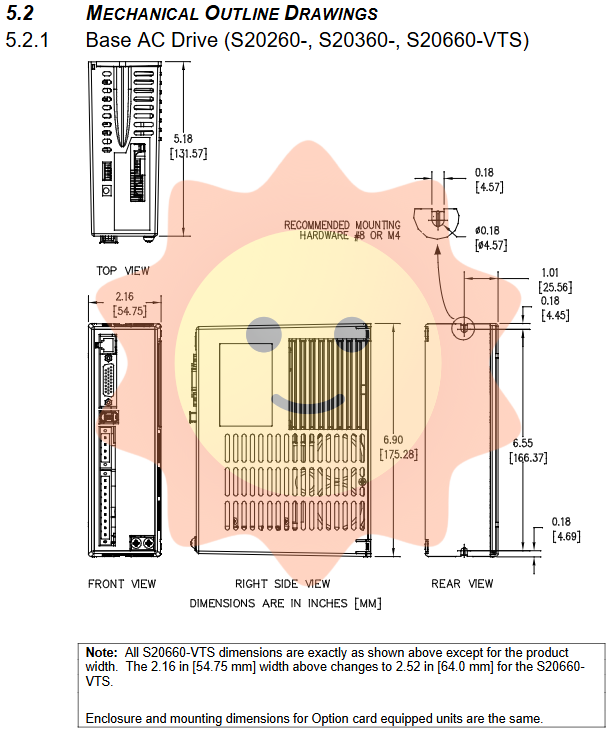
Compact design: Width ranging from 1.1 inches (28.7 millimeters) to 3.8 inches (94.6 millimeters), height ranging from 6.0 inches (152.4 millimeters) to 8.39 inches (213 millimeters), depth ranging from 3.9 inches (100.8 millimeters) to 7.57 inches (192.4 millimeters), suitable for space constrained applications.
Independent 'keep active' control power supply: allows communication and diagnosis to be maintained in case of emergency stop due to motor power failure, and can be quickly restored.
Security: Optical isolation input/output, forward locking connectors, and comprehensive fault protection, promising long machine life and resistance to accidental damage.
Detailed technical specification analysis
3.1 Drive family power
The S200 series offers multiple models to meet different power requirements. Taking the 240VAC input model as an example, its peak output current range ranges from 4.5 ARMS in S20260 to 48 ARMS in S22460. The continuous output power ranges from 600W in S20260 to 8000W in S22460 at 240VAC three-phase. For DC input models (such as S20330/S20630), the continuous output power is 250W and 500W respectively at 75VDC bus voltage. All specifications are effective within the specified ambient temperature (0-50 ° C) and line voltage range, and the derating curve needs to be considered.
3.2 AC Input Driver - Control and Power Supply
Control power supply: Input voltage range up to 85-265 VAC single-phase (47-63 Hz) or 120-375 VDC. Has the ability to temporarily maintain line voltage, for example, it can maintain over 18.5 cycles at 240VAC/60Hz.
Motor power supply: S20260/360/660 supports 0-265 VAC, S21260/22460 supports 120-265 VAC, compatible with single-phase or three-phase input. It is recommended to configure isolation transformers with corresponding capacity to limit power grid surges.
Bus voltage and faults: The nominal bus voltage is 320VDC when input at 240VAC, and 155VDC when input at 120VAC. The bus overvoltage fault point is set to 407VDC ± 5%.
Surge current and fuse: The manual provides detailed peak surge current data and recommended delay fuse models for different models, phases, and voltages (such as Bussmann FRN or JKS series).
3.3 DC Input Driver - Control and Power Supply
Control power supply: Voltage range+10 to+90 VDC, recommended to use a minimum 20W power supply to ensure reliable startup.
Bus voltage and faults: operating range+20 to+90 VDC, undervoltage fault approximately+17VDC, overvoltage fault approximately+91VDC.
3.4 Motor current control
Current loop bandwidth: AC input driver maximum is 3 kHz (recommended 2 kHz), DC input driver maximum is 5 kHz (recommended 3 kHz). The intelligent feedback device automatically sets the bandwidth to 2 kHz.
Offset current: varies with model and temperature, with a typical value of 0.2% of full scale and a worst-case (over temperature) value of 0.5%.
3.5 Speed Loop
The maximum stable bandwidth can reach 800 Hz (when using SFD).
High command resolution, below 0.001 rpm when simulating commands.
The speed loop compensation parameters (KVP, KVI, ARF0, ARF1) are adjustable to adapt to different mechanical loads and resonance characteristics.
3.6 Command I/O
Provide rich interface options:
Simulated command input: differential range ± 12.5V, high signal-to-noise ratio, adjustable offset.
High speed input: can be used as a stepper command (up to 1.5 MHz) or PWM command (0.25 to 250 kHz).
Orthogonal input/output: RS-422/485 differential interface, maximum line frequency 625 kHz.
Universal input/output: Wide voltage range (± 4-30V), compatible with source and drain logic, fast response time.
3.7 Machinery and Environment
The driver is designed for vertical installation inside the cabinet and needs to be installed on a flat, sturdy, and conductive grounding surface. The working temperature is 0-40 ° C (fully rated), and linear derating is required for 40-50 ° C. Storage temperature -35 to 85 ° C, humidity 10-90% non condensing.
3.9 Intelligent feedback device
SFD is one of the core advantages of the S200 system, providing extremely high position and velocity feedback quality.
Position signal: 24 bit resolution (0.0013 arcminutes per revolution), high repeatability, can further reduce noise through filtering.
Speed signal: resolution below 0.001 rpm, high update frequency, low noise.
Simulation encoder output: Multiple PPR values can be selected by rotating switch S1, with a maximum output line frequency of 2.5 MHz.
Installation and Configuration Guide
Quick Start
Follow different quick start guidelines based on the driver type (base unit or SynqNet version). The basic steps include software installation, hardware setup, communication wizard configuration, motor feedback configuration, and parameter saving.
S200 basic unit driver configuration:
Hardware connection: Use a serial communication cable (to be ordered separately) to connect the J5 port of the driver to the host computer.
Software configuration: Run the S200 Tools software, select the "Serial" mode through the communication wizard, and test the connection.
Feedback configuration: The basic unit only supports SFD motor feedback connected through J3. If using SinCos or ComCoder, J14 port must be used (only for models with tabs).
Parameter saving: Distinguish between "Download NV" (saved to permanent storage) and "Download Drive" (saved to temporary RAM). It is recommended to use the latter for testing, and after confirmation, use the former for permanent saving.
S200 SynqNet driver configuration:
Prerequisite: Install Motion Developer's Kit and SynqNet controller.
Network connection: Use Ethernet cables to daisy chain the J11 (IN) and J12 (OUT) ports of the SynqNet controller and each driver.
Software configuration: Select the "SynqNet" mode in S200 Tools, and the software will automatically discover nodes on the network.
Feedback source selection: In the SynqNet options tab, select "Base Unit Feedback" or "Option Card Feedback" based on the actual port (J3 or J14) connected to the feedback device.
Advanced feedback configuration: For SinCos or ComCoder, it is necessary to manually calculate and set parameters such as KIP, 2TFO, 2ITTriP to match motor characteristics.
Switch settings and basic configuration
The switches S1 and S2 on the top of the drive are used for quick basic configuration.
S2 DIP switch: Position 1 selects torque/current or speed control mode, position 2 selects SFD or 6-step (Hall) feedback type. Factory default enable switch setting.
S1 rotary switch (for SFD feedback): Set the number of lines output by the simulation encoder (such as 50010242048, etc.).
S1 rotary switch (for 6-step feedback): Set the current loop proportional gain KIP based on the motor inductance to ensure loop stability.
The driver supports automatic motor configuration with SFD, loading default motor parameters to achieve robust performance. For advanced applications that require optimization, SelSFDParam can be manually adjusted to "Drive" through S200Tools to adjust motor parameters (KVP, KIP, DPOles, etc.), but caution must be taken to avoid damage.
Advanced configuration and functional block diagram
The S200 driver provides advanced control capabilities and can be deeply customized through the S200Tools software. The manual provides detailed control diagrams to help users understand signal flow:
Basic drive torque/speed control diagram: shows the complete path from command input (analog, PWM, variable), filtering and gain adjustment, to current loop, speed loop, and finally output to motor, including feedback and feedforward channels.
Basic driver position control diagram: A position ring has been added on the basis of the speed ring, supporting step/direction or A/B orthogonal command input, and scaling through gear ratio (GearIn/GearOut).
SynqNet Drive Torque/Speed Control Block Diagram: Highlighting the path of receiving commands and exchanging data through the SynqNet network, achieving synchronization and centralized control between multiple axes.
Parameter and Variable System
The behavior of the driver is defined by non-volatile parameters, state variables, and control variables.
NV parameters: stored in persistent storage, determine the configuration and operating mode of the drive (such as OpMode, CMDSrc, KVP, KIP, etc.). Save through 'Download NV'.
State variable: read-only, reflecting the real-time status of the drive (such as PosFB, VelFB, VBus, FaultCode, etc.).
Control variables: volatile, used for real-time control of specific functions (such as Command variables).
The S200 Tools software is the core tool for configuration and monitoring, allowing users to adjust parameters and observe variables in real-time in online mode, prepare configurations in offline mode, and save and reuse settings through configuration files (*. S2C).
SynqNet Network Integration and Diagnosis
SynqNet configuration
For the S200 driver equipped with the SynqNet tab, its configuration information is defined through an FPGA table, including node type, option code, number of motors/encoders, number of dedicated I/Os, etc. This ensures that the SynqNet master station can correctly identify and drive nodes.
Accessing Drive Parameters
The parameters of the drive can be read and written using MPI library methods or specialized tools (sqDriveParam, sqDriveConfig) through the SynqNet network. This requires the use of a parameter mapping file that matches the firmware version of the drive, which defines valid parameter indexes, names, data types, and ranges.
Diagnosis and troubleshooting
The S200 integrates comprehensive fault protection circuits, including protection against output short circuits, overheating, bus overvoltage/undervoltage, overcurrent (I * t), motor overheating (via SFD), and more.
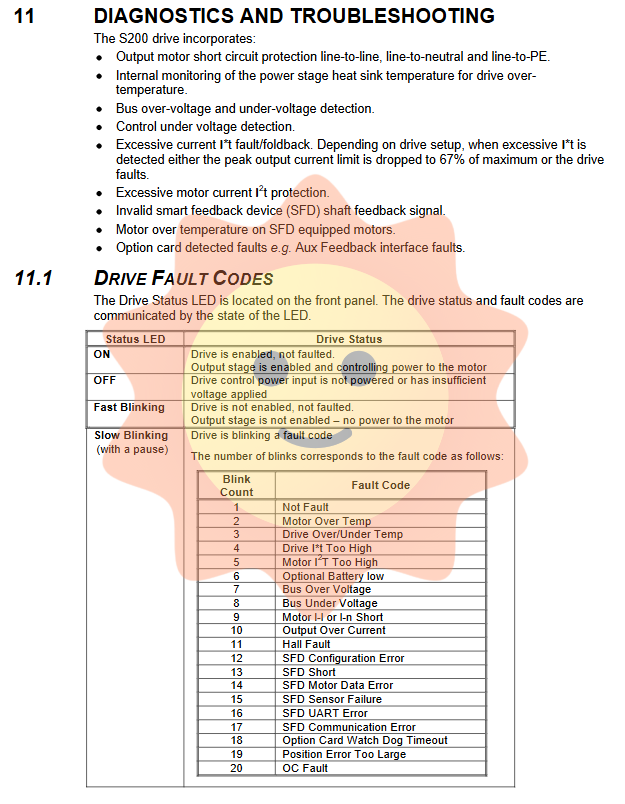
Status LED indicators: constantly on (enabled without faults), off (control power not powered on), flash (ready but not enabled), slow flash (fault code).
Fault code: Specific faults are indicated by the number of LED flashes, such as 2 (motor overheating), 7 (bus overvoltage), 11 (Hall fault), 17 (SFD communication error), etc. More detailed fault information can be read through the ExtFaults variable.
Fault handling: Some faults (such as bus overvoltage) can be self reset, while latch faults need to be cleared by disabling the enable or cycling the power supply. When multiple faults occur simultaneously, prioritize reporting the highest priority fault.
Appendix Key Technical Points
Design of DC power supply
Designing a power supply for DC input drivers is crucial:
A single power supply (20-90VDC) can be used to simultaneously power the bus and control, or two independent power supplies can be used to improve safety.
The external bus capacitor is a critical component used to absorb the energy feedback during motor deceleration, provide peak power required for acceleration, stabilize the bus voltage, and reduce the peak current demand of the power supply. For example, it is recommended to use a minimum of 4000 μ F capacitor for the S20630 driver at 75VDC.
The capacitor should be an aluminum electrolytic capacitor with a rated voltage of 100V. The wiring resistance and inductance need to be controlled to avoid excessive voltage drop or bus resonance.
Do not install emergency stop switches or contactors between the bus pins of the driver and the power capacitor to prevent damage due to motor winding energy feedback when the driver is disabled.
Cable selection and wiring
Long cable impact: For DC drives, the resistance of long motor cables can cause voltage drops, affecting peak acceleration performance. In demanding dynamic applications, it is recommended to use 14 AWG cables instead of 18 AWG cables.
Customized composite cable: If the feedback and power lines are integrated into a single cable, it is strongly recommended to use a dedicated cable with a double-layer concentric shielding structure to minimize the interference of PWM noise on sensitive feedback signals. The inner shield is usually connected to the feedback power return, while the outer shield is connected to the PE.
Safety and Compliance
The S200 driver complies with multiple international standards, including UL 508C, CE (Low Voltage Directive and EMC Directive), EN50178, and EN61800-3.
Installation responsibility: The final machine manufacturer is responsible for ensuring that the entire system complies with all applicable directives and standards.
Safety operation requirements:
Emergency stop circuit: An external hard wired emergency stop circuit must be provided, which can simultaneously cut off the motor power and disable the driver.
Prevent accidental movement: Before maintenance, the power must be disconnected and wait for at least 5 minutes for the bus capacitor to discharge.
Electrical safety: It is strictly prohibited to plug or unplug connectors or wires with power on.
Thermal safety: The temperature of the driver's heat sink and external brake resistor may exceed 60 ° C, posing a risk of burns.
EMC Compliance Recommendations:
Use recommended line filters (such as Corcom, MTE, Schaffner series).
Use original or EMC designed cables.
Separate cables of different types (power supply, motor, signal) by at least 100mm for routing.
Ensure that all cable shielding layers are terminated 360 degrees to the ground plane at the connector.
- ABB
- General Electric
- EMERSON
- Honeywell
- HIMA
- ALSTOM
- Rolls-Royce
- MOTOROLA
- Rockwell
- Siemens
- Woodward
- YOKOGAWA
- FOXBORO
- KOLLMORGEN
- MOOG
- KB
- YAMAHA
- BENDER
- TEKTRONIX
- Westinghouse
- AMAT
- AB
- XYCOM
- Yaskawa
- B&R
- Schneider
- Kongsberg
- NI
- WATLOW
- ProSoft
- SEW
- ADVANCED
- Reliance
- TRICONEX
- METSO
- MAN
- Advantest
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bently
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- Beijer
- Moxa
- Rexroth
- Johnson
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- Application field
- XP POWER
- CTI
- TRICON
- STOBER
- Thinklogical
- Horner Automation
- Meggitt
- Fanuc
- Baldor
- SHINKAWA
- Other Brands





































































































































