ABB MNS iS Motor Control Center System
ABB MNS iS Motor Control Center System
Product positioning: MNS iS is an intelligent motor control center upgraded based on MNS series technology, integrating protection, control, and monitoring functions, suitable for industrial production lines, energy facilities, and other scenarios. Through modular design, it achieves efficient operation and maintenance as well as full lifecycle cost optimization.
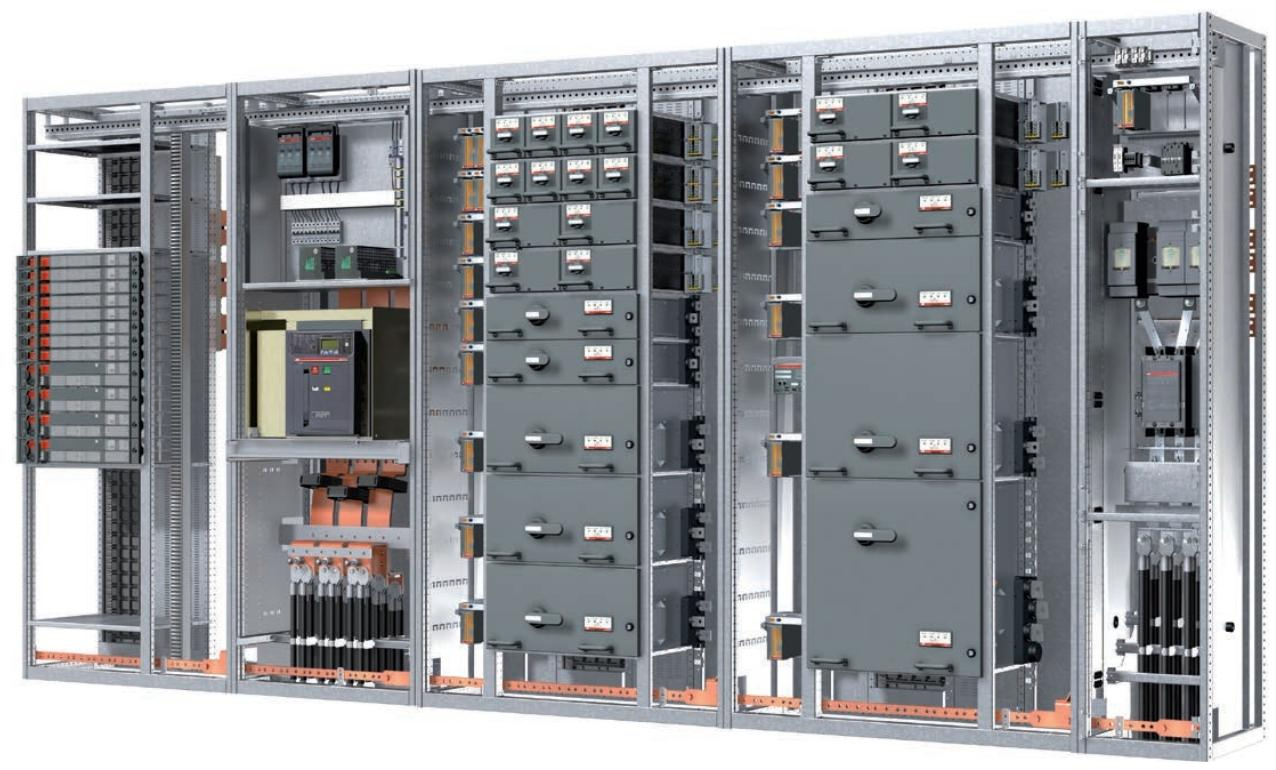

Core characteristics and values of the system
1. Core advantages
High safety: The power and control areas are physically isolated, complying with the IEC 61439 series standards, supporting arc fault protection (up to 100 kA/300 ms), ensuring the safety of personnel and equipment.
Standardization and flexibility: The fully pre installed power module (MStart) supports multiple starter types (direct start, star delta start, etc.), and the control module (MControl) can expand its functionality through software configuration without the need for additional hardware.
Low lifecycle cost: Reduce downtime through predictive maintenance (condition monitoring), standardize modules to lower inventory requirements, and simplify troubleshooting processes.
Intelligent information management: integrates web servers with industrial communication protocols (Profibus, Profinet, etc.), supports remote monitoring and data analysis, and achieves digital operation and maintenance.
2. Innovative design
Functional module separation: The power module (MStart) and control module (MControl) operate independently, supporting live module replacement and improving system availability.
Transformer free sensing technology: high-precision shunt sensors are used to measure current, voltage, and temperature, replacing traditional transformers and reducing energy consumption and space occupation.
Plug and play architecture: modules automatically identify location and type, communication networks automatically configure, reducing engineering complexity.
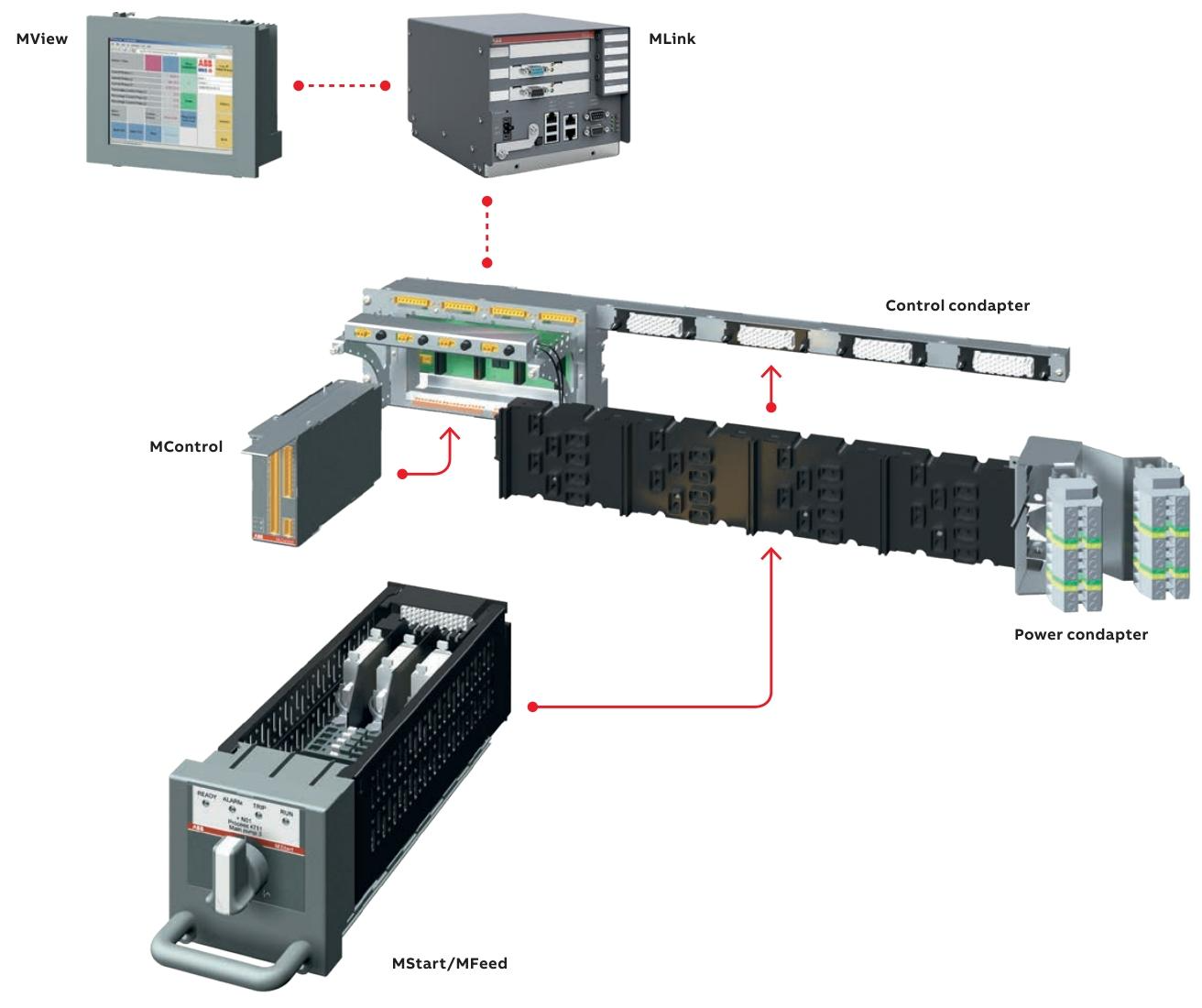
System Architecture and Components
1. Hardware composition
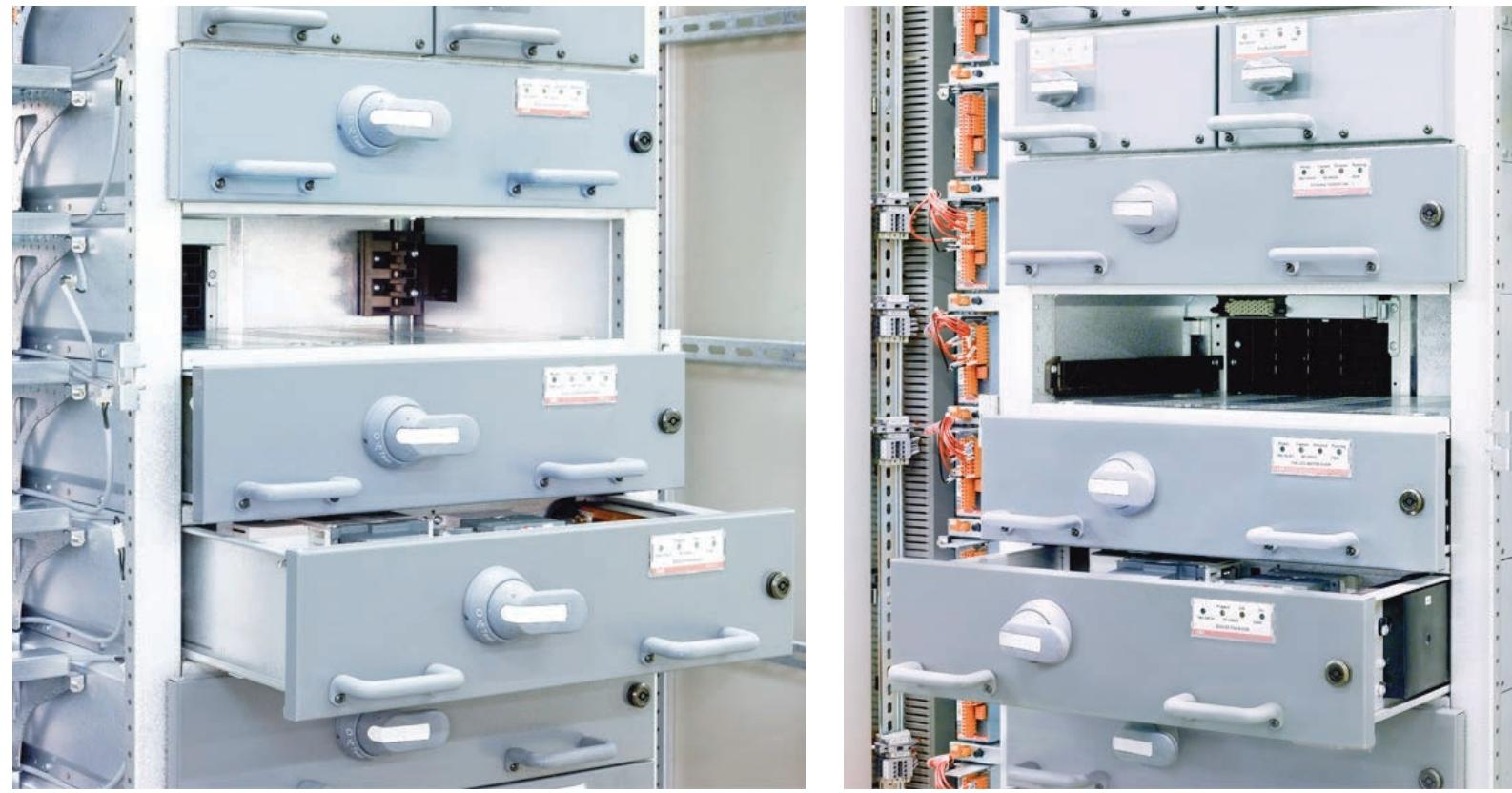
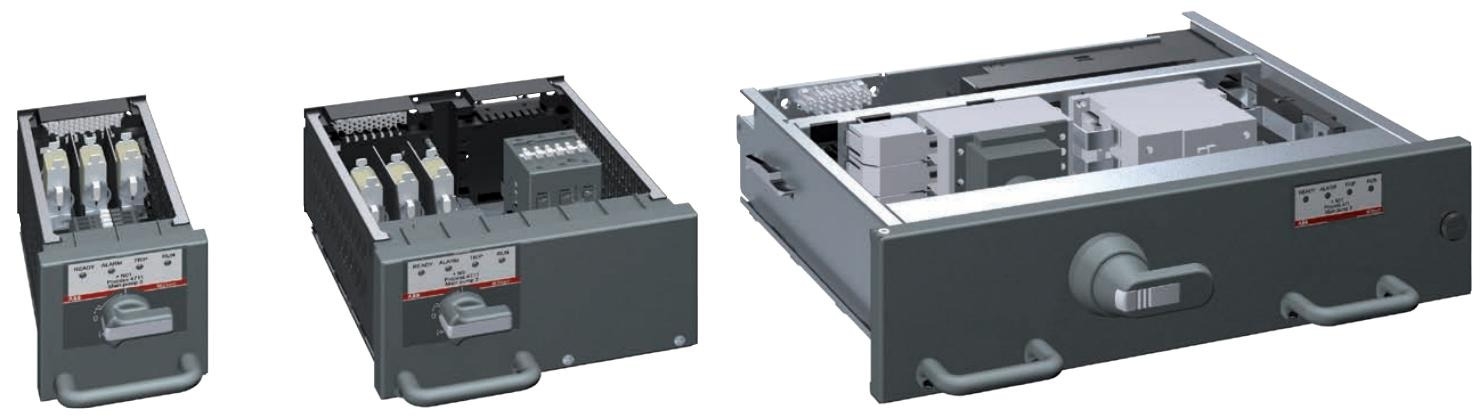
Power module (MStart):
Includes isolators, short-circuit protection devices (fuses or circuit breakers), contactors, and sensor modules.
Supports drawer style (6E/4 to 24E sizes) and fixed style (suitable for motors ≥ 250 kW) installation, compatible with voltage levels of 400 V, 500 V, and 690 V.
Control module (MControl):
The core controller is responsible for protecting algorithms (overload, phase loss, ground fault, etc.), logic control, and data acquisition.
Support the expansion of I/O interfaces (digital, analog, PTC/PT100 temperature input) to meet different on-site signal requirements.
Communication and Interface Module:
MLink: As a gateway connecting upper level systems, it supports protocols such as Profibus DP, Profinet, Modbus, and has a built-in web server.
MView: Local Human Machine Interface (HMI), supports touch operation and status monitoring, and can be accessed remotely through the network.
2. Structural design
Partition separation: Vertical and horizontal partitions strictly distinguish equipment areas, control cable areas, power cable areas, and busbar areas to avoid electromagnetic interference, and support different key lock control access permissions.
Busbar system: The main busbar is located at the rear of the cabinet and adopts a maintenance free design (copper material, optional silver plating or insulation sleeve). It is safely isolated from the equipment area through a multifunctional isolation wall (MFW).
Cable management: Power and control cable partition wiring, supporting up and down incoming lines, suitable for different installation scenarios.
Control and protection functions
1. Protection function module
Thermal Overload Protection (TOL): Based on the IEC 60947-4-1 standard, it calculates the motor's thermal capacity, provides "trip time" and "reset time" warnings, and supports ATEX certification scenarios.
Motor abnormal protection: monitors phase loss, current imbalance, undervoltage, grounding faults, etc., and can be configured with alarm or trip actions.
Process monitoring and protection: including blockage, underload, no-load, and limit of starting times, to prevent mechanical failures (such as pump cavitation).
2. Maintenance and status monitoring
Predictive maintenance: Monitor parameters such as the number of contactor actions, module insertion times, operating hours, and contact temperature, and trigger an alarm when the threshold is exceeded.
System self diagnosis: Automatically verify module type and position matching, communication status, and control voltage to ensure system integrity.

Communication and Integration
Communication architecture and core components
1. Communication nodes and hierarchy
The communication system of MNS iS adopts a distributed architecture and is divided into three levels of nodes:
On site level: With MControl as the core, responsible for the protection, control, and data acquisition of a single motor, communicating with the power module (MStart) through an internal bus.
Network level: Multi node aggregation is achieved through MLink gateway, supporting interaction with upper level systems, and can connect up to 60 MControl modules.
Monitoring level: Integrated MView local human-machine interface and web server, supporting remote access and configuration.
2. Key communication components
Component Function Description
MControl has a built-in communication interface that supports real-time data exchange with MStart modules (current, temperature, status, etc.) and can be directly connected to Profibus DP/Profinet networks.
As a system gateway, MLink supports protocols such as Profibus DP, Profinet, Modbus RTU/TCP, OPC, etc., enabling integration with PLC, SCADA and other systems, while also providing web server functionality.
MView local touch panel (optional), displaying motor status, alarm information, and operation buttons based on a web interface, supporting permission management.
Communication Protocol and Interface
1. Supported protocol types
Industrial bus protocol:
Profibus DP/DP V1 (slave mode, supporting process data and diagnostic information transmission);
Profinet I/O (compatible with ABB systems and supports real-time communication);
Modbus RTU (serial communication) and Modbus TCP (Ethernet communication).
General Agreement:
Built in web server, supporting access to monitoring interface through standard browsers;
OPC interface, easy to integrate with third-party SCADA or MES systems;
NTP (Network Time Protocol) enables system wide time synchronization.
2. Data transmission capability
Internal communication: A 10 Mbps real-time bus is used between MControl and MLink, with a command response time of approximately 2 ms for a single MControl and a total system response time of ≤ 258 ms for 60 nodes.
External interaction:
The maximum transmission rate of Profibus DP is 12 Mbps;
Profinet and Modbus TCP support 100 Mbps Ethernet transmission;
Support data block read and write (such as motor current, temperature, tripping reasons, etc.) and remote control commands (start/stop/reset).

System integration capability
1. Integration with upper level systems
Process Control System (PCS): Using MLink as a gateway, the motor status and measurement values (current, power, energy consumption) are uploaded to PLC or DCS, and control instructions are received to achieve remote operation.
Electrical network monitoring system: supports sending electrical parameters (such as harmonics and power factor) to the energy management system (EMS) to assist in energy optimization.
Maintenance management system: Push equipment health data (contactor action frequency, operating hours, temperature trend) to CMMS (computerized maintenance management system) through OPC interface, supporting the development of predictive maintenance plans.
2. Redundancy and reliability design
Dual redundant communication: supports two independent communication paths (primary/backup MLink). When the primary link fails, it automatically switches to the backup link to ensure uninterrupted operation, with a switching time of ≤ 100 ms.
Communication fault protection: Configure the "fail safe" mode (such as keeping the motor running/stopping in case of communication interruption) to avoid unexpected shutdowns caused by network issues.
Time synchronization and data consistency
Synchronization mechanism: Implement system wide time calibration through NTP protocol, support access to factory level time servers (such as GPS synchronization sources), and ensure that the timestamp accuracy of event records (alarms, trips) is ≤ 1 ms.
Data timeliness: The update cycle of key measurement values (such as current and temperature) can be configured (default 100 ms) to meet real-time monitoring requirements; Historical data (energy consumption, number of actions) is stored at the minute level and supports trend analysis.

- ABB
- General Electric
- EMERSON
- Honeywell
- HIMA
- ALSTOM
- Rolls-Royce
- MOTOROLA
- Rockwell
- Siemens
- Woodward
- YOKOGAWA
- FOXBORO
- KOLLMORGEN
- MOOG
- KB
- YAMAHA
- BENDER
- TEKTRONIX
- Westinghouse
- AMAT
- AB
- XYCOM
- Yaskawa
- B&R
- Schneider
- Kongsberg
- NI
- WATLOW
- ProSoft
- SEW
- ADVANCED
- Reliance
- TRICONEX
- METSO
- MAN
- Advantest
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bently
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- Beijer
- Moxa
- Rexroth
- Johnson
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- Application field
- XP POWER
- CTI
- TRICON
- STOBER
- Thinklogical
- Horner Automation
- Meggitt
- Fanuc
- Baldor
- SHINKAWA
- Other Brands





































































































































