REXROTH 4WRTE type electro-hydraulic proportional directional valve
REXROTH 4WRTE series pilot operated proportional directional valve: a high-performance hydraulic control solution integrating electronics and position feedback
In modern high dynamic and high-precision hydraulic control systems, proportional valves play a core role. The 4WRTE series pilot operated proportional directional valve launched by Bosch Rexroth represents the advanced level of industrial hydraulic control technology with its integrated electronic equipment (OBE), electrical position feedback, and optional spool position monitoring function. This article is based on the official technical document RE 29083, providing a comprehensive professional interpretation of the structure, principles, technical characteristics, and applications of this series of valves, aiming to provide detailed references for hydraulic system design engineers and maintenance personnel.
Product Overview and Core Advantages
The 4WRTE series valves are pilot operated, two-way proportional directional valves with electrical position feedback. Its size covers NG10 to NG35, with a maximum working pressure of up to 350 bar and a rated flow range from 25 l/min to 1000 l/min, capable of meeting a wide range of needs from medium to high flow applications. This series of valves adopts the mature 4X component series, ensuring the continuity of installation and connection dimensions.
Core design advantages:
Reliability and Safety: Adopting a validated and robust design. Its pilot valve can achieve automatic pressure compensation of the main control chamber, ensuring smooth control. The main valve core is centered by a spring (or maintained in a biased position under specific symbols), and in the event of a power failure, it can achieve equal pressure in the control chamber through a pilot valve, and ultimately be reliably reset by the spring, meeting the safety shutdown requirements of EN 60204 stop category 0.
High precision and control flexibility: extremely high response sensitivity (≤ 0.05%) and extremely low hysteresis (≤ 0.1%), combined with linear or fine tuned flow characteristics, make it very suitable for position, speed, and pressure closed-loop control.
Integration and Intelligence: The valve integrates control electronics (OBE) and inductive position sensors, achieving a compact integrated design. The optional valve core position monitoring function ("M" option, suitable for NG16 and above specifications) further enhances the safety monitoring capability of the system.
Deep analysis of structure and working principle
1. Core component composition
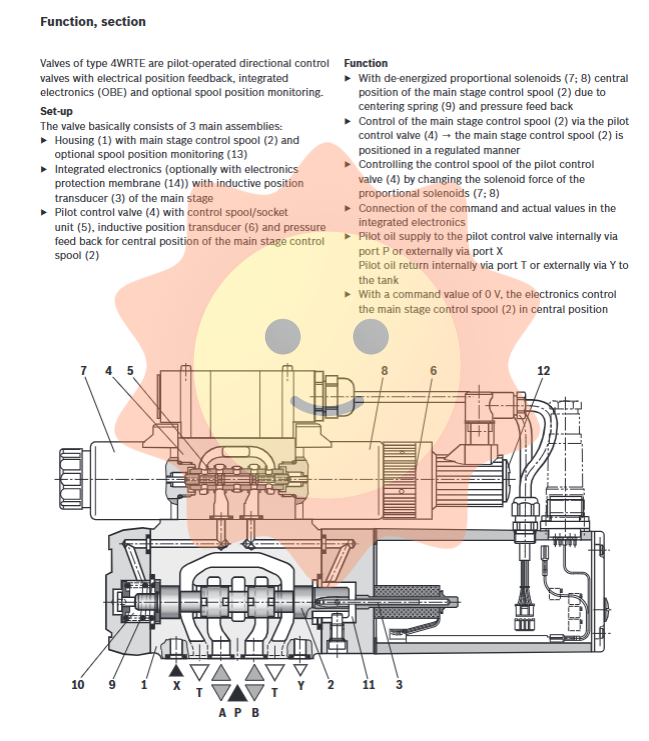
The 4WRTE valve essentially consists of three components integrated into a compact valve body:
Main valve stage: including valve body, main control valve core, centering spring, and optional valve core position monitoring sensor.
Integrated Electronic Equipment (OBE): includes an inductive position sensor with a main valve core, and can be optionally equipped with an electronic device protective film (code "-967") to prevent condensation.
Pilot control valve: an independent proportional valve unit that includes its own control spool/sleeve assembly, inductive position sensor, and pressure feedback channel for the centering position of the main spool.
2. Principle of closed-loop control
The operation of the valve is based on a precise electrical hydraulic position closed-loop control:
Command input: The external controller provides an analog setpoint signal of ± 10 V (interface A1/A5) or 4-20 mA (interface F1) to the integrated electronic device (OBE).
Force driven: OBE controls the proportional electromagnetic current of the pilot valve based on the feedback difference between the set value and the actual position of the main valve core, changes the electromagnetic force, and drives the movement of the pilot valve core.
Hydraulic amplification and positioning: The pilot valve outputs control oil pressure, which acts on the control chamber on the end face of the main valve core, pushing the main valve core to overcome the force of the centering spring and move. The actual displacement of the main valve core is detected in real-time by its integrated inductive position sensor and fed back to the OBE.
Closed loop regulation: OBE continuously compares the set value with the actual position feedback, adjusts the current of the pilot valve solenoid until the main valve core accurately reaches the target position proportional to the input electrical signal, achieving precise proportional control of flow rate.
3. Safety and monitoring features
Fault safety: When the power supply voltage fails or the cable is disconnected, the integrated electronic device will cut off the power of the electromagnet. The pilot valve balances the pressure in the control chamber at both ends of the main valve core, and then the centering spring pushes the main valve core back to the neutral position (for symbols E, E1-, W6-, W8-) or biases the safety position (for symbols V, V1-), achieving a safe reset.
Valve core position monitoring (option "M"): Use an independent inductive proximity switch (wired separately through a 4-pole M12x1 connector) to detect whether the main valve core deviates from the center position beyond a preset threshold (set within the valve core overlap area). This switch provides two PNP output signals, which can be used for safety monitoring functions of higher-level control systems, such as serving as a shut-off element for one of the channels in safety related dual channel applications that meet the EN 13849-1 standard (up to category 4, PL e).
Key Technical Parameters and Selection Guidelines
1. Hydraulic performance parameters
Working pressure: The maximum pressure for main oil ports P, A, and B is 315 bar; Return port T can reach a maximum of 350/370 bar (depending on specifications); The maximum pressure for the external pilot return port Y is 250/315 bar.
Rated flow rate: defined at a valve port pressure difference Δ p=5 bar, carefully selected based on the model size and valve core symbol (such as E, V, W, etc.). For example, NG10 has options of 25, 50, and 100 l/min; NG35 can reach up to 1000 l/min.
Flow characteristics: Linear (L) or linear (P) with fine tuning zone can be selected, the latter providing finer control resolution at small aperture.
Hydraulic oil and cleanliness: Supports mineral oil (HL, HLP, etc.), biodegradable oil (HETG, HEES), and flame retardant hydraulic fluid (HFD, HFC). The system cleanliness requirements are strict and must meet ISO 4406 18/16/13 levels, otherwise it will affect performance and lifespan. When using water-based flame retardant liquid (HFC), there are additional pressure, temperature, and lifespan limitations.
2. Electrical and electronic characteristics
Power supply: 24 VDC (allowable range 18-35 V), maximum ripple of 2.5 Vpp. The maximum current consumption is 1.6 A, the peak current is 2.7 A, and a 4A delay type external fuse is required.
control interface
A1: Differential input, ± 10 V command/actual value.
F1:4... 20 mA command/actual value input.
A5: ± 10 V command/actual value, with enable signal pin (high level 11... UB V effective). Special reminder: When upgrading from the 3X series to the 4X series, the electronic interface must be defined as A5.
Protection level: After the connector is plugged in and locked, the electronic part reaches IP65 protection level.
Coil temperature: up to 150 ° C, attention should be paid to thermal management and operational safety of the installation space.
3. Pilot oil supply options (key selection points)
This is an important part of the ordering code that determines the source and return method of the pilot oil:
No code: External pilot oil supply (X port), external pilot return oil (Y port).
Code "E": Internal pilot oil supply (taking oil from port P), external pilot return oil (port Y). The X port needs to be blocked on the bottom plate.
Code "ET": Internal pilot supply oil, internal pilot return oil (to T port). The X and Y ports need to be blocked on the bottom plate.
Code "T": External pilot supply oil (X port), internal pilot return oil (to T port). The Y port needs to be blocked on the bottom plate.
Suggestion: For applications where the system pressure is above 210 bar or water-based flame retardant fluid is used, it is recommended to use external pilot oil supply to ensure pilot control stability and valve life.
Key points for installation, debugging, and maintenance
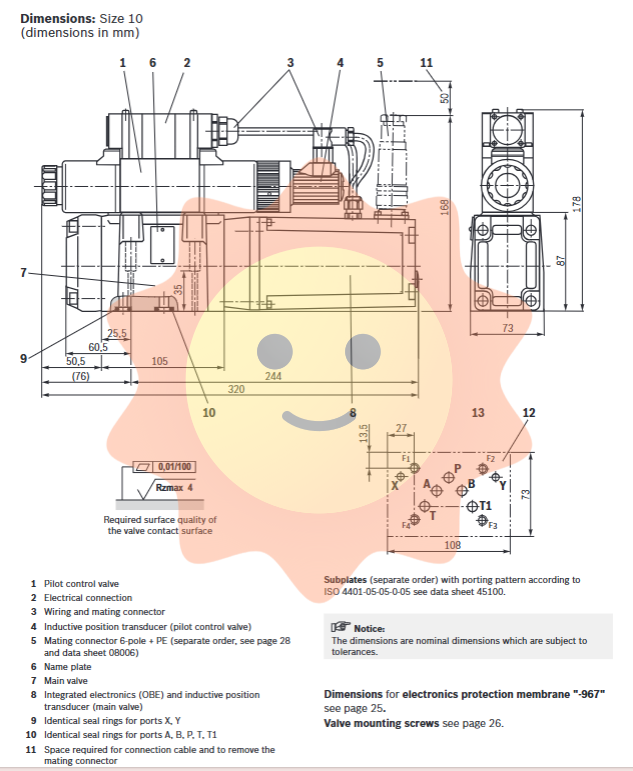
1. Size and installation
The valve provides a bottom plate connection surface that complies with ISO 4401 standard. Each specification (NG10 to NG35) has detailed installation dimension drawings, and attention should be paid to leaving sufficient space for connecting cables and plugging connectors. During installation, it is necessary to use high-strength hexagonal socket head screws (strength grade 10.9) of the specified specifications and tighten them with the precise torque specified in the document (such as 13.5 Nm ± 10% for M6 screws of NG10). This torque value is crucial for setting the maximum working pressure.
2. Electrical connection
The main electronic device is wired through a 6-pole+PE circular connector. It is recommended to use shielded cables (such as LiYCY type) and connect the shielding layer only to the PE on the power supply side.
The valve core position monitoring sensor is independently wired through a 4-pole M12x1 connector, powered by 20-32 VDC, and provides two maximum 400 mA PNP switch outputs.
Important warning: The signals provided by valve electronic devices (such as actual value feedback) must not be used for the shutdown of safety related machine functions. Safe shutdown must be achieved by safely disconnecting the power supply to the valve.
3. Debugging and zero calibration
The valve has completed zero calibration (accuracy ≤ 1%) at the factory. Users are strictly prohibited from attempting to mechanically adjust the PG plug on the valve body (which has an adjusting nut inside), otherwise it may damage the valve.
If the pilot valve or electronic equipment is replaced, it must be recalibrated by trained professionals, otherwise it may cause system damage.
The zero temperature drift is extremely small (<0.3%/10 ° C), ensuring long-term stability during operation.
Typical Applications and Selection Summary
The 4WRTE series valves are highly suitable for application in:
Speed and pressure control of high-precision injection molding machines and presses
Load simulation and position servo control of test bench
Intelligent hydraulic control system for large construction machinery such as shield tunneling machines and cranes
Any industrial hydraulic power shaft control that requires high reliability, high repeatability, and may involve safety monitoring
Suggested selection process:
Determine the main parameters: Determine the valve specification (NG number) and spool symbol (determining the flow curve and neutral position function) based on the maximum pressure and required flow rate of the system.
Choose monitoring and protection: Determine whether to choose valve core position monitoring "M" based on safety requirements; Determine whether electronic protective film "-967" is needed based on environmental humidity conditions.
Clarify the oil and pilot mode: Determine the sealing material (NBR or FKM) and pilot oil supply mode (code: N/E/ET/T) based on the type of hydraulic oil in the system.
Specify electrical interface: Select the command interface (A1, F1, or A5) that matches the controller.
Check the attachments: Ensure that the corresponding base plate, installation screws, electrical plugs, and cables have been ordered.
- ABB
- General Electric
- EMERSON
- Honeywell
- HIMA
- ALSTOM
- Rolls-Royce
- MOTOROLA
- Rockwell
- Siemens
- Woodward
- YOKOGAWA
- FOXBORO
- KOLLMORGEN
- MOOG
- KB
- YAMAHA
- BENDER
- TEKTRONIX
- Westinghouse
- AMAT
- AB
- XYCOM
- Yaskawa
- B&R
- Schneider
- Kongsberg
- NI
- WATLOW
- ProSoft
- SEW
- ADVANCED
- Reliance
- TRICONEX
- METSO
- MAN
- Advantest
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bently
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- Beijer
- Moxa
- Rexroth
- Johnson
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- Application field
- XP POWER
- CTI
- TRICON
- STOBER
- Thinklogical
- Horner Automation
- Meggitt
- Fanuc
- Baldor
- SHINKAWA




































































































































