REXRTOH ECODRIVE DKC Series Drive Controller Comprehensive Fault Diagnosis and Maintenance Guide
REXRTOH ECODRIVE DKC Series Drive Controller Comprehensive Fault Diagnosis and Maintenance Guide
Introduction: Overview of ECODRIVE DKC Diagnostic System
The ECODRIVE DKC01.1 and DKC11.1 series drive controllers from INDRAMAT (now owned by Rexroth), as the core of high-precision servo drive systems, are equipped with a comprehensive diagnostic system designed to help maintenance personnel quickly identify and handle machine faults. This document (based on DOK-ECODRV-ASE-04VRS-WAR1-EN-P) is the official troubleshooting guide for the system. This document is not only a supplement to the device operation panel, but its core goal is to assist in understanding error information, locating the root cause of faults, describing standard troubleshooting procedures, and simplifying communication with the manufacturer's technical service department. Effective diagnosis can significantly reduce downtime and improve overall equipment efficiency (OEE).
All operating states of the drive controller are characterized by "diagnostic messages". These messages are systematically classified into four categories, each of which serves a different function of information transmission:
Error Diagnostic Messages: Identify serious faults that have occurred, causing the driver to stop or malfunction, with codes starting with "F", "UL", and "PL".
Warning Diagnostic Messages: Indicates conditions that may affect performance or indicate potential risks, but the driver can still continue to run, with code starting with "E".
Command Diagnostic Messages: Display the status of complex control commands being executed by the driver, such as zeroing, parameter loading, etc. The code starts with "C" or "D".
State Diagnostic Messages: Reflecting the current normal operating mode of the driver, such as torque control, speed control, enable status, etc. The code starts with "A", "AF", "JF", etc.
Reading and parsing diagnostic messages
H1 Display and Message Structure
The H1 status display on the front of the drive controller is the primary diagnostic information window. This two digit seven segment digital display will cyclically display the current highest priority diagnostic code. A complete diagnostic message consists of a diagnostic code and corresponding diagnostic text. For example, code "F228" corresponds to the text "Excessive Deviation". In addition to viewing the code on H1, the complete diagnostic information (code+text) is also stored in parameter S-0-0095, which can be directly read through upper computer software (such as DriveTop) or operation panels that support text display.
Priority of diagnostic messages
When multiple diagnostic conditions are triggered simultaneously, the H1 display will follow the preset priority order for display. According to the priority dependency graph in the document, error diagnosis messages usually have the highest priority, followed by warning messages, and then command and status messages. This means that in the event of a fault, H1 will prioritize displaying the most severe "F" type errors rather than simultaneous warnings or status information.
Detailed explanation and coping strategies for core error diagnosis
Error diagnosis is directly related to equipment shutdown and is a key focus in maintenance. Here is an analysis of some key errors:
F218/F219/F220- Overheating shutdown: for the driver radiator, motor, and braking resistor respectively. F218 is usually caused by high ambient temperature, clogged radiator, fan failure, or insufficient ventilation in the installation space. Resolve the need to improve cooling, clean heat sinks, or replace driver modules. F219 motor overheating is caused by mechanical overload, continuous over torque operation, or temperature sensor circuit failure. It is necessary to check the mechanical load, friction conditions, and sensor circuit. If the F220 braking resistor overheats, it indicates excessive regenerative energy, and the deceleration or speed should be reduced, or additional braking modules should be considered.
F226- DC bus undervoltage: Monitor the DC bus voltage. The reasons include unexpected interruption of the main power supply (without first disabling the driver enable RF) or power disturbance. Need to check the main power logic and power quality.
F228- Excessive following error: The driver cannot keep up with the given command. Possible reasons include: acceleration demand exceeding driving capacity, motor shaft jamming, incorrect control loop parameters (such as gain) settings, or improper monitoring window S-0-0159 parameters. It is necessary to check the torque limit value S-0-0092, mechanical structure, and control parameters in sequence.
F229- Motor encoder quadrant error: There is a defect in the encoder signal. The common reasons are damage to the encoder cable, insulation failure, or internal faults in the drive controller. The encoder cable should be checked and replaced to ensure that the power line and encoder line are wired separately, and the controller should be replaced if necessary.
F248- Low battery voltage: for motors with absolute value encoders. Its memory is backed up by batteries, and an alarm is triggered when the voltage drops below 2.8V. The battery design has a lifespan of approximately 10 years. When replacing the battery (part number: 257101), attention should be paid to operating it while the control power supply is not powered on, otherwise the absolute position will be lost and the "Set Absolute Measurement" command needs to be re executed.
F262- Status output external short circuit: The digital output channel of the driver has short circuit and overload protection. Short circuit (>350mA) or thermal overload (multi-channel>80mA) will trigger this error. Check the output circuit, eliminate short circuits, and ensure that the load current is within the rated range. Attention: Load with high impulse current, such as incandescent lamps, may be misjudged as a short circuit.
F276- Absolute Encoder Error: The deviation between the position stored during power-off and the position read by the encoder after power on exceeds the monitoring window defined by P-0-0097. It may be due to manual movement of the motor during initial power on or power off, or incorrect position initialization. Confirm the mechanical zero position and reset the absolute position if necessary.
F629/F630/F643/F644- Travel limit related errors: represent exceeding the software positive/negative limit and triggering the positive/negative limit switch, respectively. Triggered when the corresponding bit of parameter P-0-0090 is set to 'view limit as error'. The solution is to clear the error and only move the axis in the direction of the allowed work area.
F822- Motor encoder signal too small: The amplitude of the encoder signal exceeds the normal range (Uss 12.0V -18.0V). The reasons include feedback cable faults or damage to the encoder itself. This error can only be cleared in parametric mode and will cause the encoder simulation function to shut down.
F860- Power level overcurrent/short circuit: If the current exceeds twice the peak value, immediately turn off. The reason may be a short circuit in the motor cable, damage to the power part of the drive controller, or incorrect current loop parameters. It is necessary to check the cables, replace the controller, or restore the default parameters of the current loop.
F870-+24V control power supply error: The 24V control voltage exceeds the allowable tolerance (± 20%). Check and ensure that the 24V power supply is stable and not overloaded.
F878- Speed Loop Error: Triggered when current saturation, excessive speed error, and abnormal acceleration direction occur. Possible causes include incorrect motor cable connections, controller malfunctions, encoder malfunctions, or improper speed loop parameter settings.
Warning and Status Diagnosis: Key to Proactive Maintenance
Warning messages are valuable signals for proactive maintenance and preventing minor issues from escalating into major failures.
E209- Parameter Storage Activation: Indicates that the parameters are being saved. Do not turn off the power at this time, as it may result in parameter loss or damage.
E250/E251/E252- Overheating Warning: Temperature warnings for radiator, motor, and brake resistor respectively. A buffer time (such as about 30 seconds for the radiator) is provided before the final shutdown (F218/219/220), allowing the control system to execute a safe shutdown sequence (such as exiting the work area). At this time, the cooling conditions and load situation should be checked.
E254- Non return to zero: Appears when the absolute positioning command is issued but the axis has not executed the reference point return to zero. You must first perform a zero return operation or use a relative positioning command instead.
E260- Current Limit Activation: Indicates that the speed regulator has reached its output limit, limiting the driving acceleration capability and causing an increase in tracking error under position control. Need to reduce command acceleration/speed, or check if torque limit needs to be increased.
The status message intuitively reflects the working mode of the drive, such as A100 (torque mode), A101 (speed mode), A203 (position mode), AF (drive enable), JF/JB (positive/negative jog), etc. It is the basis for judging whether the drive responds to commands as expected.
Command diagnosis and advanced function execution
Command diagnostic messages track the execution process of specific control commands.
C100-C203 series: related to communication phase conversion and parameter checking. When switching from parameter mode to operation mode, if the parameters are found to be invalid, exceeded, or calculated incorrectly, the switch will be prevented and the corresponding C code will be prompted. Usually, it is necessary to connect to the DriveTop software and check and correct parameters in the 'Invalid Parameter List'.
C600 series - Drive control zeroing: covers various states and errors of zeroing commands, such as C601 (drive not enabled), C605 (zeroing speed too fast), etc. The correct zeroing requires matching hardware (reference switch, encoder zero pulse) and parameter settings (S-0-0041 zeroing speed).
C700- Basic Load: Used to load preset control loop parameters (current loop, speed loop, etc.) that match the motor model from the motor feedback memory. Commonly used after replacing the motor.
D900 Series - Automatic Control Loop Adjustment: Command D9 to initiate the process of automatically optimizing the gain of the speed loop and position loop. This process will cause the axis to move automatically, so it is necessary to ensure that the enable signal is effective and that safety measures are in place within the range of motion. Subcodes D901-D906 indicate specific issues during the optimization process, such as inertia identification failure (D903), gain adjustment failure (D904), etc., which typically require adjusting relevant parameters or checking mechanical conditions.
Regulations for Safe Replacement of Driver Components
Directly replacing suspected faulty components is an effective means to quickly restore production. Chapter 6 of the document provides detailed steps for safely replacing the driver (DKC), motor, and cable.
Core security principles:
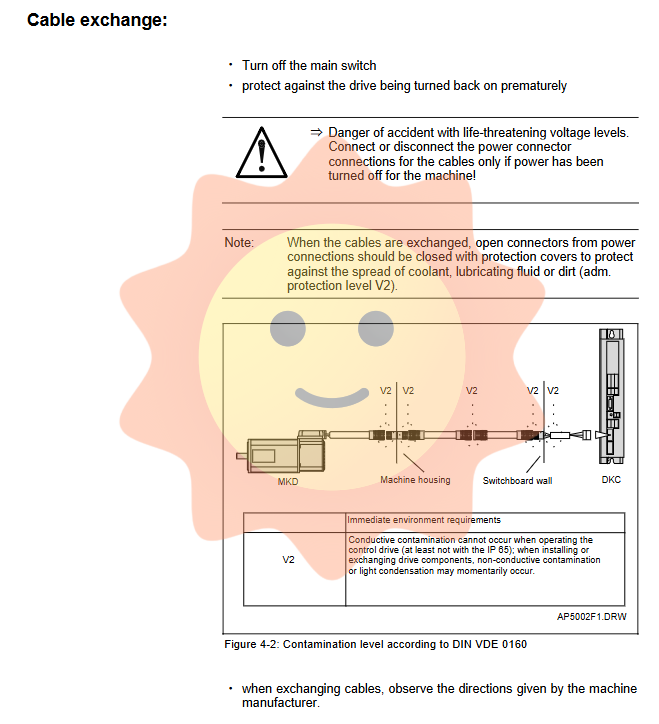
Complete power outage and discharge: Turn off the main switch and take measures to prevent accidental closing. Due to the back electromotive force generated by the rotation of the motor, it is necessary to wait for at least 1 minute for the internal capacitor to fully discharge before contacting the electrical connection parts.
Accurate model matching: Replacement parts must have the exact same model code as the original, which can be obtained from the component nameplate.
Anti pollution measures: When disassembling, the exposed joints should be immediately sealed with protective covers to prevent coolant, lubricating oil, or dust from entering (meeting the protection level requirements).
Key steps after replacement:
Replace Drive (DKC): After installing the new unit, it is necessary to correctly wire according to the drawing and use DriveTop to download the previously backed up machine parameter files to the new drive.
Replacing the motor: For systems that use built-in encoders as indirect position feedback, replacing the motor will result in absolute position loss. The absolute positional relationship between the axis and the machine coordinate system must be re established after the installation of the new motor.
Replace cable: Be sure to use cables that comply with the original factory connection diagram or machine manufacturer's specifications. Non original cables need to be carefully checked.
Collaboration with service system
The document concludes by providing INDRAMAT's customer service locations and contact information worldwide (Germany, Europe, and overseas). When encountering complex faults that cannot be solved, requiring spare parts support or deep repairs, professional personnel should be contacted in a timely manner. When returning the faulty component, attach a completed defect report (template provided in the document), detailing the fault phenomenon, environmental conditions, and steps taken, which will greatly help the service department to quickly diagnose and solve the problem.
- ABB
- General Electric
- EMERSON
- Honeywell
- HIMA
- ALSTOM
- Rolls-Royce
- MOTOROLA
- Rockwell
- Siemens
- Woodward
- YOKOGAWA
- FOXBORO
- KOLLMORGEN
- MOOG
- KB
- YAMAHA
- BENDER
- TEKTRONIX
- Westinghouse
- AMAT
- AB
- XYCOM
- Yaskawa
- B&R
- Schneider
- Kongsberg
- NI
- WATLOW
- ProSoft
- SEW
- ADVANCED
- Reliance
- TRICONEX
- METSO
- MAN
- Advantest
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bently
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- Beijer
- Moxa
- Rexroth
- Johnson
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- Application field
- XP POWER
- CTI
- TRICON
- STOBER
- Thinklogical
- Horner Automation
- Meggitt
- Fanuc
- Baldor
- SHINKAWA




































































































































