REXRTOH MDD Digital AC Servo Motor Application Guide
REXRTOH MDD Digital AC Servo Motor Application Guide
Overview and Product Positioning
The MDD series digital AC servo motor is a high-performance permanent magnet synchronous motor launched by INDRA MAT GmbH (later merged into Indramat) in Germany. It adopts electronic commutation technology and has high dynamic response, high power density, and high-precision control characteristics. This series of motors is designed specifically for industrial automation systems, especially suitable for applications that require high-speed and high-precision contour control, such as tool machines, textile machinery, printing equipment, packaging machinery, robots, and handling systems. The MDD motor, when used in conjunction with the Indramat intelligent digital drive controller, creates a responsive and cost-effective automation solution.
The MDD series includes nine different models, covering a full range of requirements from low inertia and low torque to high torque and high dynamics. among which
MDD 021、 025, 041: Compact structure, high power density, suitable for tightening devices, auxiliary shafts, and tool changing mechanisms;
MDD 065、 071, 093, 115: Excellent dynamic performance, suitable for high dynamic scenarios such as stamping, punching, and step-by-step feeding;
MDD 090、 112: Extremely high synchronization performance, suitable for precision machining operations such as grinding machines that require high synchronization.
Motor structure and core technology
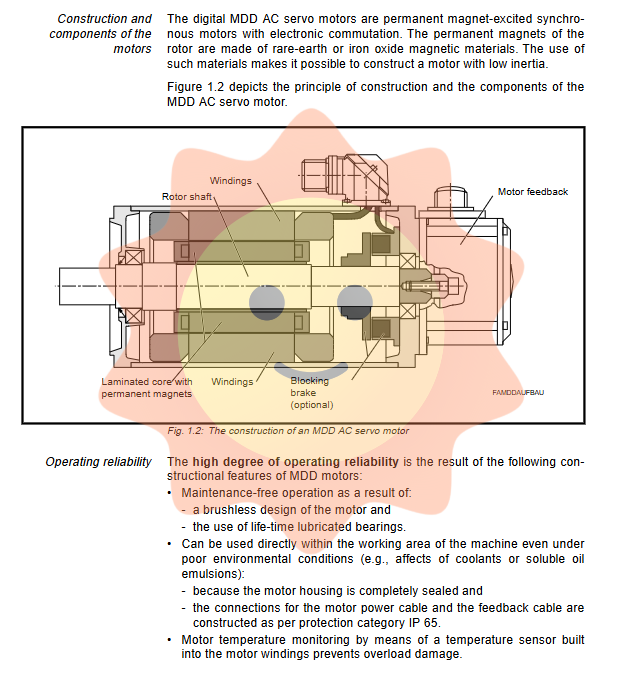
2.1 Structural Features
The MDD motor adopts a brushless design, and the rotor is made of rare earth or ferrite permanent magnet materials to achieve low rotational inertia. The motor casing is fully enclosed, and both the power supply and feedback interfaces meet the IP65 protection level, allowing it to operate directly in harsh environments such as coolant or emulsion environments. The motor is equipped with a built-in temperature sensor (PTC) to monitor the winding temperature in real-time and prevent overheating and damage.
2.2 Performance advantages
High dynamism: excellent torque inertia ratio, rapid response;
High overload capacity: high-efficiency thermal conductivity design from stator winding to shell;
Wide speed range peak torque: peak torque can be output over a wide range of speeds;
High power to weight ratio: compact structure, high power density;
High cyclic load capacity: supports high-frequency start stop operations;
High synchronization performance: using sine current drive and high-resolution motor feedback system.
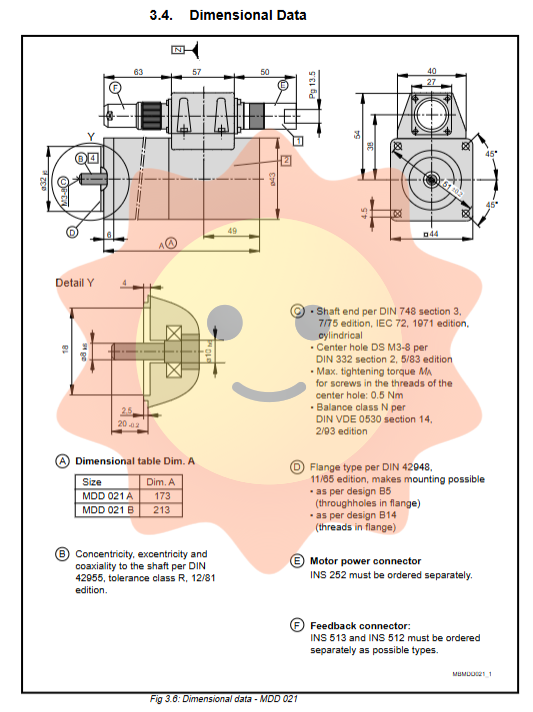
2.3 Installation and Connection
The motor supports multiple installation directions, and the flange complies with IM B5 (through-hole) or IM B14 (threaded hole) standards. The output shaft can be selected as the optical axis (recommended) or a keyway shaft. The power supply and feedback cables are directly connected through connectors, and support customization of lateral A/B or left/right output directions.
Analysis of key technical parameters
3.1 Environmental conditions
Environmental temperature: 0 ° C to+45 ° C
Installation altitude: 0-1000 meters
Protection level: IP65 (motor body), the output shaft may be IP50 or IP65 depending on the model
Mechanical environment: compliant with IEC 721-3-3 standard, suitable for 3M1 (longitudinal) and 3M6 (transverse) vibration levels
3.2 Motor Feedback System
MDD motors come standard with a high-precision feedback system, which is divided into:
Resolver Feedback (RSF): Inductive system, resolution 16384 increments/rev, system accuracy ± 7 arcminutes;
Digital Servo Feedback (DSF): Optical system, resolution 2097152 increments/rev, system accuracy ± 0.5 arcminutes.
Both types of feedback support relative position detection and absolute position detection (integrated multi turn absolute value encoder). The absolute position information can still be maintained after power failure without the need to reset to zero.
3.3 Torque speed characteristics
The torque speed curve is the core basis for selection, and the figure includes:
Maximum torque limit (horizontal line)
Speed limit (affected by DC bus voltage)
S1 continuous working curve (natural cooling or surface cooling)
S6 intermittent working curve (duty cycle 25%)
The curve varies depending on the type of power source (regulated/non regulated) and voltage fluctuation (± 10%), and the selection should be based on actual operating conditions.
3.4 Axle Load Capacity
The motor shaft can withstand radial and axial loads, and the radial force chart displays the relationship between the allowable value and the distance from the point of application, as well as the average speed. The formula for calculating axial force is:
F-axis=k ⋅ F-radial
The value of k varies depending on the model (e.g. MDD 021 is 0.60, MDD 041 is 0.53). The rated life of the bearing is 30000 hours, and the life decreases in cubic terms when overloaded.
Overview of detailed technical data for each model
MDD 021
Continuous torque: 0.15-0.30 Nm
Maximum torque: 0.64-1.3 Nm
Rated speed: 10000 rpm
Moment of inertia: 0.22-0.31 × 10 ⁻⁴ kg · m ²
Protection: IP65 (main body), IP50 (shaft)
MDD 025
Continuous torque: 0.33-0.90 Nm (slightly reduced with braking)
Maximum torque: 1.44-3.94 Nm
Optional braking torque: 1.0 Nm
Support shaft seal options
MDD 041
Continuous torque: 0.64-2.05 Nm
Maximum torque: 3.0-9.01 Nm
Thermal time constant: 25 minutes
MDD 065-115 series
As the model size increases, torque, inertia, and power significantly improve. For example:
MDD 115 can achieve a continuous torque of 28-57 Nm and a maximum torque of 87-177 Nm, suitable for high load scenarios such as spindles.
Most models support surface cooling (axial or radial fans) to cope with extreme loads or high-frequency start stop conditions.
Electrical connections and cable selection
5.1 Power Connection
Integration of motor power interface:
Three phase power cord
Temperature Sensor Cable (PTC)
Brake control line (if optional)
The connector supports crimping or welding, and the cable cross-sectional area is selected based on the motor current (starting from 0.75 mm ²). It is recommended to use Indramat matching cables (such as INK 253, INK 650, etc.) to ensure shielding and protection performance.
5.2 Feedback Connection
Adopting a 12 pin flange socket, supporting straight or curved connectors. The feedback cable (INK 209) has oil resistance, hydrolysis resistance, and halogen-free properties, with a maximum length of 75 meters.
5.3 Brakes
Most models can be equipped with a closed-loop brake system, which magnetically locks the shaft when power is off and releases it when powered on (24V DC). The brake is intelligently controlled by the driver and supports parameterized setting of clamping timing (immediate, below 10 rpm, delayed by 400 ms).
Installation, Storage, and Maintenance Guide
6.1 Installation precautions
Avoid prolonged accumulation of liquid at the output shaft end;
Shaft seals are only suitable for water spray prevention situations;
The motor can be installed in any direction, but attention should be paid to the influence of thermal deformation on the position of the A-side shaft end (up to a maximum of 0.6 mm);
The power and feedback connectors must be securely fastened, and the motor must be grounded.
6.2 Storage and Transportation
Storage temperature: -25 ° C to+85 ° C
Avoid vibration, moisture, and dust;
Both the output shaft and the joint have protective covers, do not remove them before installation;
Large motors (such as MDD 112/115) can be transported using lifting screws (M8).
6.3 Maintenance and Service
The motor is basically maintenance free (brushless design, lifetime lubricated bearings). If the brake is stored for more than two years, it needs to be operated by "re sitting" (repeatedly turning on and off the brake after low-speed operation). When there is a malfunction, you can contact technical support through the Indramat service hotline and provide the motor model, drive information, and fault code.
Selection suggestions and application summary
The MDD series servo motors have become the preferred choice for key components in industrial automation due to their high dynamics, high precision, and high reliability. When selecting, key considerations should be given to:
Torque and speed requirements: combined with S1/S2 curve and load cycle;
Environmental adaptability: protection level, cooling method;
Feedback accuracy: Choose either Resolver or DSF according to motion control requirements;
Installation space: flange type, outlet direction;
System compatibility: Compatibility with Indramat drive controllers.
This series of motors is not only suitable for traditional machine tools and robots, but also plays an important role in emerging fields such as semiconductors, laser processing, and precision inspection, providing core power support for the intelligence and efficiency of high-end equipment.
- ABB
- General Electric
- EMERSON
- Honeywell
- HIMA
- ALSTOM
- Rolls-Royce
- MOTOROLA
- Rockwell
- Siemens
- Woodward
- YOKOGAWA
- FOXBORO
- KOLLMORGEN
- MOOG
- KB
- YAMAHA
- BENDER
- TEKTRONIX
- Westinghouse
- AMAT
- AB
- XYCOM
- Yaskawa
- B&R
- Schneider
- Kongsberg
- NI
- WATLOW
- ProSoft
- SEW
- ADVANCED
- Reliance
- TRICONEX
- METSO
- MAN
- Advantest
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bently
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- Beijer
- Moxa
- Rexroth
- Johnson
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- Application field
- XP POWER
- CTI
- TRICON
- STOBER
- Thinklogical
- Horner Automation
- Meggitt
- Fanuc
- Baldor
- SHINKAWA




































































































































