REXRTOH MSK series synchronous servo motor
REXRTOH MSK series synchronous servo motor
Introduction: Overview and Technical Characteristics of MSK Series Servo Motors
Bosch Rexroth's MSK series synchronous servo motors, as the core execution components of high-performance industrial motion control systems, are widely used in various automation machinery and precision equipment due to their excellent reliability, accuracy, and power density. This article is based on the official document (DOK-MOTOR-MSK-ITO3-ZH-P, version 03/2021), aiming to provide a complete and standardized operation and maintenance framework for equipment manufacturers, system integrators, and on-site maintenance personnel.
MSK motor is a permanent magnet excitation three-phase synchronous motor, specially designed to be optimized for use with Rexroth frequency converters (such as the IndraDrive series). Its core features include:
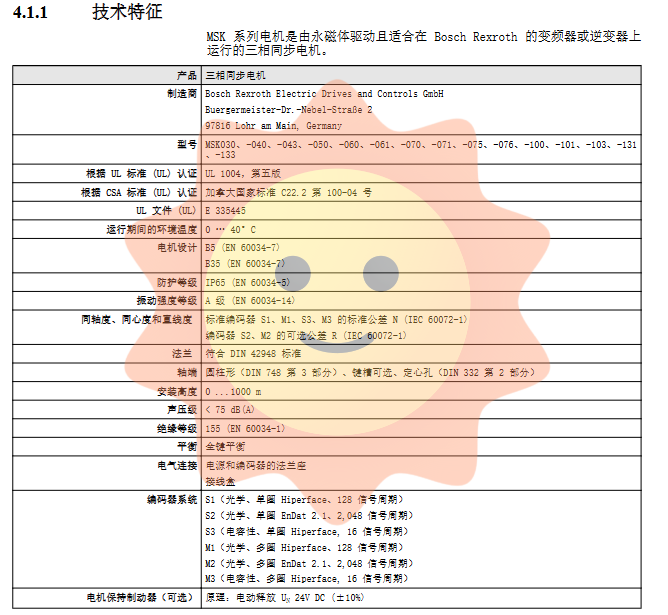
Model range: covering various machine base specifications such as MSK030, 040, 043, 050, 060, 061, 070, 071, 075, 076, 100, 101, 103, 131, 133, etc.
Certification and Standards: Complies with UL 1004 (5th edition), CSA C22.2 No. 100-04 standards, and meets the requirements of the Low Voltage Directive 2014/35/EU, EN 60034-1 (rated value), EN 60034-5 (protection level), etc.
Key design: The standard protection level is IP65 (after correctly installing the connector), and optional IP67 (requires sealing with air). The motor design complies with the B5 (flange installation) or B35 (flange with foot) type of EN 60034-7. The insulation level is 155 and the vibration intensity is A.
Encoder options: S1 (Hiperface single turn), S2 (EnDat 2.1 single turn), S3 (capacitive Hiperface single turn), and corresponding M1, M2, M3 multi turn absolute value models are available.
Optional accessories: including motor holding brake (24VDC ± 10% release), fan cooling unit (F), liquid cooling unit (N), and junction box connection method.
Core safety standards: homework prerequisites and life support
Before operating any driver component, it is necessary to thoroughly understand and strictly comply with safety regulations. The safety warning of MSK motor runs through its entire lifecycle, and the main risks are concentrated in the following aspects:
Electrical hazards:
High voltage electric shock: The driver components must operate under the premise of permanent and reliable grounding. Before carrying out any homework, the power must be cut off and the capacitor must be fully discharged (at least 1 minute).
Job Qualification: Only qualified personnel who are familiar with the electrical drive system and have received training are allowed to perform installation, wiring, and maintenance tasks. Before starting the homework, it is necessary to follow the "lockout tagout" procedure: turn off the main switch, prevent accidental connection, verify no voltage, ground and short-circuit, and isolate adjacent live parts.
Mechanical and motion hazards:
Dangerous movement area: It is strictly prohibited for personnel to stay within the working range of the moving parts of the machine. Physical barriers or electronic protection must be installed to prevent accidental entry.
Unexpected shaft movement: Before coming into contact with the hazardous area, the control system must ensure that the drive shaft comes to a complete and safe stop. For the vertical axis, relying solely on the motor brake is not sufficient to ensure personnel safety, and additional mechanical locking, external braking, or counterweight devices need to be used.
Rotating components: Transmission keys and couplings must be fixed to prevent flying out during high-speed rotation. Before starting, protective covers should be installed on all dangerous rotating parts.
Magnetic and electromagnetic field hazards:
Health hazards: The strong magnetic/electromagnetic fields generated by motor operation pose serious health risks to individuals wearing pacemakers, metal implants, or hearing aids. Such personnel are prohibited from approaching or touching the motor in operation or installation.
Item damage: Strong magnetic fields can damage watches, credit cards, magnetic stripe cards, and all ferromagnetic metal items. When operating, stay away from the motor.
Hot surfaces and burn hazards:
The surface temperature of the motor during operation may exceed 60 ° C or even 70 ° C. Before touching, ensure that the motor has cooled for at least 15 minutes. At the same time, it is necessary to ensure that insulation sensitive components (such as cables) are kept at a safe distance from the surface of the motor.
Physical hazards during transportation and installation:
Suitable lifting and transportation equipment must be used, and the correct tools and personal protective equipment (such as safety gloves) must be used.
Installation and mechanical integration: the cornerstone of accuracy and reliability
Correct mechanical installation is the foundation for ensuring motor performance, lifespan, and operational accuracy.
Flange installation (B5/B35):
Use all mounting holes to ensure that the motor is securely fixed to the machine base.
Ensure that the mating surface is flat, clean, and aligned with the center. Avoid damaging the centering protrusion on the motor side or the mating surface on the equipment side.
Strictly follow the standard (such as DIN EN ISO 4762) to select 8.8 grade screws and tighten them to the specified tightening torque (e.g. M8 screws with approximately 24.6 Nm). Excessive locking can damage the threads.
Foundation installation (B35):
Pay attention to the distance from the centerline of the motor shaft to the bottom edge of the foot, which should match the dimensions on the machine side.
During installation, it is necessary to accurately align the centerline of the motor shaft with the load shaft.
Important limitation: When installing the foundation, it can only withstand radial forces perpendicular to the installation plane (± 15 °). It is not allowed to transmit radial forces generated by gear meshing through the foundation, otherwise it may cause damage to the motor. If such force exists, flange installation must be used instead.
Installation of transmission components:
When installing transmission components such as couplings and pulleys, appropriate pulling tools must be used, and direct tapping of the motor shaft end is strictly prohibited.
Accurate installation requires the use of standard centering holes (DIN 332-2) at the shaft end. If necessary, the transmission element (heat sleeve) can be heated.
The transmission components themselves must undergo dynamic balancing, and the balance level must match the "full key balance" state of the motor. The tension of the belt shall not exceed the allowable radial force limit.
Integration of electrical connections and cooling systems
Power supply and encoder connection:
It is strongly recommended to use Rexroth original finished cables to ensure EMC performance, mechanical reliability, and protection level.
Before connecting, ensure that the plug and socket are clean, dry, and undamaged. For threaded connectors (such as RLS series), they must be fully tightened.
Equipment connectors are typically designed to be rotatable (such as RGS1000 with a maximum torque of 12 Nm, RLS1000/1200 with a maximum torque of 18 Nm) to accommodate wiring directions, but the number of rotations should not exceed 10 times and the maximum torque should not be exceeded.
The protective earth (PE) connection must be permanently reliable, which is the basic guarantee to prevent electric shock.
Junction box connection (applicable to high-power motors):
For models MSK101, 131, 133, etc., junction boxes (such as RZK3100, RLK1300) may be used.
When connecting, it is necessary to use an adapter plate and a suitable cable sealing sleeve. The core wire connection requires the use of wire end sleeves (WEF) and tightening with the specified torque (such as M6 screws with approximately 2.5 Nm).
Before installing the box cover, it is necessary to check the sealing strip and apply thread locking agent (such as Loctite 243) to the fixing screws, with a tightening torque of approximately 6.5 Nm.
For dual cable connections (to meet current carrying capacity or bending radius requirements), matching fuses (F1) should be installed near the power output in the controller cabinet.
Liquid cooling connection (for MSK -... - N models):
The cooling interface of the motor is usually a pipe thread (such as G1/8, G1/4). Remove the factory protective cover before connecting.
Strictly follow the prescribed screwing depth and tightening torque (such as G1/8 screwing 14-15mm, torque 14-15 Nm), excessive screwing or tightening will permanently damage the motor threads.
It is recommended to use a joint with an O-ring axial seal and avoid using raw tape or hemp thread to prevent debris from entering the cooling circuit or generating excessive stress.
The maximum inlet pressure is usually 6 bar, and the coolant needs to meet the requirements in the project planning manual (non corrosive, low conductivity, etc.). The machine manufacturer is responsible for the sealing inspection and regular maintenance after connection.
Fan unit connection (for MSK -... - F models):
Connect the fan (single-phase or three-phase) according to the nameplate voltage.
For axial fans, the encoder plug may be covered by the fan cover and the cover plate needs to be removed for connection.
Debugging, operation, and monitoring
Pre debugging inspection:
Take corresponding measures according to the storage time (see Table 5-1). If stored for more than 12 months, check the brake surface and electrical contacts, and may require no-load operation to "test" the bearings; After more than 60 months, it is recommended to replace the bearings and encoder.
Ensure that all electrical connections are correct and secure.
Check and ensure that the brake voltage is maintained at 24V ± 10% and functioning properly.
Confirm that the protective cover for the rotating components is installed and the keys are secured.
Operation monitoring:
Operate under the environmental conditions specified in the project planning manual (ambient temperature 0-40 ° C).
Monitor abnormal noise during operation and observe whether the vibration increases.
Regularly check the cleanliness of the motor and fan unit, and whether the heat sink has accumulated dust.
Check for signs of leakage at the coolant interface.
Pay close attention to the diagnostic information of the driver controller and promptly identify potential issues.
Maintenance, repair, and troubleshooting
Regular maintenance:
Cleaning: Regularly use a vacuum cleaner or dry compressed air to clean the surface and heat sink of the motor. Do not use corrosive cleaning agents or high-pressure water guns.
Inspection: Regularly check the cables (especially in the application of drag chains), ensure that the protective wire connections are secure, and check for signs of wear on the shaft seals (recommended to check every 5000 working hours).
Bearing replacement: It is recommended to consider replacing the bearings after approximately 30000 working hours, as the actual lifespan depends on the load, speed, and operating mode.
Troubleshooting (Frequently Asked Questions):
Motor not turning: Check whether the controller enable signal, power supply voltage, and brake are released.
Excessive vibration: Check if the coupling is aligned accurately, if the transmission components are balanced properly, and if the installation screws are loose.
Abnormal operating noise: Stop immediately, there may be foreign objects or damaged bearings inside, and contact professional service is required.
Motor overheating: Check for overload operation and obstruction of heat dissipation (for air-cooled motors, check the fan; for water-cooled motors, check the flow and temperature of the cooling circuit).
Temperature sensor alarm: Check if the sensor connection is reliable or if the sensor itself is faulty.
Storage, disposal and environmental protection
Storage: The motor should be stored in its original packaging in a dry, dust-free, and vibration free environment. The storage temperature range is -20 ° C to+60 ° C. For water-cooled motors, the coolant must be thoroughly drained before storage to prevent freezing and cracking.
Disposal and Recycling: Motors mainly consist of materials such as steel, aluminum, copper, and permanent magnets (rare earth metals), which can be recycled and reused. Special attention should be paid to the strong magnetism and potential health hazards of permanent magnets during handling. The product can be returned to Bosch Rexroth for professional disposal (the cost will be borne by the sender). Batteries need to be classified and recycled according to local regulations.
- ABB
- General Electric
- EMERSON
- Honeywell
- HIMA
- ALSTOM
- Rolls-Royce
- MOTOROLA
- Rockwell
- Siemens
- Woodward
- YOKOGAWA
- FOXBORO
- KOLLMORGEN
- MOOG
- KB
- YAMAHA
- BENDER
- TEKTRONIX
- Westinghouse
- AMAT
- AB
- XYCOM
- Yaskawa
- B&R
- Schneider
- Kongsberg
- NI
- WATLOW
- ProSoft
- SEW
- ADVANCED
- Reliance
- TRICONEX
- METSO
- MAN
- Advantest
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bently
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- Beijer
- Moxa
- Rexroth
- Johnson
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- Application field
- XP POWER
- CTI
- TRICON
- STOBER
- Thinklogical
- Horner Automation
- Meggitt
- Fanuc
- Baldor
- SHINKAWA




































































































































