Siemens SINAMICS S120 AC frequency converter
Single machine drive scenarios, such as centrifuges, presses, extruders, elevators, conveyors, and transportation systems, have high requirements for accuracy, stability, and smooth operation.
Specific driving demand scenarios include drives without feedback to the grid (wire drawing, extrusion), drive groups with high availability requirements (incoming line failures do not cause all shafts to fail), as well as central drives (presses, printing, packaging) and modular machine single axis drives.
CU310-2 DP: PROFIBUS interface, interface type similar to CU310-2 PN, PROFIBUS address set through two rotary encoding switches (0-127dec), supports synchronous operation, can connect to remote diagnostic teleservice adapter, and other functions (such as LED status, reset, analog input switching) are similar to CU310-2 PN.
Control Unit Adapter (CUA Series):
CUA31: Used to connect the power module as an additional axis to the existing DC/AC group, requiring a higher-level closed-loop control module with DRIVE CLiQ interface, EP terminal/temperature sensor interface, etc., and LED display status.
CUA32: Similar in function to CUA31, with additional support for evaluating HTL/TTL/SSI encoders, and corresponding addition of encoder interfaces for interface configuration. Other features (such as power supply and connection method) are similar to CUA31.
3. DC link components
Braking resistor (Blocksize): Used for energy conversion during regenerative operation of PM240-2 and PM340 power modules (such as braking rotating mass), with a constant temperature switch to monitor overheating. The resistance value, rated power, and size of the braking resistor vary depending on the frame size (such as FSA-FSF), and attention should be paid to installation clearance (such as 100mm on each side of PM340 braking resistor) and protection (to avoid contact burns and fire prevention).
Braking module and resistor (Chassis): The braking module is installed in the power module slot, with forced air cooling, including power electronics and control, requiring an external braking resistor. The interface includes DC link connection, braking resistor connection, digital input/output, etc. The braking resistor (25kW/50kW) is installed outside the cabinet, with temperature protection switch, and needs to be installed vertically and independently, maintaining a 200mm cooling gap to avoid water intrusion (IP20 protection, outdoor canopy required).
4. Power components on the motor side
Motor reactors: available in Blocksize and Chassis formats to reduce voltage stress on motor windings, lower capacitor charging and discharging currents, and adapt to different power modules. For example, Blocksize format is compatible with PM240-2 and PM340, while Chassis format is compatible with Chassis power modules. Technical parameters include inductance, rated current, power loss, etc. Attention should be paid to installation (near the power module, maximum 5m connecting cable), ventilation gap (around 100mm), and frequency limitation (maximum 150Hz output frequency, 4kHz pulse frequency).
Sinusoidal filter (Chassis): enables the power module to output a voltage close to sine, can use unshielded cables, does not require derating of motor power, adapts to Chassis power module, pulse frequency needs to be set to 4kHz (causing derating of power module output current), output voltage needs to be reduced by 15%, avoid no motor operation (damaging the filter), install and maintain a ventilation gap of 100mm, pay attention to the connection direction (input to power module, output to motor).
Dv/dt filter: includes dv/dt reactor and voltage peak limiter, which limits the voltage rise rate (such as<500V/μ s) and voltage peak value. It is used in scenarios where the voltage resistance of the motor insulation system is unknown or insufficient. It is divided into ordinary and compact types, and attention should be paid to grounding protection (to avoid high discharge current risks), installation clearance, frequency limitation (maximum 150Hz output, 4kHz pulse frequency), and cannot operate without a motor.
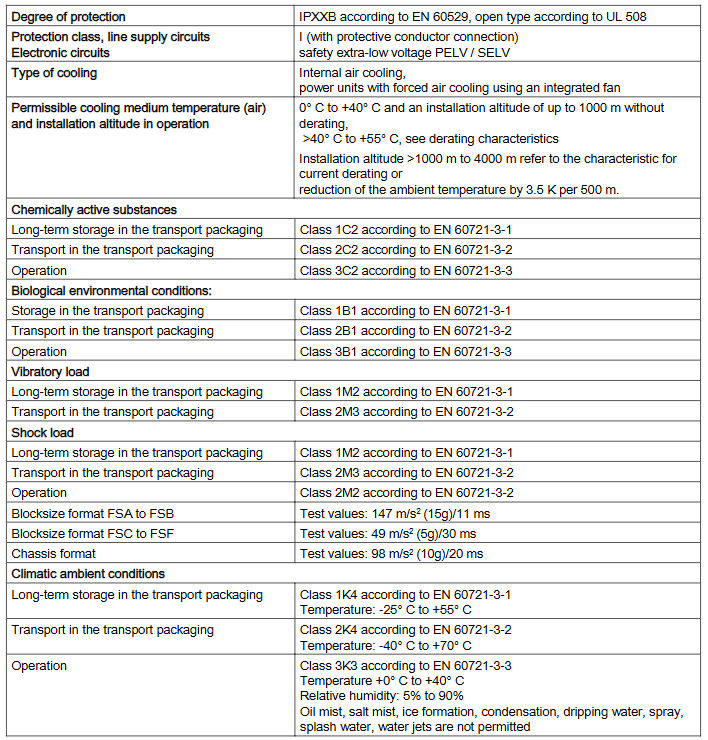
Installation and debugging related
1. Grid connection and line components
Connection component selection: Line circuit breakers, overcurrent protection (line fuses, circuit breakers), line contactors (electrical isolation), line filters (EMC compliance), line reactors (limiting low-frequency line harmonics) are required to adapt to different voltages (such as 1-phase 200-240V, 3-phase 380-480V) and power grid systems (TN, TT, IT systems, IT systems require motor reactors).
Installation and safety: Attention should be paid to the installation direction of line filters and reactors (correct connection of input and output terminals), ventilation gap (such as 100mm above and below the line filter), grounding (protective grounding in accordance with specifications), and overvoltage protection. It is recommended to install surge arresters (such as VZCA/VZCA2) at the incoming terminal. Residual current equipment (RCD/RCM) should be selected according to system requirements (such as TT system, RCM required for high-power incoming lines).
2. Cabinet design and EMC
Cabinet manufacturing safety: Follow safety instructions to ensure cabinet protection (such as IP54 to avoid conductive contamination), reasonable component layout (considering heat dissipation and electromagnetic interference), 24V DC power supply needs overcurrent and overvoltage protection, and select appropriate power units (based on component current consumption).
EMC compliance: Cable shielding and wiring must comply with specifications (such as DRIVE CLiQ signal cable selection and shielding connection), component grounding (protective grounding, equipotential connection), and follow the EMC installation guidelines (Configuration Manual 6FC5297-0AD30-0xPx). Different EMC categories (C1/C2/C3/C4) correspond to different application environments (such as C1 for public systems and C3 for industrial systems), and corresponding measures (such as line filters and reactors) must be taken to meet the limits.
- ABB
- General Electric
- EMERSON
- Honeywell
- HIMA
- ALSTOM
- Rolls-Royce
- MOTOROLA
- Rockwell
- Siemens
- Woodward
- YOKOGAWA
- FOXBORO
- KOLLMORGEN
- MOOG
- KB
- YAMAHA
- BENDER
- TEKTRONIX
- Westinghouse
- AMAT
- AB
- XYCOM
- Yaskawa
- B&R
- Schneider
- Kongsberg
- NI
- WATLOW
- ProSoft
- SEW
- ADVANCED
- Reliance
- TRICONEX
- METSO
- MAN
- Advantest
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bently
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- Beijer
- Moxa
- Rexroth
- Johnson
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- Application field
- XP POWER
- CTI
- TRICON
- STOBER
- Thinklogical
- Horner Automation
- Meggitt
- Fanuc
- Baldor
- SHINKAWA
- Other Brands





































































































































