COTEK SD Series Pure Sine Wave Inverter
Comprehensive Technical Analysis and Application Guide for SD Series Pure Sine Wave Inverter
Product Overview and Core Features
The SD series pure sine wave inverter is a new generation of power conversion equipment launched by COTEK Electronic IND. CO. It covers three power levels: SD1500, SD2500, and SD3500, supports 12V, 24V, and 48V DC inputs, and provides two AC output specifications: 100-120VAC and 200-240VAC. This series of inverters adopts advanced pure sine wave output technology to ensure stable and clean power supply for various sensitive electronic devices, especially suitable for scenarios such as RVs, ships, solar off grid systems, and industrial backup power sources.
The core design concept of the SD series is "flexibility and reliability". It has N+1 parallel redundancy function, and users can achieve power expansion or system redundancy by paralleling up to 5 devices, significantly improving the reliability and capacity of the power supply system. In addition, the inverter is equipped with an automatic transfer switch (ATS), which supports seamless switching between mains power and inverter output, and can be optionally equipped with a static transfer switch (STS) module to shorten the switching time to less than 4 milliseconds, meeting the extremely high requirements for power continuity in application environments.
In terms of protection mechanisms, the SD series provides comprehensive input and output protection functions, including reverse connection protection (implemented through fuses), undervoltage protection, overvoltage protection, short circuit protection, overload protection, over temperature protection, etc. These protective functions not only extend the lifespan of the equipment itself, but also greatly enhance the safety of the entire electrical system.
In depth analysis of electrical performance
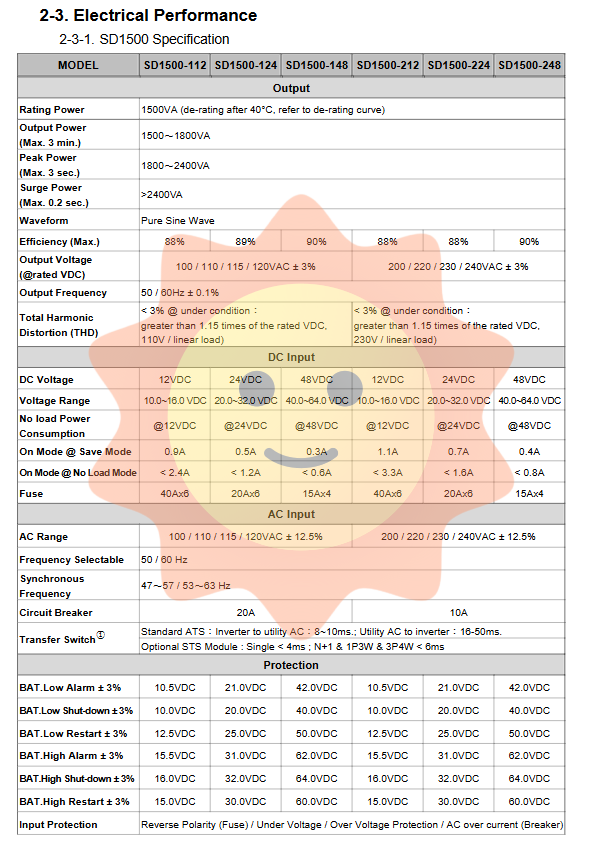
The electrical performance of each model in the SD series has been carefully designed to adapt to different load requirements and environmental conditions. Taking the SD2500 model as an example, describe its key parameters in detail:
Output capability: The rated power is 2500VA, and the derating curve should be referred to when the ambient temperature is above 40 ° C. The device has short-term overload capability, with peak power (lasting for 3 seconds) reaching 3000-4000VA and surge power (lasting for 0.2 seconds) exceeding 4000VA, making it easy to start inductive loads such as motors.
Waveform quality: The output is a pure sine wave, with a total harmonic distortion (THD) of less than 3% under rated conditions, ensuring compatibility with precision electrical appliances such as laptops and medical equipment, and avoiding damage or interference.
Conversion efficiency: The maximum conversion efficiency can reach up to 90%, especially in energy-saving mode, with extremely low no-load power consumption (such as only 0.3A in 48V model energy-saving mode), effectively reducing energy waste and extending battery life.
Input/output range: Wide DC input voltage range (e.g. 20.0-32.0VDC for 24V models), suitable for battery voltage fluctuations. The communication input has a wide voltage adaptation range of ± 12.5% and supports 50/60Hz frequency selection and synchronization.
All models can operate in ambient temperatures ranging from -20 ° C to+60 ° C, with a wider storage temperature range of -40 ° C to+70 ° C, demonstrating strong environmental adaptability. The equipment has passed safety certifications such as UL 458 (hardware part) and EN 62368-1, as well as electromagnetic compatibility certifications such as FCC Class B and EN 55032, ensuring reliable quality.
Safety instructions and installation specifications
Safety is the primary prerequisite for the use of electrical equipment. The SD series manual emphasizes important safety information at the beginning.
1. General safety precautions:
Environmental requirements: The inverter must be installed in a dry, cool, well ventilated, and dust-free environment. The ambient temperature should be between -20 ° C and 50 ° C, and a gap of at least 30 centimeters should be maintained around to ensure smooth heat dissipation. It is strictly prohibited to install in places with combustible gases (such as engine compartments, fuel storage areas) or metal dust or sawdust flying.
Battery safety: Wear protective equipment when operating the battery to avoid metal objects short circuiting the battery terminals and generating arcs. The inverter should be installed close to the battery to reduce line loss, but it must not be placed in the same enclosed space as the battery to prevent corrosive gases generated by the battery from damaging the equipment.
Electrical safety: Before performing any wiring operation, it is necessary to confirm that the inverter has been disconnected from all power sources (batteries and AC power). It is strictly prohibited to connect the output terminal to an external AC power source.
2. Key points for DC wiring installation:
Cable selection: High quality copper cables must be used and the length should be minimized as much as possible (ideally less than 1.8 meters). The cable cross-section should be strictly selected according to the model and current. For example, the SD3500-112 model recommends using a 4/0 AWG (approximately 120mm ²) cable and is equipped with a 500A DC fuse. The fuse must be installed on the positive (+) cable.
Connection specification: When connecting the battery, the red terminal is the positive pole (+) and the black terminal is the negative pole (-). All connections must be firm, with a recommended torque of 3-3.5 N · m. There may be small sparks during the connection, which is a normal phenomenon of internal capacitor charging.
Grounding requirement: The inverter housing must be reliably connected to the vehicle chassis or grounding system using at least 8 AWG (approximately 10mm ²) wires, otherwise there may be a risk of electric shock.
3. Key points for communication wiring installation:
The inverter provides two connection methods: hard wired terminals and output sockets, which are connected in parallel internally. When the load current approaches or exceeds the rated current of the socket, it is strongly recommended to use hard wired terminals.
The communication input/output wiring should comply with local electrical regulations, and it is recommended to be operated by professional electricians. When wiring, it is necessary to distinguish between live wire (L), neutral wire (N), and ground wire (GND). For the SD1500 model, special attention should be paid to the setting of its neutral grounding option, as incorrect settings may lead to safety risks.
Advanced Features: Parallel Mode and Multiphase System Construction
The most striking feature of the SD series is its powerful parallel capability, which can not only be used for power expansion, but also for building complex multiphase power supply systems.
1. Parallel configuration steps:
Pre setting: Set all main switches of the inverters to be connected in parallel to "OFF". Set the terminal resistance through the parallel jumper on the green terminal: the first and last devices in the parallel system need to set the jumper to "ON" and the intermediate device to "OFF".
Parameter synchronization: Set the DIP switches (S1-S3) of all devices to the same output voltage and frequency.
Physical connection:
Use RJ-45 Ethernet cable (parallel connection cable) to sequentially connect the CAN1 port and CAN1 port (or CAN2 and CAN2) of each device in series.
Connect the DC input terminals (positive and negative) of each device in parallel to the battery.
Connect the AC output terminals (live wire and live wire, neutral wire and neutral wire) of each device in parallel.
System architecture: The system adopts a master-slave architecture and supports automatic election of master devices. Users only need to set the parameters of the master device, and the slave devices will automatically synchronize. By using different combinations of DIP switches S4-S6, the roles of devices in parallel systems can be configured (such as master device, 0 ° slave device, 120 ° slave device, etc.).
2. Multiphase system applications:
Single phase three wire system (1 Φ 3W): By setting two inverters to 0 ° main equipment and 180 ° slave equipment in parallel, a set of single-phase three wire outputs with doubled voltage (such as L1-L2 voltage being twice the L-N voltage) can be obtained, which is suitable for situations where higher line voltage is required.
Three phase four wire system (3 Φ 4W): By setting three inverters in parallel at 0 ° (L1), -120 ° (L2), and+120 ° (L3), a complete three-phase four wire power supply system can be constructed. For example, when each inverter output is set to 100V/50Hz, a three-phase balanced power supply with a phase voltage of 100V and a line voltage of approximately 173V can be obtained, which can directly drive three-phase industrial equipment.
This flexibility enables the SD series to go beyond the scope of ordinary vehicle inverters and become an ideal solution for small commercial, off grid energy stations, and special equipment power supply.
Operation, Control, and Communication
1. Front panel and status indicator:
The front panel of the inverter is equipped with a power switch (ON/OFF/REMOTE), LED status indicator lights, and an 8-bit DIP switch.
LED indicator light: Through different flashing modes of green, orange, and red LEDs, the device status is intuitively displayed, such as normal operation, energy-saving mode, bypass mode, undervoltage/overvoltage warning, overheating, overload, and various faults.
DIP switch: used for basic settings, including output voltage (100/110/115/120VAC or corresponding 220V range), output frequency (50/60Hz), energy-saving mode threshold (4% -8% rated power), and phase role in parallel systems.
2. Remote control and communication interface:
LCM port: used to connect LCD remote monitoring panels (such as CR-6, CR-8, CR-10) to achieve remote power on/off, parameter setting, and status monitoring.
RS-232 port: Provides serial communication capability with the computer. By sending specific ASCII code commands (ending in CR/LF), users can remotely query device status (such as input/output voltage and current, output power, frequency), control output switches, and enter the settings menu to adjust up to 19 advanced parameters, including various protection voltage thresholds, synchronous frequency windows, energy-saving mode parameters, LCD display settings, buzzer alarm options, and interface language.
Ethernet (optional) and CAN bus: supports more advanced networked monitoring and management, and the CAN bus is designed specifically for high-speed communication within parallel systems.
Fault diagnosis and maintenance
When there is an abnormality in the inverter, a preliminary judgment can be made by observing the LED indicator lights:
Red LED flashing rapidly: Input overvoltage (OVP). Check the voltage of the battery or charging system.
Red LED flashing slowly: Input undervoltage (UVP). Check the battery level, whether the cable connection is secure, and whether the cable specifications meet the standards.
Red LED intermittent flashing: Over temperature protection (OTP). Check the ventilation of the installation environment, clean the fan and ventilation openings of debris.
Red LED always on: Output overload (OLP) or short circuit. Check the load device, disconnect all loads and try restarting.
Orange LED flashing: Voltage abnormality warning (not turned off), prompting the user to handle it in a timely manner.
Daily maintenance requires ensuring that the equipment is clean and well ventilated, and regularly checking for loose cable connections. COTEK provides a 24 month limited warranty for this series of products, but the warranty does not cover damage caused by misuse, abuse, improper installation, natural disasters, or unauthorized alteration of serial numbers.

- ABB
- General Electric
- EMERSON
- Honeywell
- HIMA
- ALSTOM
- Rolls-Royce
- MOTOROLA
- Rockwell
- Siemens
- Woodward
- YOKOGAWA
- FOXBORO
- KOLLMORGEN
- MOOG
- KB
- YAMAHA
- BENDER
- TEKTRONIX
- Westinghouse
- AMAT
- AB
- XYCOM
- Yaskawa
- B&R
- Schneider
- Kongsberg
- NI
- WATLOW
- ProSoft
- SEW
- ADVANCED
- Reliance
- TRICONEX
- METSO
- MAN
- Advantest
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bently
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- Beijer
- Moxa
- Rexroth
- Johnson
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- Application field
- XP POWER
- CTI
- TRICON
- STOBER
- Thinklogical
- Horner Automation
- Meggitt
- Fanuc
- Baldor
- SHINKAWA
- Other Brands





































































































































