SIMATIC MODNIM Module Deep Analysis: A Reliable Bridge for Industrial Modbus Communication
Test button: Used in combination with the Reset button (press and hold Reset and press Test for 5 seconds) to initiate a comprehensive diagnostic test triggered by the user. At this time, the network cable needs to be disconnected and a loopback connector needs to be installed.
Three layer diagnostic testing:
Power on self-test: automatically executed every time power on or reset, checking the processor, RAM, and ROM.
Run time self-test: The backend continuously performs ROM integrity checks, PLC communication status monitoring, and prevents software deadlocks through watchdog timers.
User triggered self-test: Conduct comprehensive hardware testing, including communication ports. By observing the status of the LED after diagnosis (see Table 1-3), faults such as ROM/RAM faults, PLC communication failures, and port A/B faults can be quickly located.
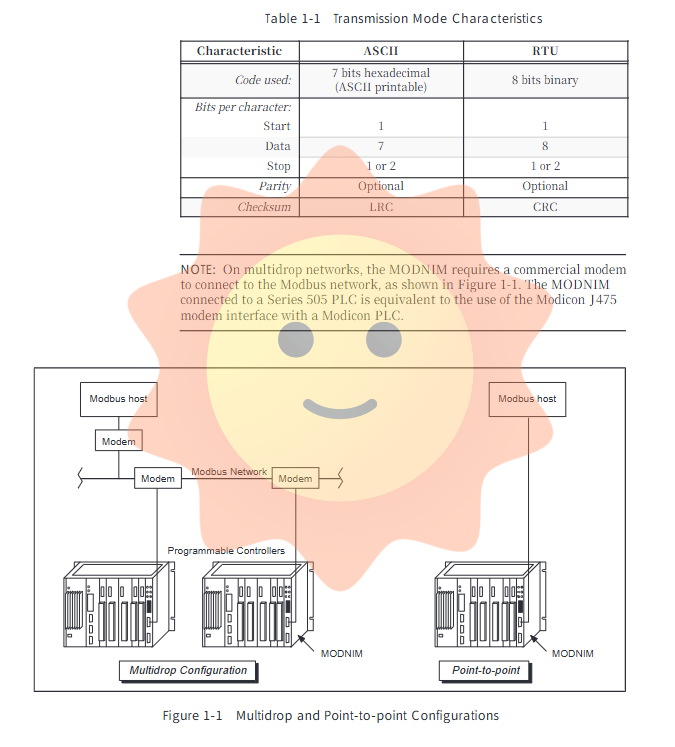
Deep Mapping and Function Implementation of Modbus Protocol
The essence of the MODNIM module lies in its precise mapping between the Modbus protocol and the internal data structure of SIMATIC TI PLC.
Protocol frame structure: The module fully supports Modbus ASCII and RTU frame formats. ASCII frames start with ":" and contain address field, function code field, data field, LRC checksum, and CR/LF terminator. RTU frames are defined by time intervals and include addresses, function codes, data, and CRC checks.
Function code support and TIWAY mapping: The module supports a series of core function codes in the Modbus standard and translates them into corresponding TIWAY I network "primitive" commands. The key mappings include:
01/02 (Read coil/input status) → TIWAY primitive 20, TT type 7/8 (Y/C packaging) or 6 (X packaging).
03/04 (Read Hold/Input Register) → TIWAY Primitive 20, TT Type 1 (V Memory) or 9 (WX Word Input).
05/06 (write single coil/single register) → TIWAY primitive 30, TT type 4/5 (Y/C) or 1 (V memory).
15/16 (write multiple coils/registers) → TIWAY primitive 30, corresponding to the packaged data type.
Advanced features such as 08 (diagnosis), 11/12 (communication events), and 17 (reporting slave ID) are also fully supported.
Key difference in address mapping: Engineers must pay attention to a core difference: the memory addresses of SIMATIC TI PLCs are usually numbered from 1, while many Modbus PLCs (and protocol conventions) start from 0. If the host application does not adjust this offset, it may result in accessing the wrong data location. The address mapping of the module adopts absolute positional addressing, with a maximum supported address of 65535 (FFFF hex).
Data limit: Due to Modbus buffer limitations, there is an upper limit on the amount of data per request: coil/discrete input is 2000 points, registers are 125 (read) or 100 (write), and writing multiple coils is 800 points. Exceeding the limit request will trigger an exception code 03 response.
Advanced Diagnostic and Configuration Tool (MODASST)
Siemens provides powerful PC side auxiliary software MODASST with the module, greatly simplifying the configuration and debugging process.
Main functions:
Interactive configuration: Guide users to gradually set communication ports, baud rates, parity checks, stop bits, modes (ASCII/RTU), handshakes, Y/C mappings, and network addresses.
DIP switch diagram: Based on the set parameters, visually display the position of the DIP switch on the module.
Cable Pin Diagram: Provide the cable wiring diagram required to connect MODNIM to the host or modem.
Communication testing: Provides a "dialogue with module" function, allowing manual sending of formatted Modbus requests and viewing of raw responses, or automatic sending of test requests to verify communication.
Automatic parameter recognition: When the module parameters are unknown, the "Find Module Settings" function can automatically attempt all possible parameter combinations until communication is established and the current settings are reported.
Diagnostic execution: Integrated Modbus function code 08 (diagnostic), convenient for users to perform various diagnostic sub functions, such as loop testing, counter reset, event log query, etc.
Usage value: The MODASST program visualizes complex protocol details and hardware configurations, reducing the entry barrier and on-site debugging time for engineers. It is an indispensable tool to ensure the fast and accurate operation of MODNIM modules.
Error Handling and System Integration
A reliable system must include a comprehensive error handling mechanism. The MODNIM module reports an error to the main station through an exception response code:
01- Illegal Function: A function that is not supported by the module was requested.
02- Illegal data address: The requested data address exceeds the valid range of the PLC.
03- Illegal data value: The value in the requested data field is unacceptable (such as exceeding the quantity limit).
04- Associated device failure: PLC not responding or communication failure (PC GOOD light off).
06- Memory parity error: A parity check error occurred while reading PLC memory.
These exception codes have been carefully mapped with the internal TIWAY exception codes of SIMATIC TI PLC to ensure accurate transmission of error messages.
- ABB
- General Electric
- EMERSON
- Honeywell
- HIMA
- ALSTOM
- Rolls-Royce
- MOTOROLA
- Rockwell
- Siemens
- Woodward
- YOKOGAWA
- FOXBORO
- KOLLMORGEN
- MOOG
- KB
- YAMAHA
- BENDER
- TEKTRONIX
- Westinghouse
- AMAT
- AB
- XYCOM
- Yaskawa
- B&R
- Schneider
- Kongsberg
- NI
- WATLOW
- ProSoft
- SEW
- ADVANCED
- Reliance
- TRICONEX
- METSO
- MAN
- Advantest
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bently
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- Beijer
- Moxa
- Rexroth
- Johnson
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- Application field
- XP POWER
- CTI
- TRICON
- STOBER
- Thinklogical
- Horner Automation
- Meggitt
- Fanuc
- Baldor
- SHINKAWA
- Other Brands
- UniOP