SIEMENS SIMOVERT MASTERDRIVES Vector Control Series
SIEMENS SIMOVERT MASTERDRIVES Vector Control System
The SIEMENS SIMOVERT MASTERDRIVES series is a fully digital modular component system for the industrial drive field, and its vector control (VC) version is particularly suitable for application scenarios that require high torque accuracy and dynamic response. This article is based on the official technical manual and provides an in-depth analysis of the system's architecture, functions, parameterization methods, key safety features, and electromagnetic compatibility design. The aim is to provide a complete, professional, and practical reference guide for engineering design, debugging, and maintenance personnel.
System Overview and Core Features
SIMOVERT MASTERDRIVES VC offers a wide power range from 0.55 kW to 2300 kW, supporting various structures such as compact, compact PLUS, and rack mounted. Its core lies in the use of vector current control technology, which achieves high dynamic and high-precision control of AC motor torque through decoupling control of motor excitation current and torque current. This system not only has basic U/f control modes to operate synchronous or asynchronous motors, but also supports speed control with or without encoders, as well as torque control with encoders, and can drive externally excited synchronous motors.
The outstanding feature of the system lies in its high modularity and flexibility. Through a variety of optional boards (such as sensor board SBx for speed/position detection, communication board CBx for fieldbus integration, and SIMOLINK board SLx for fast data exchange) and software function options, users can customize drive solutions based on specific process requirements (such as positioning, synchronization, cam profiling). All closed-loop control functions are implemented by freely interconnected functional blocks, combined with the BICO (Binary Interconnect) system. Users can flexibly configure signal flow through software "wiring", greatly enhancing the software's adaptability to diverse applications.
System Configuration and Connection Example
The system supports single axis drive, multi axis drive (up to 3 axes), and multi axis drive configurations based on a common rectifier unit. In the compact PLUS multi axis drive, a rectifier unit can provide DC bus voltage to multiple inverters, achieving energy feedback and utilization between axes. The manual provides a detailed list of components required for various configurations, such as main contactors, incoming reactors, filters, braking resistors, 24V external power supplies, etc. It emphasizes the correct wiring sequence and safety precautions, such as the need to disconnect the electronic power supply (24V DC) and main power/DC bus voltage before connecting or disconnecting control and encoder cables.
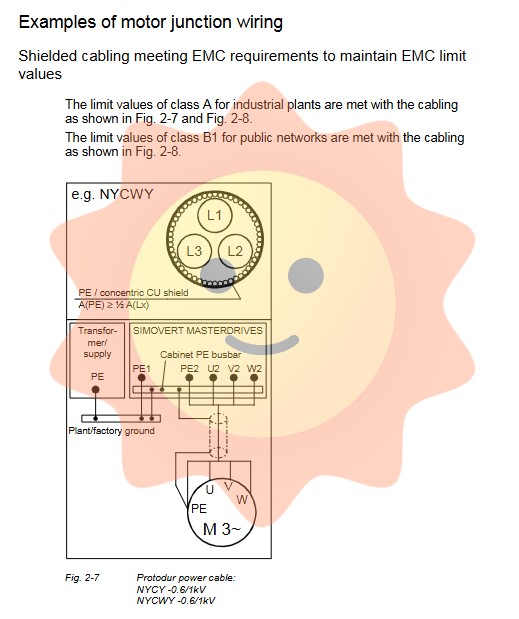
To ensure electromagnetic compatibility, the manual strongly recommends using shielded motor cables (such as Siemens PROTOFLEX-EMV-CY), and the shielding layer must be connected extensively and with low inductance at both ends of the frequency converter and motor, providing a clear return path for high-frequency interference currents, which is a key measure to suppress electromagnetic interference (EMI).
Parameterization: From Quick Settings to Deep Customization
Parameterization is the core of driver debugging, and the system provides multiple ways: through the device's built-in PMU (parameterization unit), external OP1S operation panel, running DriveMonitor software on PC, or through fieldbus (such as PROFIBUS).
1. Fast parameterization (P060=3):
For standard applications or replacement devices, the system has pre-set a "parameter module" function. Users only need to select in sequence: motor type (such as standard IEC motor or Siemens specific model), control type (such as U/f control, vector control without encoder, speed control with encoder, etc.), set value/command source (such as PMU, fixed set value, analog input, etc.). The system will automatically calculate and set a large number of parameters based on the selection, including automatic parameterization based on motor nameplate data (P115=1), greatly simplifying initial debugging.
2. Detailed parameterization:
For complex or special applications, detailed parameterization is required, mainly divided into three steps:
Power section definition (P060=8): Clearly define the model and rated data of the frequency converter.
Circuit board configuration (P060=4): Activate and configure installed optional boards (such as encoder board, communication board).
Drive settings (P060=5): This is the core step, which includes inputting accurate motor nameplate data, encoder parameters, selecting control type (P100), and optimizing controller settings (P235, etc.) based on process boundary conditions such as "torsion and gear clearance", "acceleration drive", "load impact", etc. At this stage, more comprehensive motor recognition operations can be performed (P115=2,3) to obtain accurate motor model parameters and optimize control performance.
3. BICO system and data group:
The flexibility of the system comes from BICO technology. Parameters are divided into functional parameters, BICO parameters, and visualization parameters. The BICO parameter is used to connect the input of the functional block to the internal signal source (connector K or binary connector B), enabling free "wiring" at the software level. In addition, the system supports multiple sets of data sets:
Functional Data Set (CDS): switchable online, used to change process parameters such as acceleration and amplitude limit.
Motor Data Set (MDS): It needs to switch between shutdown states to drive different motors or change motor control modes.
BICO dataset: switchable online, used to change the signal source for commands and set values.
The data group mechanism allows a driver to flexibly adapt to multiple operating modes.
Safety Function Design: STO and SS1
The manual extensively elaborates on the implementation of safety functions in accordance with DIN EN 61800-5-2 (equivalent to IEC 61800-5-2), which is a key requirement for modern drive systems.
1. Safe Torque Off (STO):
The STO function is designed to prevent the motor from accidentally starting. After activation, the pulse enable power supply is cut off through the safety relay (option K80) to ensure that the power semiconductor cannot generate a rotating magnetic field and the motor is in a torque free state. Important reminder: STO is not an electrical isolation and cannot provide protection against electric shock; And it does not enable parking itself, it must be activated after the drive has come to a complete stop, otherwise the motor will stop freely. Additional mechanical braking is required for vertical axes, etc.
2. Safe Stop 1 (SS1- Safe Stop 1):
SS1 is a controlled safety stop. After triggering, the driver first decelerates and stops along the emergency stop slope. After a safety monitoring delay, the STO function is automatically activated. This achieves behavior that complies with EN 60204-1 stopping category 1.
3. Application examples and performance level (PL) calculation:
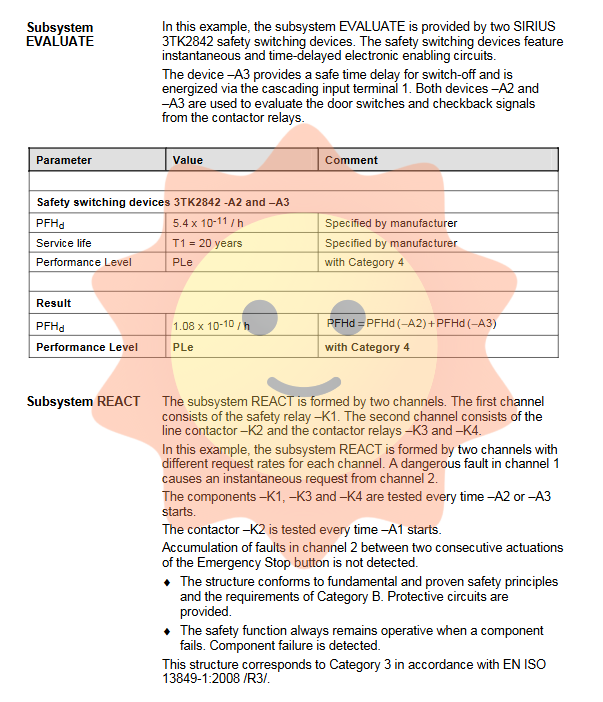
The manual provides detailed circuit diagram examples, such as combining emergency stop button and protective door monitoring with STO or SS1 functions. Each example follows the safety architecture of "detection evaluation response" and has undergone detailed performance level (PL) calculations to demonstrate its ability to achieve the required PLr=d (according to EN ISO 13849-1). The calculation takes into account the average time to failure (MTTFd), diagnostic coverage (DC), and measures to resist common cause failures (CCF) of sensors (such as emergency stop buttons, position switches), evaluation units (such as Siemens SIRIUS safety relays), and actuators (safety relay K1, main contactor K2). These examples demonstrate that solutions that meet high safety standards can be constructed through a dual channel structure (such as pulse cutoff+main contactor disconnection) and appropriate diagnostics.
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design Criteria
The frequency converter is both a high-frequency interference source (derived from fast switching of power semiconductors) and a potential interference receiver (affecting control circuits). The manual emphasizes that installing an incoming filter alone is not enough to ensure the EMC of the entire system.
The core principles include:
Partition concept: Separate interference sources (frequency converters, braking units, contactors) from sensitive equipment (controllers, sensors) in space (minimum distance of 20cm) inside the cabinet, preferably using grounded metal partitions.
Cable wiring: Power cables and signal cables must be laid separately. The motor cable must be shielded, and both ends of the shielding layer must be grounded.
Grounding and Connection: All metal cabinet components should be interconnected through a large area of metal surface (non painted surface to painted surface) to ensure a low impedance grounding network.
Signal cable processing: Digital signal cables such as encoders and transformers need to use shielded cables with both ends grounded. To avoid low-frequency interference (humming), analog signal cables can be grounded at one end of the receiving end and grounded at the other end through a capacitor (such as 10nF) to maintain high-frequency shielding continuity.
Filter installation: The RF interference suppression filter should be installed near the frequency converter and on the same unpainted metal mounting plate as the frequency converter to ensure good high-frequency electrical contact.
Following these rules, combined with the use of recommended incoming reactors and filters, can ensure that the drive system meets the emission and immunity requirements for industrial environments (secondary environment) in EN 61800-3 standard.
6GK1900-0AB00
- ABB
- General Electric
- EMERSON
- Honeywell
- HIMA
- ALSTOM
- Rolls-Royce
- MOTOROLA
- Rockwell
- Siemens
- Woodward
- YOKOGAWA
- FOXBORO
- KOLLMORGEN
- MOOG
- KB
- YAMAHA
- BENDER
- TEKTRONIX
- Westinghouse
- AMAT
- AB
- XYCOM
- Yaskawa
- B&R
- Schneider
- Kongsberg
- NI
- WATLOW
- ProSoft
- SEW
- ADVANCED
- Reliance
- TRICONEX
- METSO
- MAN
- Advantest
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bently
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- Beijer
- Moxa
- Rexroth
- Johnson
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- Application field
- XP POWER
- CTI
- TRICON
- STOBER
- Thinklogical
- Horner Automation
- Meggitt
- Fanuc
- Baldor
- SHINKAWA