Technical Analysis and Application Guide for Siemens SIMATIC TI505/TI500 MODNIM Module
Technical Analysis and Application Guide for Siemens SIMATIC TI505/TI500 MODNIM Module
Overview and Main Features of MODNIM Module
Siemens SIMATIC TI505/TI500 MODNIM (Modbus Network Interface Module) is a network interface module designed specifically for industrial environments, with models PPX: 505-5184 (applicable to TI505 series) and PPX: 500-5184 (applicable to TI500 series). As a Modbus slave device, this module can achieve efficient data communication between PLC and hosts (such as industrial computers and SCADA systems), supporting up to 247 nodes running in the same network.
The MODNIM module has the following core features:
Supports both Modbus ASCII and RTU transmission modes;
Dual RS-232-C/423 communication ports with redundant connection capability;
Network addresses and communication parameters can be flexibly configured through DIP switches;
Built in multi-level self diagnostic function, including power on self-test, runtime self-test, and user self-test;
Provide local/remote operation mode switching and support read-write permission management;
Compatible with TIWAY I network commands, it can achieve seamless integration with SIMATIC TI PLC.
Technical specifications and detailed explanation of functions
2.1 Communication Protocol and Transmission Mode
The MODNIM module follows the Modbus protocol and supports master-slave communication architecture. The host can communicate with the slave through request response or broadcast (no response) mode. The module supports both ASCII and RTU frame formats:
ASCII mode: Each frame starts with a colon (:) and ends with CR/LF, using 7-bit character encoding, suitable for debugging environments with high readability requirements.
RTU mode: adopting 8-bit binary encoding, with at least 3.5 character silence as frame interval, higher transmission efficiency, suitable for industrial scenes with strong real-time requirements.
Both modes support parity and error detection mechanisms (LRC or CRC) to ensure the integrity of data transmission.
2.2 Hardware Configuration and Installation Points
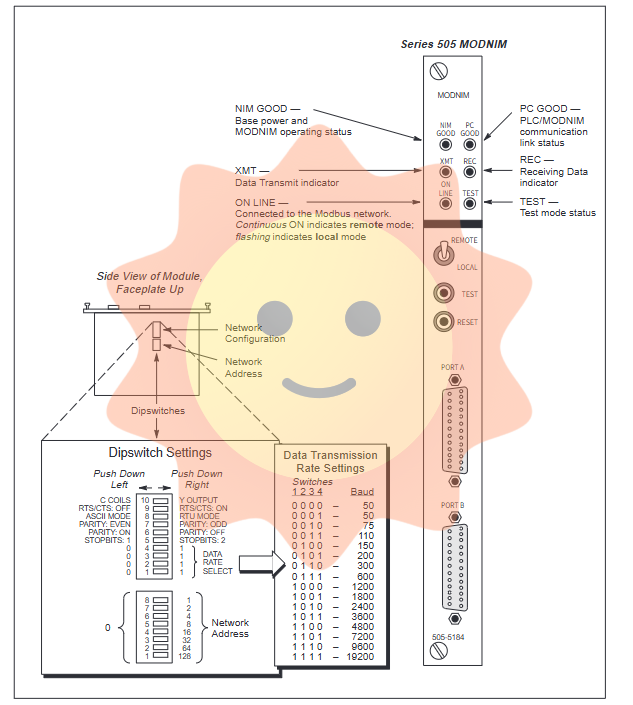
The MODNIM module is configured through two sets of DIP switches:
8-bit switch: Set module network address (1-247), address 0 is the broadcast address, 248-255 is the invalid address;
10 bit switch: Configure communication parameters, including baud rate (50-19200 bps), stop bit (1/2), parity check, transmission mode, RTS/CTS handshake signal, and coil type (Y output/C relay) mapping.
Attention should be paid during installation:
Inserting or unplugging modules in a power-off state;
Use anti-static measures to avoid damaging integrated circuits;
Ensure that the module and PLC are correctly registered through I/O mapping, which can be verified by viewing the I/O definition table through programming devices.
2.3 Status indication and diagnostic function
The module panel provides 6 LED indicator lights, which respectively represent:
NIM GOOD: Module self-test passed;
PC GOOD (PC/NIM COMM GOOD): Communication with PLC is normal;
ONLINE: Network connection status (constantly lit for remote mode, flashing for local mode);
Receive (REC): Receiving data;
Transmit (XMT): Sending data;
TEST MODE (TEST): The module is in test mode or has failed self-test.
The module provides three-level self diagnosis:
Power on self-test: detecting the processor RAM、ROM;
Run time self-test: continuously monitor ROM integrity, PLC communication status, and watchdog timer;
User self-test: triggered by the TEST button, comprehensively test the hardware and communication ports (requiring the use of a loopback connector).
Detailed explanation and application examples of Modbus commands
MODNIM supports standard Modbus function codes and maps them with the TIWAY I command to achieve data read/write, diagnosis, and status reporting.
3.1 Common Function Code Description
01 (Reading coil status): Read the switch status of Y output or C relay;
03 (Read and hold register): Read integer data from V memory;
05 (write single coil): Control the switch status of a single coil;
06 (Write a single register): Modify the value in the V memory;
08 (Perform Diagnosis): Supports multiple sub diagnostic codes for network testing and status queries;
17 (Report slave ID): Returns information such as PLC type, operating status, software version, etc.
3.2 Communication Example (Using ASCII Mode as an Example)
For example, reading the status of the 5 coils starting from the 10th coil in the module with station address 7:
Request frame:
: 07 01 00 09 00 05 LRC CR LF
Response frame:
: 07 01 01 1A LRC CR LF
Among them, 1A (binary 00011010) represents the state of coils 10-14 (1=ON, 0=OFF).
3.3 Error Handling and Exception Response
When the request cannot be executed normally, MODNIM returns an exception response with the highest position of function code 1 (such as 81 indicating 01 exception), accompanied by the exception code:
01: Illegal function code;
02: Illegal data address;
03: Illegal data values;
04: Associated device failure;
06: Memory parity error.
System integration and debugging tools
4.1 Cable and Connection Suggestions
The module provides two 25 pin D-type ports (DTE configuration), supporting point-to-point or multi-point connections. It is recommended to use Siemens standard communication cables (such as 2601094-8001 or VPU200-3605), or self-made shielded twisted pair cables according to manual requirements to reduce noise interference.
- ABB
- General Electric
- EMERSON
- Honeywell
- HIMA
- ALSTOM
- Rolls-Royce
- MOTOROLA
- Rockwell
- Siemens
- Woodward
- YOKOGAWA
- FOXBORO
- KOLLMORGEN
- MOOG
- KB
- YAMAHA
- BENDER
- TEKTRONIX
- Westinghouse
- AMAT
- AB
- XYCOM
- Yaskawa
- B&R
- Schneider
- Kongsberg
- NI
- WATLOW
- ProSoft
- SEW
- ADVANCED
- Reliance
- TRICONEX
- METSO
- MAN
- Advantest
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bently
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- Beijer
- Moxa
- Rexroth
- Johnson
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- Application field
- XP POWER
- CTI
- TRICON
- STOBER
- Thinklogical
- Horner Automation
- Meggitt
- Fanuc
- Baldor
- SHINKAWA