Kollmorgen H series brushless servo motor and Silverline driver
Thermal parameters: including thermal time constant and thermal resistance. For example, the thermal resistance of H-344-H is 1.6 ° C/W. The smaller this value, the stronger the motor's heat dissipation ability and the higher the sustainable output torque.
Theoretical acceleration: calculated by dividing the peak torque by the rotor inertia, reflecting the maximum dynamic capability of the motor body. The theoretical acceleration of H-342-H reaches 255300 rad/s ².
2.3 Important Selection Annotations
The manual emphasizes the parameter conversion when matching with the driver:
When using a sine wave driver, the Kt of the six step commutation (trapezoidal wave) needs to be multiplied by 1.2828 to obtain the torque constant based on RMS current; Divide Kb by 1.414 to obtain the back electromotive force constant based on RMS voltage.
The maximum speed is limited by the lowest value among electrical limits, mechanical structure, feedback devices, and bearings. The motor must be used in conjunction with a driver with overspeed protection function.
The performance curve is usually drawn based on an ambient temperature of 40 ° C, and in practical applications, heat dissipation conditions need to be considered.
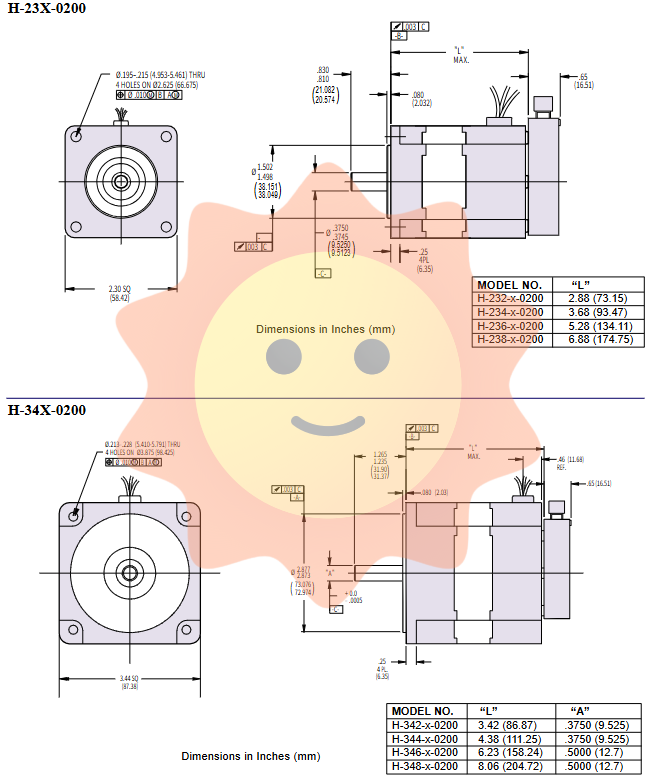
Mechanical interface and installation dimensions
The manual provides detailed dimension drawings, covering models with different feedback options (0200, 0600, 0802, etc.).
Installation flange: Fully compatible with NEMA standards, easy to install.
Shaft extension specifications: The H-23X series typically offers a 0.250 "shaft diameter; in the H-34X series, the H-342/H-344 has a 0.375" shaft diameter, and the H-346/H-348 has a 0.500 "shaft diameter.
Axle load: The allowable axle load curve calculated based on a 20000 hour L10 life is provided on page 11 of the manual. The distance between the application point of radial load and the installation surface is clearly specified (0.75 "for H-23X and 1.0" for H-34X), and the selection must ensure that the actual load is within the curve range.
Detailed explanation of supporting drivers
One of the advantages of Silverline servo system is its highly matched and economically efficient matching driver family.
4.1 SO/RO/OL series amplifiers
This is a type of compact driver that focuses on providing high-performance current loops.
Product positioning: Economical and efficient, suitable for cost sensitive applications.
Model differentiation:
SO series: Low voltage DC input (20-40 VDC), suitable for battery powered or low-voltage applications.
RO series: High voltage DC input (135-190 VDC).
ROL series: AC input (90-130 VAC), built-in rectifier, the most convenient to use.
Working mode (selected through jumper):
Current loop mode: With a bandwidth>2500 Hz and extremely fast response, it is the preferred choice for achieving precise position control in conjunction with upper level motion controllers.
Open loop mode: used in situations where speed accuracy is not required.
Encoder speed loop mode (ROL only): Convert the motor encoder feedback into an analog speed signal for closed-loop speed regulation.
Speed loop mode of speedometer (ROL only): external analog speedometer for speed control.
Key features: Four quadrant regeneration operation, comprehensive protection function (overcurrent, overvoltage, overheating, short circuit), built-in heat sink, six step commutation, optically isolated I/O.
4.2 BJR/BJRL Series Amplifier/Positioner
This is a highly integrated "all-in-one" solution that combines an amplifier with a motion controller.
Core features:
Built in motion control: Using the BASIC like BDS5 programming language, complex functions such as point-to-point positioning, electronic gears, and electronic camshafts can be completed without the need to purchase additional motion control cards.
Rich I/O: Provides 14 digital inputs, 6 digital outputs, 3 analog inputs, and 1 analog output, making it easy to directly connect sensors and actuators.
Communication interface: Standard RS-232 and RS-485, supporting multi station networks.
Model differentiation: BJR is DC input, BJRL is AC input.
Applicable scenarios: Very suitable for single axis or simple multi axis independent automation equipment, such as feeders, indexing tables, small assembly machines, etc., which can significantly reduce system complexity and total cost.
4.3 SPS power module
Specially designed for SO amplifiers, it can convert single-phase AC power (115/230 VAC optional) to DC bus voltage and can power up to 4 SO amplifiers, with optional regenerative resistors.
System Matching and Selection Guide
The "Compatibility Matrix" on page 12 of the manual is the core tool for selection. It specifies the recommended driver model for each motor to ensure performance and safety margin.
For example:
The H-342-H motor can be paired with RO (L) -20004, BJR-20004, or BJR-20012 drivers.
When making a choice, it is necessary to consider comprehensively:
Voltage matching: The required bus voltage is determined by the back electromotive force and speed requirements of the motor, and the input voltage of the driver must meet them.
Current matching: The continuous current and peak current of the motor must be less than the continuous output current and peak (overload) output current of the driver.
- ABB
- General Electric
- EMERSON
- Honeywell
- HIMA
- ALSTOM
- Rolls-Royce
- MOTOROLA
- Rockwell
- Siemens
- Woodward
- YOKOGAWA
- FOXBORO
- KOLLMORGEN
- MOOG
- KB
- YAMAHA
- BENDER
- TEKTRONIX
- Westinghouse
- AMAT
- AB
- XYCOM
- Yaskawa
- B&R
- Schneider
- Kongsberg
- NI
- WATLOW
- ProSoft
- SEW
- ADVANCED
- Reliance
- TRICONEX
- METSO
- MAN
- Advantest
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bently
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- Beijer
- Moxa
- Rexroth
- Johnson
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- Application field
- XP POWER
- CTI
- TRICON
- STOBER
- Thinklogical
- Horner Automation
- Meggitt
- Fanuc
- Baldor
- SHINKAWA
- Other Brands





































































































































