GE Multilin MLJ synchronous inspection relay
Function: As a digital synchronous check relay, it can measure bus and line voltage, test voltage difference, frequency slip, and phase angle between two voltages. When all values are within the set range and maintained for a set time, it provides output to allow the circuit breaker to close; If the conditions are not met, a closed condition failure signal will be issued one minute later.
Operation mode: divided into continuous mode (continuous check synchronization) and manual mode (starting synchronization control when voltage is applied through manually activated input).
Other features: Equipped with two undervoltage units to control synchronization function, allowing synchronous operation only when both voltages are higher than the set value; It also has DLDB (Dead Line Dead Bus), DLLB (Dead Line Active Bus), and LLDB (Active Line Dead Bus) functions, which can be independently set to select any combination.
GE Multilin MLJ synchronous inspection relay
Product Description and Application
Main applications: including connecting the generator to the system, re establishing the connection between two parts of the system, manually closing circuit breakers, automatic reclosing of circuit breakers after relay tripping, etc.
Function: As a digital synchronous check relay, it can measure bus and line voltage, test voltage difference, frequency slip, and phase angle between two voltages. When all values are within the set range and maintained for a set time, it provides output to allow the circuit breaker to close; If the conditions are not met, a closed condition failure signal will be issued one minute later.
Operation mode: divided into continuous mode (continuous check synchronization) and manual mode (starting synchronization control when voltage is applied through manually activated input).
Other features: Equipped with two undervoltage units to control synchronization function, allowing synchronous operation only when both voltages are higher than the set value; It also has DLDB (Dead Line Dead Bus), DLLB (Dead Line Active Bus), and LLDB (Active Line Dead Bus) functions, which can be independently set to select any combination.
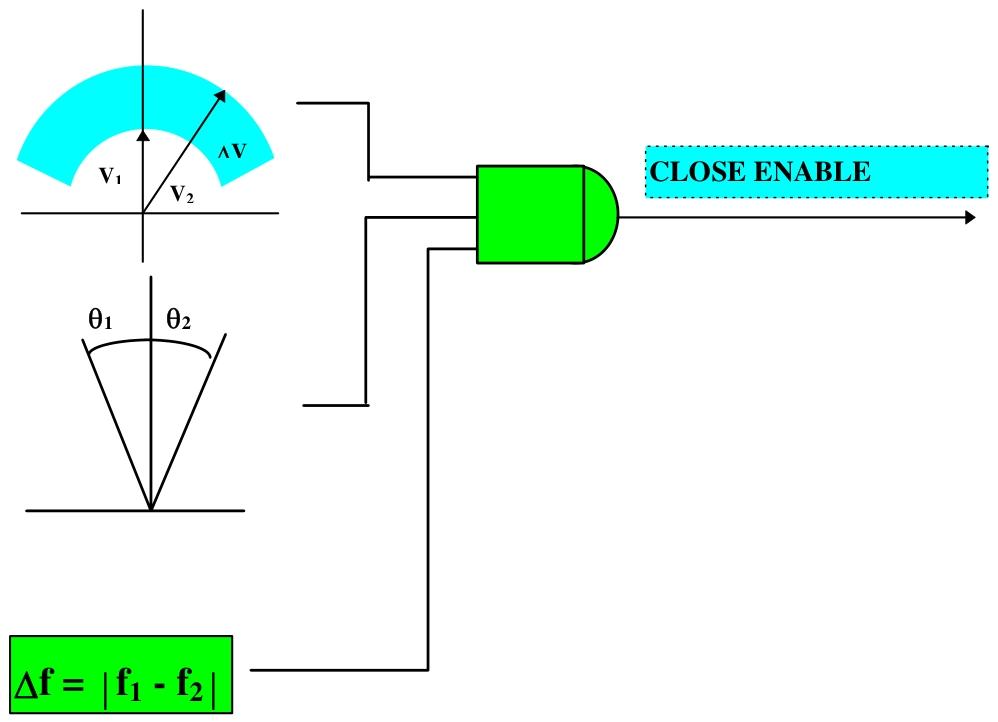
Design Features and Application Scenarios
Measurement accuracy: Differential angle measurement has high accuracy, limited only by the error of available voltage transformers, and the measurement is almost independent of voltage. High accuracy is achieved by numerical calculation of digital voltage samples, rated as 2 °, which is superior to other technologies.
Harmonic influence: Based on discrete Fourier transform for measurement and calculation, it is essentially a harmonic filter. Voltage and line measurements are not affected by frequencies other than the fundamental wave, and have the ability to resist harmonics in frequency measurements.
Voltage limitation: When the voltage is below 9 volts, the relay stops measuring phase and frequency and is not allowed to close.
Time parameter: The minimum closing time is set to 100ms, but it is actually 160ms; there is a fixed allowable signal maintenance time of about 130ms.
Synchronization conditions: including the amplitude difference, angle difference, and frequency slip between two voltage signals, all of which must meet the set conditions.
Application scenario: Suitable for situations where two parts of the system are connected through circuit breakers and interconnected at other points in the system. Different scenarios have different requirements for measuring time and frequency slip settings.
Operating principle
Configuration unit: Parameters such as frequency (50 or 60Hz), unit number, communication speed, etc. can be selected and changed.
Synchronization check unit: Analyze the voltage amplitude, input status, and settings on both sides of the circuit breaker, and provide synchronization signals when conditions are met. There are two operating modes, manual and continuous, based on the manual input status, with corresponding time delay mechanisms and setting parameters.
Undervoltage unit: an independent unit with multiple undervoltage and overvoltage functions, which allows the circuit breaker to be closed in dead wire and/or busbar situations. It can operate under different undervoltage conditions (DLDB, DLLB, LLDB) without time delay through settings.
Input unit: Three digital inputs are activated by DC voltage. The input unit reads the input status and filters out possible bounce or noise. Different inputs have different functions, such as indicating the status of the circuit breaker with the input of 52 B, and changing the delay time of the synchronization unit with the input of manual mode.
Self checking unit: The relay continuously performs internal checks during operation to verify the integrity of components, including program memory, working memory, etc. When a fault is detected, it is indicated on the display screen through code, generating an alarm signal and disabling the output.
Output unit: There are 5 outputs, which are relay contacts that can be configured as normally open or normally closed through internal jumpers. They receive signals from the synchronization, undervoltage, and self-test units and activate the corresponding relays according to the configuration.
Power supply: Generate internal voltage required for relay operation from auxiliary voltage, isolate internal circuits from external interference, and be a wide range switch mode power supply.

Technical characteristics
Model List: Define MLJ models through different code combinations, involving communication methods, auxiliary and input voltages, casings, etc.
Technical parameters: including frequency, rated voltage, auxiliary power supply, maximum allowable voltage, temperature range, environmental humidity, and the breaking capacity of each contact.
Insulation: Complies with IEC 255-5 standard, with specified insulation voltage and testing time between each terminal and ground, as well as between independent circuits.
Type test: Multiple tests including 1MHz noise test, impact test, and electrostatic discharge test were conducted, which comply with relevant standards.
- ABB
- General Electric
- EMERSON
- Honeywell
- HIMA
- ALSTOM
- Rolls-Royce
- MOTOROLA
- Rockwell
- Siemens
- Woodward
- YOKOGAWA
- FOXBORO
- KOLLMORGEN
- MOOG
- KB
- YAMAHA
- BENDER
- TEKTRONIX
- Westinghouse
- AMAT
- AB
- XYCOM
- Yaskawa
- B&R
- Schneider
- Kongsberg
- NI
- WATLOW
- ProSoft
- SEW
- ADVANCED
- Reliance
- TRICONEX
- METSO
- MAN
- Advantest
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bently
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- Beijer
- Moxa
- Rexroth
- Johnson
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- Application field
- XP POWER
- CTI
- TRICON
- STOBER
- Thinklogical
- Horner Automation
- Meggitt
- Fanuc
- Baldor
- SHINKAWA
- Other Brands





































































































































