MOOG QAIO 16/4 Analog I/O Module Technology Analysis and Application Guide
MOOG QAIO 16/4 Analog I/O Module Technology Analysis and Application Guide
In industrial automation and control systems, accurate acquisition and reliable output of analog signals are the foundation for achieving process monitoring and closed-loop control. The QAIO 16/4 analog I/O expansion module, jointly launched by Moog and Berghof Automation, serves as the M3000 ® The control system and CANtrol automation system are important components that provide engineers with high-density and high-precision analog signal processing capabilities. This article will provide a comprehensive and in-depth analysis of this classic module from multiple perspectives, including module overview, technical details, safety specifications, installation and wiring, signal processing, and system integration.
Product Overview and System Positioning
The QAIO 16/4 module is an extension module designed specifically for expanding the analog I/O capabilities of cell controllers. It is connected to the system through direct E-Bus coupling, providing two input type variants: QAIO 16/4-V (voltage input) and QAIO 16/4-A (current input). The core function of the module is to serve as a high-precision bridge between the on-site analog sensor and the upper control unit.
Its design strictly follows the international standard IEC 61131 (Programmable Logic Controller) series and meets the EMC (Electromagnetic Compatibility) requirements in industrial environments (EN 50081-2/EN 50082-2). The module emphasizes reliable operation in industrial noise environments and provides detailed safety operation guidelines and shielding wiring specifications for this purpose.
Core functions and electrical characteristics
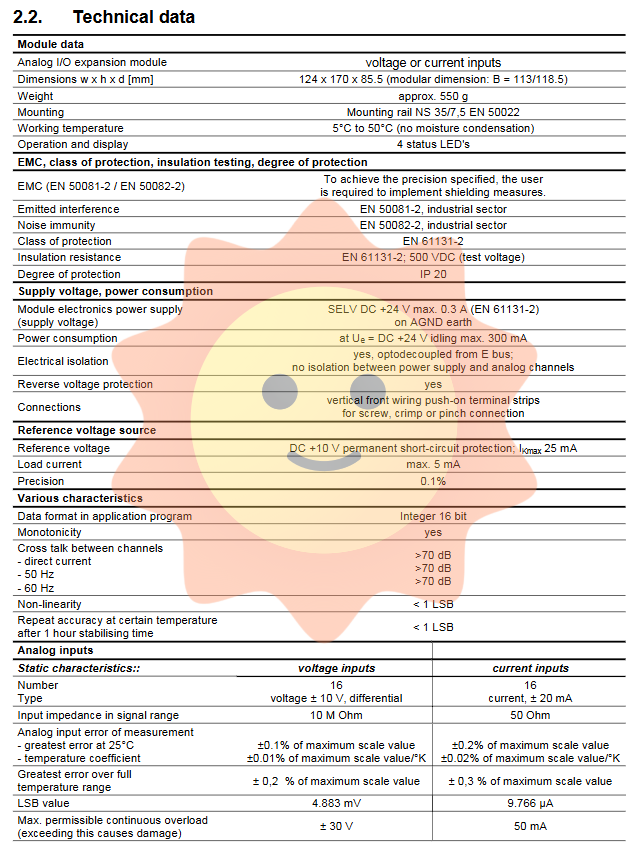
1. Analog input channel
Number of channels: 16.
Input type:
V version: Differential voltage input, with a range of ± 10V.
Version A: Current input, with a range of 0... 20mA (actual support ± 20mA).
Resolution: 11 bits+sign bit, equivalent to a 16 bit integer representation (-32768 to+32752).
Accuracy (25 ° C):
Voltage input: ± 0.1% full scale.
Current input: ± 0.2% full range.
Temperature coefficient: extremely low, at ± 0.01%/K (voltage) and ± 0.02%/K (current) respectively, ensuring stability over a wide temperature range (0-50 ° C operating temperature).
Input impedance: voltage input up to 10M Ω, current input is 50 Ω.
Overload protection: Equipped with protective diodes, it can withstand continuous overload up to ± 30V (voltage) or 50mA (current) without damage.
Common mode rejection ratio: ≥ 70 dB, effectively suppressing common mode interference.
2. Analog output channel
Number of channels: 4.
Output type: Floating voltage output, with a range of ± 10V.
Resolution: 11 bits+sign bit.
Accuracy (25 ° C): ± 0.15% of full scale.
Output capability: Maximum output current of 5mA, with permanent short-circuit protection (short-circuit current limit of 25mA).
Dynamic performance: setup time<1ms, slew rate>8 V/μ s.
Load requirements: minimum load resistance of 2k Ω, maximum capacitive load<1000 pF.
3. Module reference voltage source
Output:+10 VDC.
Accuracy: ± 0.1%.
Load capacity: Maximum load current of 5mA, also equipped with permanent short-circuit protection (current limit of 25mA). This power supply can provide stable excitation for external sensors such as potentiometers and bridges.
4. General module characteristics
Power supply: 24 VDC SELV (safe extra low voltage), maximum current consumption of 0.3A, with reverse polarity protection.
Isolation: The electronic part of the module is isolated from the E-Bus through optocouplers; But there is no electrical isolation between the module power supply (24V) and the analog channel, and they share AGND (analog ground). This is a key point in design and application.
Physical characteristics: Dimensions 124 x 170 x 85.5 mm, weight approximately 550g, installed on NS 35/7.5 DIN rails.
Protection level: IP20, suitable for installation inside cabinets.
Status indication: 4 LED indicator lights, respectively indicating L+(24V power supply), ± 15V (analog unit power supply),+5V OUT (E-Bus communication), and OUT-INA (output enabled) status.
Safe operation and qualified user requirements
The manual emphasizes safety at the beginning and defines four levels of warning signs:
danger Failure to comply will result in death, serious injury, or significant property damage.
Warning! Failure to comply may result in death, serious injury, or significant property damage.
Caution: Failure to comply may result in minor injuries or property damage.
Annotation: Provide important product information or document guidance.
The module only allows qualified users to operate, that is, professionals who have been trained, authorized, and able to debug, ground, and mark equipment according to safety engineering standards. The system is designed for environments with overvoltage category I, with a rated supply voltage not exceeding 1000 VAC or 1500 VDC.
The manual specifically warns that any malfunction of specific components in an electronic control system may result in uncontrollable operation. When designing safety related systems, all failure modes must be considered and manufacturers may need to be consulted.
Guidelines for Shielding, Wiring, and Practical Applications
1. Implementation of Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC)
The high precision and fast conversion rate of the module make it sensitive to electromagnetic interference. To ensure performance, users must implement effective blocking measures.
Cabinet requirements: Modules must be installed in metal shielded cabinets.
Wiring separation: Signal lines should be spatially separated from interference sources such as power lines.
Shielding layer connection: The shielding layer of the on-site cable should be grounded on both sides of the cabinet and make extensive contact with the metal surface when entering the cabinet to achieve optimal discharge of high-frequency interference.
Design concept: The manufacturer emphasizes that although module design focuses on EMC, a large part of the responsibility for reliable system operation lies in the overall installation design of the user. Therefore, the module itself has not been affixed with the CE mark, and the user is responsible for CE compliance of the entire application system.
2. Principle of Analog Signal Wiring
The analog circuit design of the module is based on the concept of "common potential island".
Public Ground (AGND): It is strongly recommended that all connected sensors, actuators, and modules use the same 24V power supply to make AGND the common reference point of the system.
Common mode range limitation: Each analog channel is allowed to be connected to different ground potentials, but it must be ensured that the potential difference is within the common mode voltage range of ± 2V. Exceeding this range will result in measurement errors or even module damage.
Fault current protection: Despite internal protection, incorrect wiring, power supply, or high potential difference may still cause permanent damage. Before powering on, the polarity of the wiring must be checked repeatedly.
3. Example of Sensor Connection
The manual provides three typical connection methods:
Floating sensor: Use dual core shielded wires to connect IN+and AGND. Unused IN input terminals must be bridged to AGND to release the common mode voltage accumulated due to high input impedance and avoid random measurement errors.
Non isolated sensors with auxiliary power supply: The sensor must use the same power supply as the module. Signal connection IN+and IN - (polarity correct), AGND suspended. It is necessary to ensure effective potential balancing through public power sources.
Sensors that use internal reference voltage, such as potentiometers or bridge circuits, are connected to IN+, IN -, Uref, and AGND using 3-core or 4-core shielded wires. Ensure that the reference voltage source is not overloaded.
4. actuator connection
For analog output, in addition to signal lines (OUT) and analog ground (AGND), SENSE connection points are also provided. The SENSE line should be directly connected to the local ground of the actuator to compensate for the ground potential offset on the long cable, provided that the offset | U-REF | is less than 2V. Note: The SENSE line cannot be used alone as feedback.
System integration and software operation
Module identification and initialization: automatically completed by the operating system of the upstream unit controller, without the need for dip switch settings. The identification feature codes stored in the module are read by the controller.
Data conversion: Measurement and data transmission are controlled through an API (Application Process Interface) loop. AD conversion does not require a startup signal.
Data format: Analog values are passed as 16 bit integers. When the range is exceeded, the input channel will report a fixed limit value (+32752 corresponds to+9.995V, -32768 corresponds to -10.000V).
Sensor fault detection: When a sensor fails, the corresponding channel will report a value of+9.995V to the controller.
Software dependency: Specific operations (such as calling function blocks, setting sampling periods) depend on the software environment used (such as CP1131 or CPC++), and should refer to the corresponding programming manual.
Installation, maintenance, and service
Installation: Ensure that all ventilation openings are unobstructed. All power sources (including externally powered sensors) must be disconnected during work.
Maintenance: The module is maintenance free. Only dry, lint free cloths should be used for cleaning, and the use of cleaning agents is prohibited.
Repair: Users are strictly prohibited from repairing on their own. All repair work must be carried out by the manufacturer or its authorized service engineer, otherwise the warranty will be invalidated.
Scrap disposal: After the product lifecycle ends, it can be returned to the manufacturer for professional recycling at a fee.
- ABB
- General Electric
- EMERSON
- Honeywell
- HIMA
- ALSTOM
- Rolls-Royce
- MOTOROLA
- Rockwell
- Siemens
- Woodward
- YOKOGAWA
- FOXBORO
- KOLLMORGEN
- MOOG
- KB
- YAMAHA
- BENDER
- TEKTRONIX
- Westinghouse
- AMAT
- AB
- XYCOM
- Yaskawa
- B&R
- Schneider
- Kongsberg
- NI
- WATLOW
- ProSoft
- SEW
- ADVANCED
- Reliance
- TRICONEX
- METSO
- MAN
- Advantest
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bently
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- Beijer
- Moxa
- Rexroth
- Johnson
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- Application field
- XP POWER
- CTI
- TRICON
- STOBER
- Thinklogical
- Horner Automation
- Meggitt
- Fanuc
- Baldor
- SHINKAWA
- Other Brands




































































































































