ABB RE.216 series digital protection and control device operation
ABB RE.216 series digital protection and control device operation
Hardware description
System composition
Modular structure: Composed of electronic equipment racks (such as 216MB66) and input/output units (I/O), the number of modules can be expanded according to demand (such as redundant power supplies and processor units).
Two versions:
Cabinet version: includes a 216MB66 rack, input transformer unit (216GW61), output relay unit (216GA61), etc., suitable for complex protection scenarios.
Compact version: Higher integration, such as 216MB68 rack, suitable for small switchgear, supports single system or redundant system configurations.
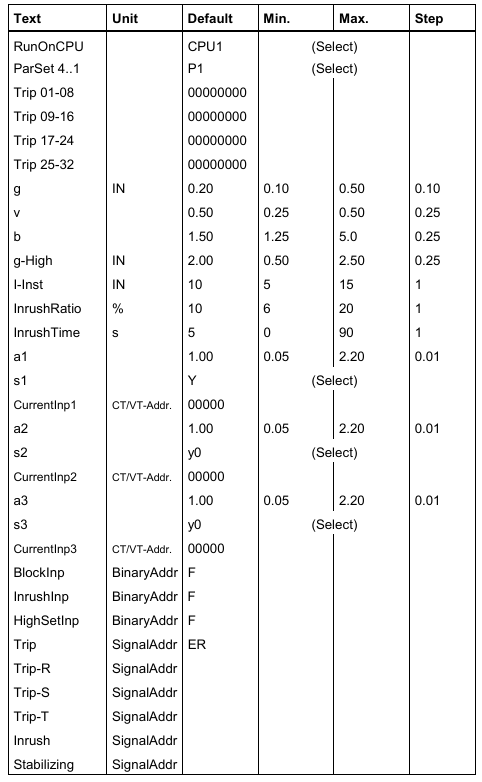
Core modules
Module Type Model Example Function Description
The auxiliary power supply unit 216NG61/62/63 converts the station battery voltage to 24V DC, supports redundant configuration, and is compatible with 48/60V, 110/125V, and 220/250V DC inputs.
The processor unit 216VC624 runs protection logic, stores configuration parameters, supports communication protocols such as SPA BUS and LON BUS, and has a computing power of 425%.
The analog input unit 216EA61 receives CT/VT signals and digitizes them, providing 24 analog input channels.
The binary input/trip unit 216DB61 processes 16 binary inputs and 8 trip outputs, supporting trip logic matrix control.
Injecting unit REX010 provides injection signals for stator/rotor ground fault protection, used in conjunction with REX011 transformer block.
Redundant Design
Support dual auxiliary power supply and dual processor unit configuration to ensure that a single fault does not affect system operation.
Parallel bus B448C enables communication between modules, and redundant power supply lines USA/USB ensure power continuity.
Protection function settings
Function Overview
Protection Library: Contains over 30 protection functions that can be flexibly activated and support multiple configurations (such as multi-stage overcurrent protection).
Computing power: A single processor unit supports up to 48 activation functions, and the complexity and repetition rate of these functions affect the computational load (such as differential protection accounting for 40% and overcurrent protection accounting for 2-5%).
Core Protection Functions
Differential protection
Generator Differential (Diff Gen): Suitable for two winding generators, based on nonlinear current characteristics, high stability against ride through faults, minimum operating current of 0.1IN, slope of 0.25.
Transformer Differential (Diff Transformer): Supports two winding/three winding transformers, including excitation inrush current suppression (second harmonic braking), compensating for differences in transformer ratio and wiring group.
Overcurrent protection
Current DT: Can be set as overcurrent or undercurrent, supports single-phase/three-phase measurement, with a delay of 0.02-60 seconds.
Current Inv: Compliant with BS142 standard, providing normal inverse time, extreme inverse time and other characteristics, suitable for different fault current levels.
Voltage and frequency protection
Stator EFP: 100% stator winding grounding fault is detected by injecting signals, and 95% voltage type protection covers the entire range.
Overexcitation protection: monitors the V/f ratio to prevent overheating of the iron core and supports inverse time characteristics.
special protection
Pole Slip protection: detects generator and system out of step, determines slip direction through impedance trajectory, and can set alarm and trip angle thresholds.
Distance protection: Multi segment impedance protection, suitable for power lines, supports power swing locking, weak feedback logic, and is compatible with multiple grounding systems.
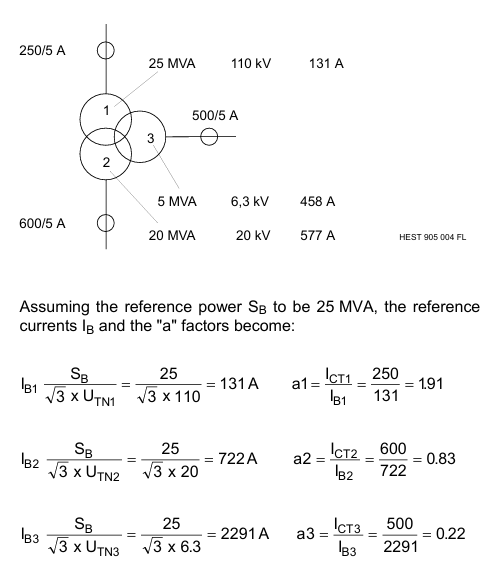
Operation and maintenance
Human Machine Interface (HMI)
Configure parameters through PC or portable terminal, support function activation, fixed value modification, and event record viewing.
The local indicator light (LED) displays the operating status (such as "AL" alarm, "RUN" running).
Self monitoring and testing
Built in self-test function, monitoring power supply, module communication, and I/O channel faults, triggering corresponding alarms.
Support offline testing mode, inject simulated signals to verify protection logic, without affecting the actual circuit.
Installation and Wiring
The cabinet version requires the installation of racks and I/O units according to the drawing layout to ensure reliable grounding.
The compact version can be embedded in a 19 inch rack to save space, and the wiring needs to meet insulation requirements.
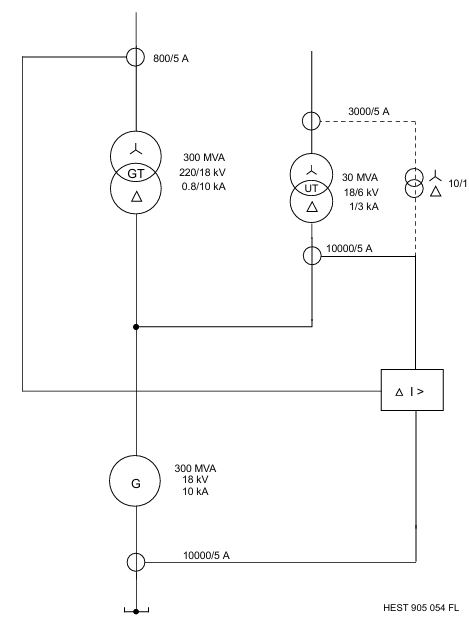
Application scenarios
Generator protection: covering differential, stator/rotor grounding, overcurrent, overexcitation, etc., suitable for different capacity units.
Transformer protection: Differential protection combined with backup overcurrent, suitable for two winding/three winding transformers.
Line protection: distance protection is the main protection, combined with directional overcurrent to achieve rapid selective tripping.
Industrial scenario: Suitable for overload and stall protection of motors such as pumps and fans, supporting integration of multiple communication protocols into automation systems.
- ABB
- General Electric
- EMERSON
- Honeywell
- HIMA
- ALSTOM
- Rolls-Royce
- MOTOROLA
- Rockwell
- Siemens
- Woodward
- YOKOGAWA
- FOXBORO
- KOLLMORGEN
- MOOG
- KB
- YAMAHA
- BENDER
- TEKTRONIX
- Westinghouse
- AMAT
- AB
- XYCOM
- Yaskawa
- B&R
- Schneider
- Kongsberg
- NI
- WATLOW
- ProSoft
- SEW
- ADVANCED
- Reliance
- TRICONEX
- METSO
- MAN
- Advantest
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bently
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- Beijer
- Moxa
- Rexroth
- Johnson
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- Application field
- XP POWER
- CTI
- TRICON
- STOBER
- Thinklogical
- Horner Automation
- Meggitt
- Fanuc
- Baldor
- SHINKAWA
- Other Brands





































































































































