SERVOSTAR ® Usage of CD-LITE servo amplifier
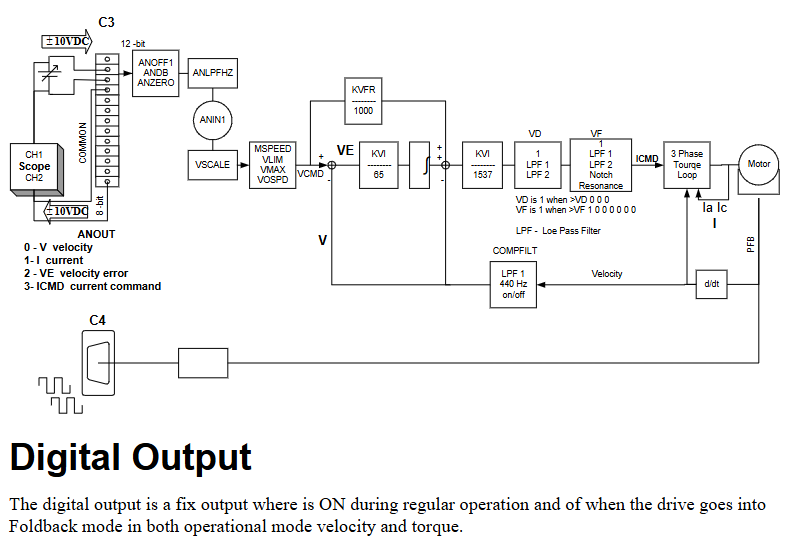
(2) Control loop principle
Current loop: fully digital pole configuration, sampling rate of 16kHz (62.5 μ s), converts current command into three-phase PWM signal, includes adaptive gain compensation for nonlinearity, monitors A/C phase current (IA/IC) and calculates equivalent current (I).
Reversing loop: With a frequency update of 16kHz, it converts single-phase signals into three-phase position modulated sine waves and supports the patented technology of "torque angle lead". It needs to be aligned with the back electromotive force of the motor (feedback alignment is crucial).
Speed loop: Sampling rate 4kHz, using PDFF (pseudo differential feedforward) algorithm, calculating actual speed through feedback, filtering the difference between the actual speed and the instruction speed, and sending it to the commutation loop, suitable for high-precision speed control.
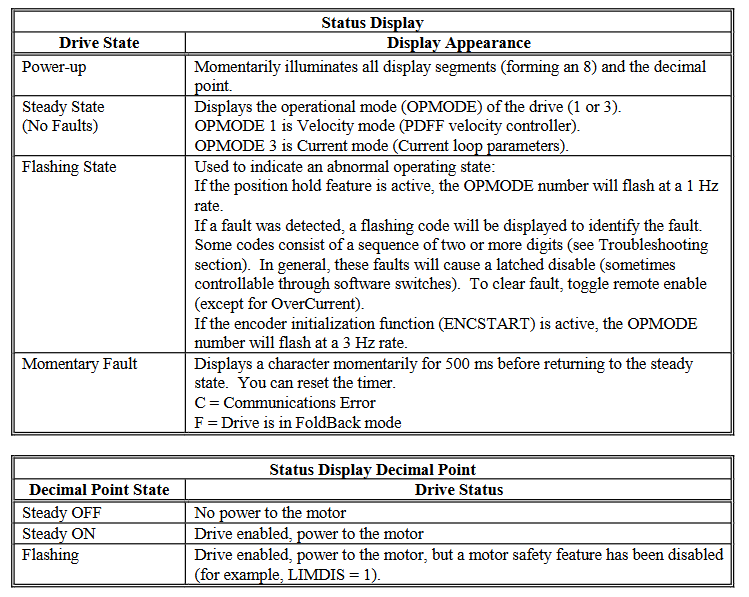
Fault handling and maintenance
(1) Fault classification and troubleshooting
Fatal malfunction (driver disabled, some require power-off reset):
Overheating (t): Overload, fan failure, or power level damage, reset after cooling;
Overvoltage (o): During the regeneration process, the bus voltage is too high. Check the braking resistance or deceleration curve;
Overcurrent (P): Power level surge current, requiring power-off reset, checking for motor short circuit or power level fault;
Feedback fault (r1/r2/r4/r6): Rotary transformer/encoder disconnected or illegal Hall combination, check the feedback cable.
Non fatal fault (disabled drive, can be reset by enabling):
Undervoltage (u): Input voltage too low or power failure, check power supply;
Motor overheating (H): The motor thermostat detects overheating (PTC>12.4k Ω or NTC<0.5k Ω) and needs to cool down before resetting;
Overspeed (J/J1): If the speed exceeds VOSPD (or 1.8 × VLIM), check the speed setting or tuning parameters.
No message fault (only displayed in the status bar):
Limit switch (L1/L2/L3): Hardware limit trigger (CW/CCW switch open circuit), check the limit wiring;
Watchdog (≡): Software malfunction, need to contact the manufacturer;
RAM/EPROM malfunction (I/c): Memory test failed, hardware replacement is required.
(2) Firmware upgrade
Preparation files: The upgrade includes firmware (Lccd_ xxx. emb), Windows tools (Cdlignit. exe), and DOS tools (Ignite. exe).
Steps:
Turn off the power and set DIP switch 8/10 to 1;
Power on and confirm that the status bar displays "E" (entering Ember mode);
Run Cdlignit.exe, select the serial port and baud rate (default 115200), load the firmware file and start downloading;
After successful download, power off and restore DIP switch. After powering on, verify the version through the "VER" command.
Extended Configuration and Appendix
(1) Personality Module
Function: Quickly copy drive parameters, configure one and upload it to the module, then download it to other drives, including All parameters of the SSV file and the CONFIG/SAVE command.
Operation:
Upload: Insert the module into port C1, press and hold the hide switch for 2 seconds, and the status bar will flash with three bars: bottom, middle, and top;
Download: Press the explicit switch, and the status bar will flash up, middle, and down bars;
Fault: Upload error shows "-6", download error shows "-7", module or wiring needs to be checked.
(2) Appendix Key Information
Wiring diagram: Appendix A provides the pin correspondence of motor power supply (such as GOLDLINE B/M/EB/XT series), rotary transformer (LR), and encoder (LE), including line color labeling (such as motor MA corresponding to GOLDLINE B series PinA, brown wire).
Linear motor configuration: Appendix C provides the formula for converting linear parameters to rotational parameters (such as MSPEED=Vmaxl × 60/pole pitch, unit RPM), and the driver parameters need to be calculated based on the motor pole pitch, maximum linear velocity, etc.
Motor Thermostat: Appendix D supports PTC (THERMOTYPE=0) and NTC (THERMOTYPE=1), monitored through pin 13/25 of the C2 interface, triggering an "H" fault when overheated.
- ABB
- General Electric
- EMERSON
- Honeywell
- HIMA
- ALSTOM
- Rolls-Royce
- MOTOROLA
- Rockwell
- Siemens
- Woodward
- YOKOGAWA
- FOXBORO
- KOLLMORGEN
- MOOG
- KB
- YAMAHA
- BENDER
- TEKTRONIX
- Westinghouse
- AMAT
- AB
- XYCOM
- Yaskawa
- B&R
- Schneider
- Kongsberg
- NI
- WATLOW
- ProSoft
- SEW
- ADVANCED
- Reliance
- TRICONEX
- METSO
- MAN
- Advantest
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bently
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- Beijer
- Moxa
- Rexroth
- Johnson
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- Application field
- XP POWER
- CTI
- TRICON
- STOBER
- Thinklogical
- Horner Automation
- Meggitt
- Fanuc
- Baldor
- SHINKAWA
- Other Brands





































































































































