Allen Bradley DeviceNet Communication Module (1203-GK5/1336-GM5)
Features 1203-GK5 module 1336-GM5 board
Physical form independent module embedded board
Installation method: 35 × 7.5mm DIN rail mounting (compatible with 199-DR1 and other models of rails) directly installed inside specific SCANPort products (such as 1336 series drives)
Connection method: 8-pin mini DIN interface+SCANPort cable (up to 10m), 14 pin internal SCANPort connector (no additional cables required)
Most SCANPort products, such as 1305/1336 PLUS/1394, are only compatible with 1336 series drives (compatibility needs to be confirmed for some low-power models)
The packaging accessories include 5-pin/10 pin Phoenix connectors, DIN rail buckles with grounding wristbands, installation screws, nylon support columns, and communication housings
SCAnport: Insert the 8-pin mini DIN interface into the cable and confirm installation with a snap sound. The cable length should be ≤ 10m and kept away from high-power cables to prevent interference.
Power on verification: The SCANPort LED is constantly green, and the DeviceNet LED is flashing green (no connection established). If there is an abnormality, refer to the troubleshooting section.
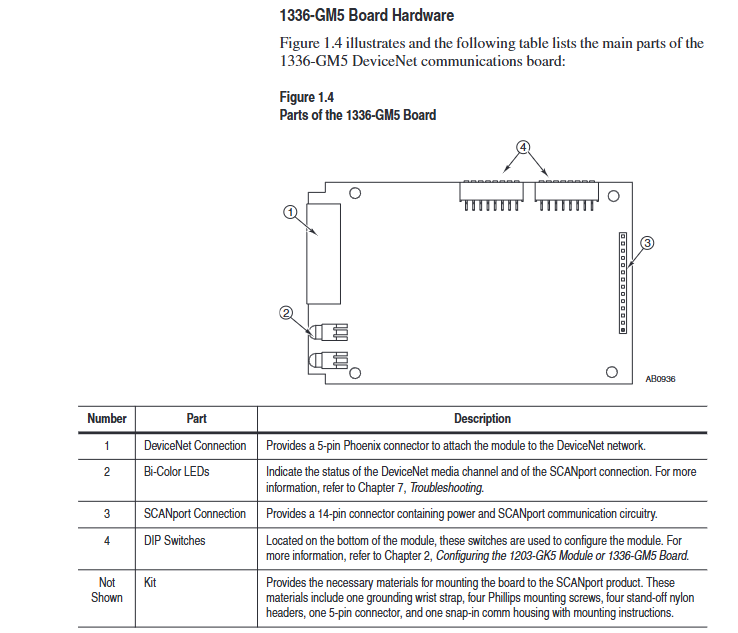
3. Installation steps for 1336-GM5 board
Preparation: Disconnect the power supply of the drive, remove the casing, and install 4 nylon support columns on the drive main control board.
Card fixing: Align the 14 pin pin of the card with the SCANPort interface and insert it, then fix it with 4 screws (to avoid damaging the card due to over tightening).
DeviceNet wiring: Connect 5-pin Phoenix connectors by color, insert them into the card interface, and tighten the screws.
Power on verification: Install the communication enclosure, restore the driver power, keep the SCANPort LED on green, and the DeviceNet LED flashing green.
DeviceNet Network Configuration (DeviceNet Manager)
1. Configuration tools and prerequisites
Software: DeviceNet Manager (Windows application) or RSNetWorx for DeviceNet, requires a 1784-PCD card or 1770-KFD adapter to connect the PC to the DeviceNet network.
Prerequisite: DIP switch configuration has been completed, module/board has been connected to the network, and RSLinx (communication interface software) has been installed on the PC.
2. Core configuration steps
(1) Online mode connection
Start DeviceNet Manager, select "Utilities>Set Up Online Connection", and choose the corresponding driver (such as 1770-KFD).
Configure communication ports (COM1/COM2), baud rate (default 38400bps), PC node address (avoid 63), network data rate (consistent with DIP switch), click "OK" to enter online mode.
(2) Create EDS file (initial configuration)
Select "Who>Network Who" to scan the network, double-click on unrecognized devices (displaying the universal icon), and a prompt "Create EDS file" will pop up. Click "Yes".
Click on 'Load from Device', enter the module/board node address, automatically load the device description, select the device icon (such as 1336. BMP) and SCANPort adapter icon (SCANPORT. BMP).
Enable "Polled Connection", set the I/O size (default 4 bytes, formula: 4+number of enabled Datalinks x 4), click "OK" to save, and rescan the network to confirm that the device icon is displayed normally.
(3) Configure PLC/SLC scanner
Taking 1771-SDN (PLC scanner) as an example:
Double click the scanner icon to enter "1771-SDN Module Configuration", click "Edit Scan List", select "Add Devices From>Who", and drag the target node into the scan list.
Select the node, click "Edit I/O Parameters", and set the polling I/O size (same as EDS configuration) and polling rate (Every Scan/Background).
Click on "Auto Map" to configure the storage address for input/output data (such as PLC N90/N100 files), and click "Map" to complete the mapping.
Select "Save To>SDN", download the configuration to the scanner, prompt "Scanner offline for 5-10 seconds", confirm and complete the configuration.
(4) Save and Verify
Save configuration file (for PLC) Used for SL7 and SLC SL4), Before exiting, confirm that the DeviceNet LED is always green (indicating connection establishment) and the SCANPort LED is always green (indicating normal communication).
Programming and Communication Implementation
1. Ladder diagram programming (RSLogix)
Implementing SCAnport product control through polling I/O requires N-file mapping (input=SCAnport → DeviceNet, output=DeviceNet → SCAnport). Example functions are as follows:
Start stop control: 1336 PLUS driver logic instruction bit definition (bit 0=stop, bit 1=start, bit 2=jog, bit 3=fault clearing), writes the operation signal to the output N-file (such as N10:1) through MOV instruction.
Reference value transmission: The frequency reference value 0-32767 corresponds to 0-maximum frequency, and N7:0 (operator set value) is written to N10:2 (driver reference value) through MOV command.
Status monitoring: Read the drive status bits (bit 1=running, bit 8=fault) from the input N-file (such as N9:1) and output them to the operator display terminal (such as O: 000).
2. Explicit message communication
Support explicit message reading and writing of parameters and fault queries through DeviceNet, following the 8:16 format (8-bit class field+16 bit instance field). The core rules are as follows:
(1) PLC scanner (1771-SDN)
Write the message to the scanner buffer (10 available buffers) using 64 block transfer write (BTW), and retrieve the response through 64 block transfer read (BTR) after completion.
Message format: including transaction ID (1-255), command (1=execute, 2=query status), port (0=channel A), size (in bytes), service code (e.g. 0x0E=get attribute), node address, class/instance/attribute.
(2) SLC scanner (1747-SDN)
Write the message to the M0 file (e.g. M0: 1.224), the scanner processes it and stores the response in the M1 file. After reading, send a "delete command" (command 4) to release the buffer.
- ABB
- General Electric
- EMERSON
- Honeywell
- HIMA
- ALSTOM
- Rolls-Royce
- MOTOROLA
- Rockwell
- Siemens
- Woodward
- YOKOGAWA
- FOXBORO
- KOLLMORGEN
- MOOG
- KB
- YAMAHA
- BENDER
- TEKTRONIX
- Westinghouse
- AMAT
- AB
- XYCOM
- Yaskawa
- B&R
- Schneider
- Kongsberg
- NI
- WATLOW
- ProSoft
- SEW
- ADVANCED
- Reliance
- TRICONEX
- METSO
- MAN
- Advantest
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bently
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- Beijer
- Moxa
- Rexroth
- Johnson
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- Application field
- XP POWER
- CTI
- TRICON
- STOBER
- Thinklogical
- Horner Automation
- Meggitt
- Fanuc
- Baldor
- SHINKAWA
- Other Brands




































































































































