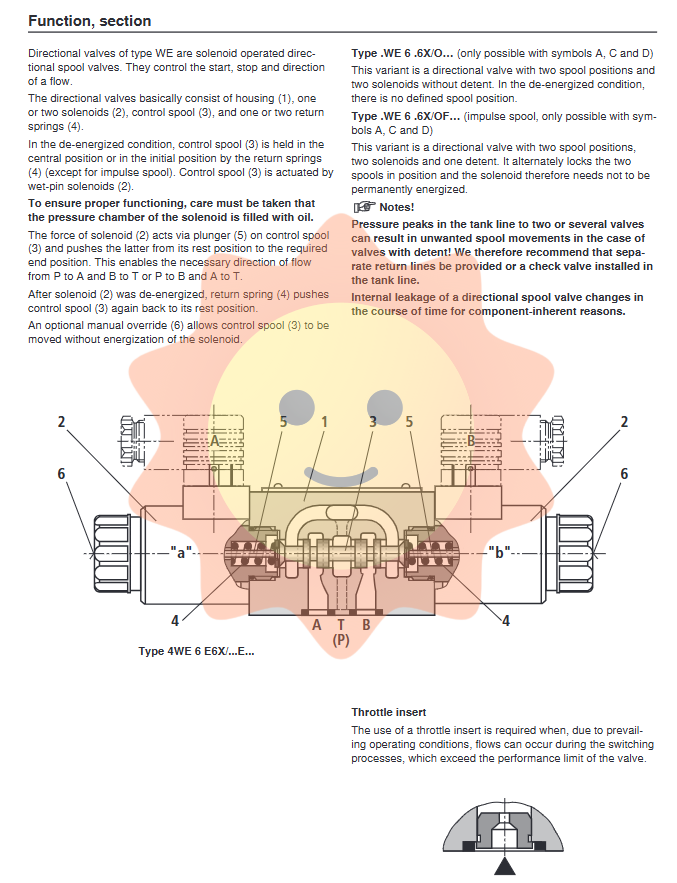
REXROTH WE 6X series directional valve
Internal leakage: Due to the inherent wear characteristics of the components, the internal leakage of the directional valve will change over time.
Key technical data and work limitations
1. Hydraulic and medium requirements
Hydraulic oil: It is recommended to use mineral oil (HL, HLP) that meets the DIN 51524 standard. It is also applicable to rapidly biodegradable hydraulic fluids that comply with VDMA 24568, such as HETG (rapeseed oil), HEPG (polyethylene glycol), and HEES (synthetic esters). When using HETG, HEPG, and HEES, attention should be paid to seal compatibility (usually FKM sealing is required).
Oil cleanliness: The system oil cleanliness must reach ISO 4406 level 20/18/15. Maintaining efficient filtration is key to preventing malfunctions and extending component lifespan.
Viscosity range: The working viscosity range is 2.8 to 500 mm ²/s.
Temperature range: The oil temperature range is usually -30 ° C to+80 ° C (NBR seal) or -15 ° C to+80 ° C (FKM seal).
2. Electrical characteristics and safety
Voltage tolerance: ± 10% of rated voltage.
Power consumption: approximately 30W.
Work schedule: 100% continuous work schedule (ED%).
Switching frequency: up to 15000 times/hour.
Coil surface temperature: The maximum allowable temperature is 120 ° C. The document specifically warns that for AC electromagnets, in the event of a malfunction (such as a stuck valve core), the coil surface temperature may sharply rise to over 180 ° C. Therefore, system design must consider the flash point of the working medium used (which needs to be at least 15K higher than the highest coil surface temperature) and assess potential hazards.
Fuse protection: Unless the ignition hazard can be eliminated in other ways, a circuit breaker with "K" type trip characteristics must be used for protection. The tripping current value should be 8-10 times the rated power consumption current (for 0.6 seconds), and the specific selection should refer to the lower limit current (I1) and upper limit current (I2) tables provided in the document.
3. Performance curve and commutation capability
The document provides a detailed performance curve chart (based on HLP46, oil temperature 40 ° C ± 5 ° C) to determine the passable flow rate of the valve at different pressure differentials (Δ p).
A crucial concept is the 'Switching Performance Limit'. This limit defines the maximum flow rate at which a valve can reliably complete a directional action under given pressure conditions. Attention must be paid to:
The maximum reversing capability values given in the chart are determined for the operating conditions of dual oil flow simultaneously (e.g. P → A and B → T).
If the actual working condition is a single oil flow (such as P → A, while port B is closed), the allowable reversing ability limit may be significantly reduced due to the different distribution of hydraulic forces acting on the valve core. In such applications, it is essential to consult the manufacturer.
The commutation capability test is conducted under the conditions that the electromagnet is at operating temperature, the voltage is 90% of the nominal value (undervoltage 10%), and there is no back pressure (preload) at the T port.
Installation, dimensions, and accessories
1. Mechanical installation
Installation location: Any.
Valve installation surface: It is necessary to ensure the specified surface roughness and flatness to ensure sealing.
Installation screws: The document strictly specifies the screw model, specifications, and tightening torque used to secure the valve to the base plate. According to different clamping lengths (42mm or 22mm), metric (ISO 4762-M5) and American (UNC 10-24 UNC) screw options and corresponding Bosch Rexroth material numbers are provided. The specified torque must be used to tighten to prevent leakage or damage to the valve body.
Oil port sealing: Use the same sealing ring for ports A, B, P, and T. The function definition of the oil port is clear, and it is strictly prohibited to exchange or block it at will.
2. Electrical connection and protection
Protection level: When using "K4" or "K7xL" series plugs and installing the docking plug, it can reach IP65; Using a "C4" plug can achieve IP66 rating; The use of the "K40" plug can achieve IP69K.
Terminal allocation (when connected centrally):
Single electromagnet: always connect terminals 1 and 2.
Double electromagnet: electromagnet "a" is connected to terminals 1 and 2, and electromagnet "b" is connected to terminals 3 and 4.
The protective grounding wire (PE) must always be correctly connected to the PE terminal.
3. Recommended attachments
Base plate: Choose according to the thread specifications of the oil port (G1/4, G3/8, G1/2 or SAE-6, -8, -10) and whether it has a locating pin hole.
Docking plug: The document provides material numbers for multiple plug options, including models without circuits, with indicator lights, with rectifiers, or with Zener diode suppression circuits.
Cable connector: such as Pg 16 or 1/2 "NPT cable gland.
Special tool: To avoid damage when operating the manual operator, it is recommended to use the special tool (material number R900024943).
- ABB
- General Electric
- EMERSON
- Honeywell
- HIMA
- ALSTOM
- Rolls-Royce
- MOTOROLA
- Rockwell
- Siemens
- Woodward
- YOKOGAWA
- FOXBORO
- KOLLMORGEN
- MOOG
- KB
- YAMAHA
- BENDER
- TEKTRONIX
- Westinghouse
- AMAT
- AB
- XYCOM
- Yaskawa
- B&R
- Schneider
- Kongsberg
- NI
- WATLOW
- ProSoft
- SEW
- ADVANCED
- Reliance
- TRICONEX
- METSO
- MAN
- Advantest
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bently
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- Beijer
- Moxa
- Rexroth
- Johnson
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- Application field
- XP POWER
- CTI
- TRICON
- STOBER
- Thinklogical
- Horner Automation
- Meggitt
- Fanuc
- Baldor
- SHINKAWA




































































































































