AMS 2140 Machinery Health ™ How to operate Analyzer?
AMS 2140 Machinery Health ™ Analyzer
Overview
This document is AMS 2140 Machinery Health ™ The user guide for Analyzer covers the basic introduction, operation methods, functional applications, data processing, and other aspects of this portable vibration analyzer. It is suitable for vibration analysts, reliability data collection technicians, and reliability engineers who monitor rotating machinery in process factory environments.
Introduction to analyzer
Basic equipment: including firmware media, Micro USB cable for connecting to AMS Machinery Manager, power supply for charging battery pack, screen protector, shoulder strap, etc.
Appearance and buttons
Front view: Includes Home key, Reset key, Function key, Enter key, Keyboard backlit key, LCD backlit key, Help key, Power key, Battery LED, Status LED, Arrow key, ALT key, Back key, etc. Each key has its specific function.
Top view: There are power connectors, Ethernet ports, Micro USB ports, wireless LEDs, Bluetooth LEDs (not available for newer models), etc.
First power on: The battery pack needs to be activated first, connect the provided power cord to the power outlet and analyzer, then press and hold the power button to turn on the device. After turning on, you can set the time and date.
battery pack
For rechargeable lithium-ion battery packs, they can usually be used continuously for more than 8 hours on a single charge, and a warning will be issued when the battery level is low.
The battery pack is in storage mode when it leaves the factory and needs to be activated according to the steps.
There are many usage and maintenance precautions, such as using only Emerson battery packs and chargers, environmental temperature limitations for charging and operation, temperature and power requirements during storage, etc.
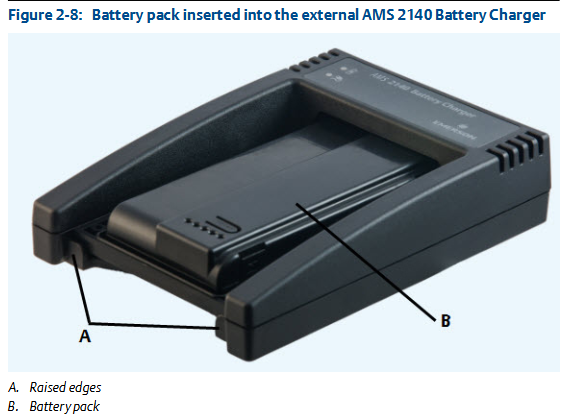
External battery charger: It can charge the battery pack separately, with corresponding charging steps and precautions, such as ensuring good ventilation and temperature restrictions in the charging environment.
Power on and off: Press and hold the power button to operate, and you can also perform a hard restart and enter standby mode.
Main screen: Contains information such as time and date, Bluetooth connection status, battery level, supported channels, etc. There are two alternating screens displaying different programs and settings options.
Backlight: LCD backlight and keyboard backlight can be set, with different adjustment methods and energy-saving settings.
Touch screen: can be locked/unlocked, calibrated, supports gesture operation and on-screen keyboard input.
Menu navigation: Navigating through touch screen and function keys, with ALT screen for entering text and viewing help information.
Settings: Key buzzer, standby timer, backlight timer, print mode, low battery warning level, etc. can be set.
Memory card: It can be inserted into an SD memory card to store routing or job files, with steps and precautions for insertion and removal.
Bluetooth: If supported by the analyzer, it can be used to connect related devices and requires pairing, connection, and other operations, with different status icons.
Utility programs: including file utilities (for copying, deleting, and moving files), memory utilities (for viewing memory information, etc.), and battery utilities (for viewing battery status, etc.).
Cleaning the analyzer: Suitable cleaning products should be used in non hazardous areas to avoid the use of corrosive or abrasive substances.
Four channel input adapter: expandable analyzer function, with connection and usage methods.
Multiple inputs: The analyzer supports collecting data from multiple channels simultaneously, with connection options for different input quantities.
Dangerous place use: Different labeled analyzers have different applicable places, and there are specific precautions when using them.

Transfer files with AMS 2140
AMS Machinery Manager data transfer: can manage files in the analyzer, achieve routing and job transfer, storage, etc.
Independent data transfer application: suitable for computers without AMS Machinery Manager installed, capable of transferring files but with certain limitations.
Communication settings: including compatible AMS Machinery Manager versions, changing analyzer IDs, setting connection types (USB, Ethernet, wireless), etc.
Routing and Jobs: Routing and jobs can be loaded from AMS Machinery Manager, or transferred from the analyzer to AMS Machinery Manager or computer folders.
Analyzer firmware and programs: You can view version numbers, upgrade firmware, add or upgrade programs.
Screenshot: Screenshot can be taken and saved.
Start screen: The main screen image can be changed.
Printing: You can create a cover page and print charts to AMS Machinery Manager or a storage card.

Routing
Routing Overview: Routing is a list of devices and measurement points selected from a certain area of the AMS Machinery Manager database, which can be used to collect data and transmit it back to the database.
Manage routes: including viewing loaded routes, activating routes, deleting route data or routes, etc.
Set data collection and display parameters, such as setting plot type, enabling/disabling automatic advancement to the next measurement point, setting high-frequency detection average value, etc.
Tachometer: It can set tachometer parameters, save and call settings, etc.
Multiple inputs and measurements: Data can be quickly collected using multi-channel functionality and three-axis accelerometers.
Collecting routing data: Collect data step by step, including monitoring real-time vibration data, re measuring, skipping devices or points, etc.
Annotation: Annotations can be created, deleted, or added to routing measurement points.
Draw routing data: The collected data can be drawn and modified.
Run analysis to collect routing measurement point data: If abnormal data is found, the analysis program can be opened to further collect data.
View routing measurement point settings and history: You can view stored data, group status, trend history, etc.
Routing report: The routing report can be printed to AMS Machinery Manager or storage card.
Chart
View full screen chart: The chart can be displayed in full screen.
Select activity chart: Use the button to select the activity chart and operate it.
Switch chart type: Switch between different chart types based on the collected data type.
Add/Remove cursor: You can add and move a cursor to analyze data.
Change cursor type: There are multiple cursor types to choose from, suitable for different analysis needs.
Change the ratio of the x and y axes: You can set parameters such as the axis scale.
Expand or compress X-axis: You can zoom in or out of the X-axis to view data.
View the highest frequency peak on the spectrum: List the highest peak and view it.
Set RPM: Set RPM for routing points.
View the failure frequency on the chart: You can view the frequency related to equipment failures.

Analysis and Advanced Analysis
Analysis Overview: Can be used to collect data for troubleshooting, with different analysis experts and manual analysis modes.
Manage assignments: including creating, opening, editing, deleting assignments, etc.
Set display parameters, such as setting overlap rate and selecting the data type to be displayed when collecting spectra.
Multi input measurement: Multiple inputs can be used simultaneously to collect data, with corresponding setting methods.
Sensors and inputs: The number of inputs and sensor parameters can be set.
Tachometer: The setting method is similar to that in routing.
Common data collection parameters include Fmax and Fmin, resolution lines, window, average, PeakVue, demodulation, trigger, etc.
Collect data using analysis experts: Different analysis experts are suitable for different troubleshooting tests, with corresponding usage methods and recommended uses.
Collecting data through manual analysis: Different analysis modes can be set, such as waveform, spectrum, overall, etc., and relevant parameters can be set.
Monitor real-time vibration data in analysis: Monitor through Bluetooth devices, but do not store audio.
Re measure in analysis: data can be collected again.
Storing data to routing or analysis jobs: Data needs to be manually saved.
View previously collected data in the analysis: View temporarily stored data.
Print analysis charts to AMS Machinery Manager or storage card: Follow the corresponding steps.
Reset analysis default values: Reset the settings of the analysis program.
Advanced laser alignment
Overview of Basic and Advanced Laser Alignment Applications: Can be used for horizontal and vertical machine alignment and straightness measurement, with different modes and application scenarios.
Setting up lasers and sensors: including installing brackets, installing lasers and sensors, turning on equipment, adjusting laser beams, pairing sensors, etc.
Manage homework: can create, activate, copy, edit, delete homework, transfer homework, etc.
Set homework parameters, such as homework mode, alignment method, operation mode, etc.
Horizontal alignment: including steps such as inputting machine dimensions, obtaining alignment data, checking soft feet, viewing and adjusting machines.
Vertical alignment: Similar to horizontal alignment, there are corresponding steps and parameter settings.
Straightness measurement: including inputting contour dimensions, obtaining straightness data, viewing surface contours, etc.
Chart: You can view tolerance charts, etc., to analyze the alignment situation.
Transfer alignment tasks: can transfer tasks and tolerance tables, print summary reports.

Advanced Transient
Advanced Transient Overview: It can collect large and complete time waveforms for analyzing the behavior of equipment under changing conditions.
Manage assignments: including creating, activating, editing, deleting assignments, etc.
Sensors and inputs: Set the number of inputs and sensor parameters.
Tachometer: The setting method is similar to other modules.
Select a part of the complete transient waveform: set the number of displayed data points, lines, etc.
Set the number and type of charts to display in advanced transients: Select the type of chart to display.
Set data collection parameters such as Fmax, sampling rate, sample size, etc.
Collect transient data: Follow the steps to collect data, which can be remeasured or deleted.
Plotting data in advanced transients: displaying and analyzing collected data, printable charts.
ODS/Modal
ODS/Modal Overview: Cross channel ODS and modal data can be collected to determine the modal characteristics of elastic structures.
Manage assignments: including creating, activating, editing, deleting assignments, etc.
Sensors and inputs: Set the number of inputs and sensor parameters.
Tachometer: The setting method is similar to other modules.
Set Chart: Set the type and format of the displayed chart.
Set up homework: including setting measurement parameters, homework modes, collection parameters, etc.
Collect ODS/modal data: Collect data step by step, and perform related operations such as changing polarity, deleting data, etc.
Display data of ODS/modal measurement points: View collected data.
Print ODS/modal charts to AMS Machinery Manager or storage card: Follow the corresponding steps.
- ABB
- General Electric
- EMERSON
- Honeywell
- HIMA
- ALSTOM
- Rolls-Royce
- MOTOROLA
- Rockwell
- Siemens
- Woodward
- YOKOGAWA
- FOXBORO
- KOLLMORGEN
- MOOG
- KB
- YAMAHA
- BENDER
- TEKTRONIX
- Westinghouse
- AMAT
- AB
- XYCOM
- Yaskawa
- B&R
- Schneider
- Kongsberg
- NI
- WATLOW
- ProSoft
- SEW
- ADVANCED
- Reliance
- TRICONEX
- METSO
- MAN
- Advantest
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bently
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- Beijer
- Moxa
- Rexroth
- Johnson
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- Application field
- XP POWER
- CTI
- TRICON
- STOBER
- Thinklogical
- Horner Automation
- Meggitt
- Fanuc
- Baldor
- SHINKAWA
- Other Brands




































































































































