YOKOGAWA AQ7290 Series Optical Time Domain Reflectometer OTDR
YOKOGAWA AQ7290 Series Optical Time Domain Reflectometer OTDR
Product basic information
1. Product positioning and core applications
The AQ7290 series OTDR is a professional equipment used for fiber link detection. Its core function is to analyze the transmission loss, joint loss, fault location (such as breakage, bending) and other parameters of the fiber by emitting optical pulses and receiving reflected light. It is mainly used for:
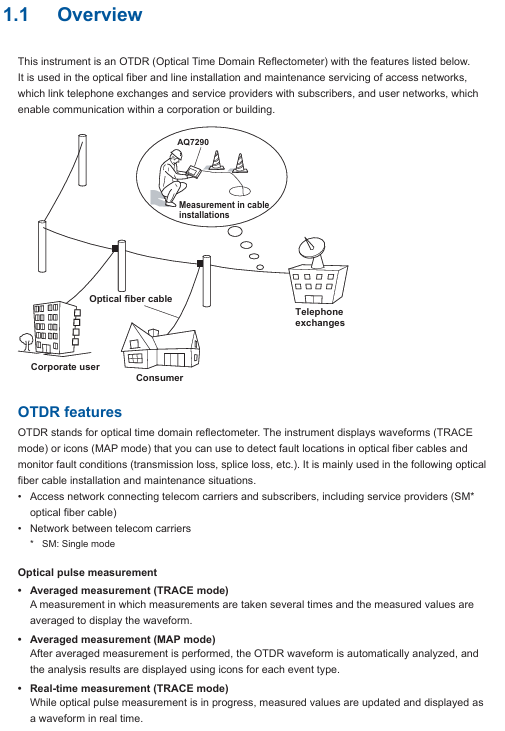
Access network: Fiber optic installation and maintenance between telecommunications operators and users (mainly single-mode fiber optic).
Enterprise network: Fiber optic detection of internal communication networks within enterprises or buildings.
Long distance network: troubleshooting and performance monitoring of backbone fiber optic links between telecommunications operators.
2. Manual system and version information
Supporting documents: including Chinese specific documents (IM 739883-92Z1), European language safety manual (IM 00C01C01-01Z1), global contact list (PIM 113-01Z2), and communication interface manual (IM AQ7290-17EN) stored in device memory, which needs to be downloaded to PC for viewing.
Language code: In the manual number, "EN" represents English, "Z1" represents Chinese and other languages. Users can access it through the Yokogawa Customer Portal( https://myportal.yokogawa.com/ )Obtain the corresponding version.
Version iteration: The current version is the first edition in April 2025, and the content may change without prior notice due to product feature upgrades. The latest version should refer to the official website.
Trademark Statement: Mentioning brand trademarks such as Microsoft, Apple, Google, etc., omitted in the manual ® The TM symbol and other brand names belong to their respective holders.
Core functions and operating procedures
1. Basic measurement function (OTDR core)
(1) Optical pulse measurement mode
Support two core measurement modes to meet different scenario requirements:
Measurement mode, functional characteristics, applicable scenarios
Average measurement (TRACE/MAP mode): Take the average of multiple measurements to reduce noise interference; Automatically analyze events after measurement, and switch between "TRACE" or "MAP" to accurately detect weak events (such as low loss connectors) and generate formal detection reports
Real time measurement (only available in TRACE mode) updates waveforms in real-time, supports dynamic adjustment of parameters such as wavelength and distance range, real-time monitoring during fiber installation, and quick troubleshooting of obvious faults
(2) Key measurement parameter settings
Wavelength: Different models support 1310nm, 1550nm, 1625nm, 1650nm, etc. For example, AQ7293F supports 1310/1550/1650nm, and AQ7293H supports 1310/1550/1625nm.
Distance range: Supports AUTO (automatic matching of fiber length) and manual setting of 100m-512km. It is necessary to select a range greater than the actual length of the fiber to ensure complete measurement.
Pulse width: Short pulses (3ns-30ns) are suitable for close range high-resolution measurement, while long pulses (1 μ s-20 μ s) are suitable for long-distance measurement, and can be manually set or automatically matched with a distance range.
Average frequency/duration: The average frequency supports 2 ¹⁰ -2 ² ⁰ times, with a duration of 5-30 minutes. The larger the frequency/duration, the higher the measurement accuracy but the longer the time consumption.
(3) Event analysis function
Automatically detect "events" (such as joints, fractures, bends) in fiber optic links and calculate key parameters:
Event types: including joint loss, reflection loss, bending loss, splitter loss, fiber optic endpoint (Fresnel reflection), etc., visually displayed in MAP mode through icons (such as "⊡" for joints and "■" for endpoints).
Analysis parameters: The joint loss threshold (0.01-9.99dB), reflection loss threshold (20-70dB), and fiber endpoint threshold (3-65dB) can be set. Events exceeding the threshold will be marked as "fault".
Manual adjustment: supports inserting/deleting events, editing event marker positions, and solving noise misjudgment or weak event missed detection problems.
2. Utility function
The device supports parallel use of multiple tools and can synchronously perform other detections during OTDR measurement, improving work efficiency:
Key parameters/options for the core purpose of tool functionality
Light Source fiber loss measurement, fiber identification output wavelength consistent with OTDR (such as 1310/1550nm), supports continuous light (CW) or modulated light (270Hz/1kHz/2kHz)
Visible light source (/VLS option) visually locates fiber breakpoints, checks multi-core fiber core sequence, fixed wavelength 650nm, supports CW or 2Hz modulation light
Optical power meter (/SPM//HPM option) measures optical signal power, fiber loss/SPM (standard): 800-1700nm,/HPM (high power): maximum+27dBm, supports logging (CSV format)
Power checker (/PC option) detects the presence of communication light in the fiber (to avoid interference) and measures wavelengths of 1310/1490/1550/1625/1650nm
Fiber end face detection probe (/FST option) can detect stains and scratches on the fiber end face. It supports USB or wireless connection and can determine the size of the fiber core/cladding/contact area (in accordance with IEC 61300-3-35 standard)
3. Advanced Application Features
Provide specialized solutions for complex scenarios, covering requirements such as multi-core fiber optics and long-term monitoring
(1) OTDR Smart Mapper
Function: Take multiple average measurements of the same wavelength using different pulse widths, automatically concatenate waveforms (narrow pulses for resolution at close range and wide pulses for coverage at far range), and generate link event maps.
Advantages: No need to manually switch pulse width, more accurate event localization for complex links (including spectrometers), and beginners can quickly understand the link structure.
(2) Multi Fiber Project
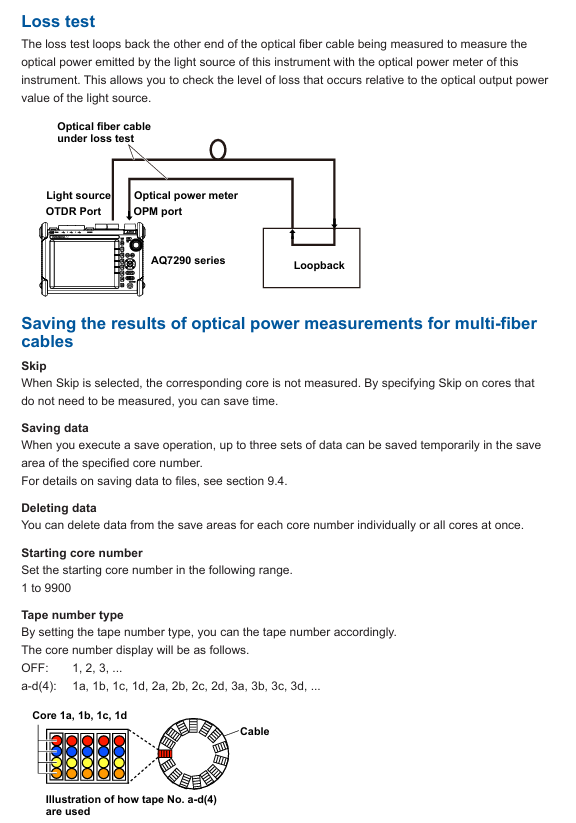
Project management: Package the measurement conditions (wavelength, distance range), number of cores (1-2000 cores), and core sequence (such as numbered 1a-1d) of multi-core optical fibers into a "project", supporting batch measurement and unified data management.
Batch operation: The screen displays the chip numbers in a table, and the measurement status is marked with colors (gray=stored data, green=qualified, red=unqualified) to quickly skip chip numbers that do not need to be measured and avoid omissions.
(3) Fiber optic monitoring (Schedule Measurement,/MNT option)
Timed measurement: Automatically perform OTDR measurement at set intervals (1-60min) and durations (1-120 days) to monitor changes in fiber loss (such as aging and external damage).
Data storage: Measurement data is automatically classified and stored by timestamp (SOR format waveform, CSV format log), supporting post analysis of fault occurrence time.
(4) Auto Loss Test/Multi Fiber Loss Test
Single core testing: Two devices work together, one as a light source and the other as an optical power meter, automatically switching wavelengths (1310/1550nm) to measure fiber loss.
Multi core testing: Synchronize multi-core fiber loss testing through the "master-slave mode", where the master device sends project configurations and the slave device performs measurements. The results are automatically transmitted back to the master device, making it suitable for batch acceptance of multi-core links.
(5) Advanced Analysis
Multi waveform comparison: Load up to 4 waveforms, support vertical offset adjustment, visually compare the loss differences of different time periods/links.
Bidirectional trajectory analysis: Combine waveforms measured from both ends of the fiber to accurately calculate the joint loss of fibers with different backscattering coefficients.
Differential trajectory analysis: Display the difference between two waveforms to quickly locate newly added loss points (such as fiber damage caused by later construction).

Data Management and Report Generation
1. Data storage and loading
Supporting media: Internal memory (approximately 1GB), USB storage device (USB 1.0/1.1/2.0), microSD card (SDC/SDHC/SDXC), up to 2 USB devices can be connected simultaneously.
File format:
SOR: Complies with Telcordia SR-4731 standard, stores waveform data and measurement conditions, and can be used for post analysis or imported into PC simulation software.
SET: Only stores measurement/analysis conditions for rapid reproduction of the same testing environment.
PDF: Generate reports for waveforms, event lists, and measurement conditions, supporting custom inclusion items such as company name and fiber optic identification.
CSV: Stores event data or optical power logs for easy secondary analysis using tools such as Excel.
BMP/JPG: Screenshots used to record on-site inspection results.
Auto Save: After the average measurement is completed, the data can be automatically saved, supporting storage by date or custom path classification to avoid data loss.
2. Report generation
Real time report: After the measurement is completed, the current waveform and event analysis results can be generated into PDF reports, including link maps, event lists, measurement conditions, and other information.
Batch report: Select multiple SOR files to automatically generate multi page PDF reports, support sorting by file name/date/ID, suitable for batch project acceptance.
Custom settings: tags such as company name, fiber ID, and tester can be added, and the report format supports comparing 1 waveform per page or 2 waveforms per page.
System settings and remote control
1. Basic system settings
Display settings: Supports screen themes (dark/light), brightness adjustment (4 levels, including OFF), wavelength/distance units (km/m), and decimal places (1-3).
Power management: In battery mode, automatic sleep mode can be set (1/5/10/30min no operation), LCD backlight can be turned off to extend battery life; The USB-AC adapter can maintain high brightness when powered.
Language and Shortcut Keys: Supports multiple languages (based on device suffix code), and can assign commonly used functions (such as saving and report generation) to the UTIL key for one click calling.
2. Network and Remote Control
Wired network (/LAN option): Supports 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX Ethernet, realizes PC remote control through TCP/IP protocol, and can transmit measurement data to the server.
Wireless network: Connect to a wireless LAN adapter (recommended model required), supporting access point mode (device as hotspot) or site mode (connected to existing WiFi), suitable for remote operation in Ethernet free scenarios.
LTE Dongle: Inserting an LTE adapter can connect remote devices through mobile networks, suitable for outdoor environments without WiFi/Ethernet.
Web server: PC browser input device IP address, can be accessed through "control mode" (remote device operation) or "view mode" (only view screen and download files), without the need to install dedicated software.
Safety and Maintenance
1. Safety regulations
Laser safety: When the equipment emits high-power laser (OTDR port, VLS port), it is forbidden to directly look at the port or disconnect the fiber during operation. If the fiber is not connected, the port cover should be covered to avoid eye damage.
Wiring safety: Before measurement, confirm that the fiber optic connection is correct (voltage line connected to voltage terminal, current line connected to current terminal). Do not touch the terminals during high voltage/high current output, and regularly check whether the terminals are overheated or loose.
Fault handling: If there is smoke, odor, or abnormal noise, immediately cut off the power and disconnect the load; When the output is automatically turned off (such as overload protection), troubleshoot and then turn it back on.
2. Maintenance and repair
Filter cleaning: Check and clean the rear air inlet filter every 3 months. If it is dirty, clean it with neutral detergent and let it dry naturally. Blockage can cause the equipment to overheat; The filter screen is damaged and needs to be replaced by contacting a Yokogawa dealer.
Self check function: Automatically perform self check (check fan, voltage/current range, internal circuit) when turned on, or manually trigger. If the self check fails, an error code will be displayed (such as E.901 indicating fan fault).
Calibration and replacement: It is recommended to calibrate once a year to ensure accuracy. Cooling fans (3 years), filters (1 year), and LCDs (approximately 40000 hours) should be replaced according to the recommended cycle, and maintenance should be carried out by Yokogawa certified personnel.
Storage conditions: When not in use for a long time, it should be stored in an environment with a temperature of -20~60 ℃ and a humidity of 10%~90% (no condensation), avoiding direct sunlight, vibration, or corrosive gases.
- ABB
- General Electric
- EMERSON
- Honeywell
- HIMA
- ALSTOM
- Rolls-Royce
- MOTOROLA
- Rockwell
- Siemens
- Woodward
- YOKOGAWA
- FOXBORO
- KOLLMORGEN
- MOOG
- KB
- YAMAHA
- BENDER
- TEKTRONIX
- Westinghouse
- AMAT
- AB
- XYCOM
- Yaskawa
- B&R
- Schneider
- Kongsberg
- NI
- WATLOW
- ProSoft
- SEW
- ADVANCED
- Reliance
- TRICONEX
- METSO
- MAN
- Advantest
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bently
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- Beijer
- Moxa
- Rexroth
- Johnson
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- Application field
- XP POWER
- CTI
- TRICON
- STOBER
- Thinklogical
- Horner Automation
- Meggitt
- Fanuc
- Baldor
- SHINKAWA
- Other Brands




































































































































