Yokogawa ROTAMASS TI Coriolis Mass Flow Meter
Yokogawa ROTAMASS TI Coriolis Mass Flow Meter
Basic Information
Focusing on the application scenarios of SIS equipment, clarifying the responsibilities of users in installation, operation, maintenance and other aspects, covering key contents such as verification testing, maintenance and replacement, reliability data, etc., to ensure that the equipment maintains the design safety level.
SIS application core requirements
(1) Safety functions and signal transmission
Function positioning: Supports HART communication and can be used as a mass flow rate, fluid density, and fluid temperature measurement component in SIS, equipped with 1-2 4-20mA analog outputs and other I/O interfaces.
Signal connection: The signal needs to be transmitted to the logic solver of SIS (such as safety PLC/DCS) through 4-20mA output; The fault alarm mechanism is "simulated current out of range", which needs to be connected to enable the automatic diagnostic function of the device.
(2) Key technical parameters
Specific requirements for parameter categories
The safety accuracy is set at 2%, which means that internal component failures that result in measurement errors ≥ 2% will be included in the equipment failure rate
Diagnostic response time amplitude error: Report within 3 minutes after the fault occurs; Other errors (such as frequency errors, signal failures): reported within 7 seconds
Generate a valid signal within 20 seconds after powering on the startup time
The expected service life is 10 years, and only reliability data within this period is valid; After more than 10 years, the equipment failure rate may increase, and the safety integrity level (SIL) calculation results based on the original data may become invalid

(3) Set up and validate testing
Device Settings
During installation, it is necessary to configure the engineering unit parameters through a field communicator or display, and verify the correctness of the parameters (which can be read from the local display or checked for actual calibration of the equipment).
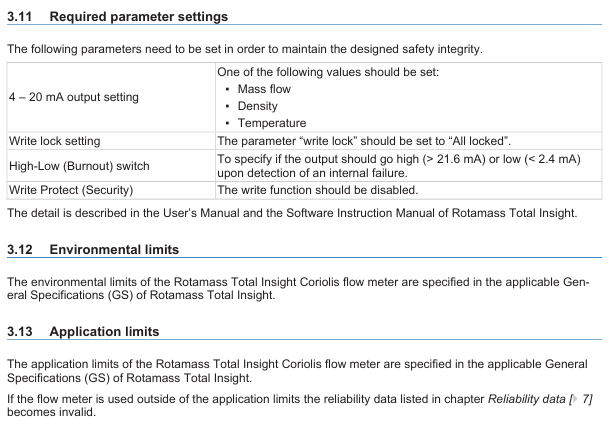
Key parameters need to be set according to the following requirements to maintain safety integrity:
|Parameter Category | Setting Requirements|
|4-20mA output | Select one of "Mass Flow", "Density", or "Temperature"|
|Write lock | Set to "All locked"|
|High Low (Burnout) switch | Specify the output current state in case of internal fault (High:>21.6mA; Low:<2.4mA)|
|Write Protect | Disable write function|
Proof Testing
Purpose: To detect faults that have not been detected by the equipment's self diagnosis (especially undetected faults that may cause safety instrument function (SIF) failure), the testing frequency should be determined based on the reliability calculation results of SIF, and the actual execution frequency should not be lower than the calculation requirements.
Test steps:
|Step | Operation Content|
|1 | Bypass safety function, take measures to avoid accidental tripping|
|2 | Verify the rationality of the output current (in compliance with the specified accuracy) when the flow tube is full and in a zero flow state|
|3 | Verify the rationality of the output current when the flow tube is filled with two different flow rates (which can be independently estimated with an accuracy of about 10%)|
|4 | Read the temperature measurement value of the process fluid through digital communication and compare it with the independent measurement value for verification|
|5 | Read diagnostic information through digital communication and take corresponding measures|
|6 | Send digital commands to the transmitter to enter the high and low alarm level output state, verify whether the analog current reaches the corresponding value (test static current, low loop voltage, high loop impedance related faults)|
|7 | Restart the transmitter power supply and clear the RAM soft error|
|8 | Release bypass and restore normal operation|
Detection effect: Both non intrinsic safety (non IS) and intrinsic safety (IS) 4-20mA outputs can detect 93.3% of potential hazard undetected (DU) faults.
Required tools: device display (or digital communication tools such as HART field communicator, PRM, FieldMate, etc.), output current verification instrument, reference temperature measurement tool close to the tested device.
Personnel requirements: Testers must receive SIS operation training, master bypass processes, equipment maintenance, and company change management processes.
(4) Repair, replacement, and firmware update
Repair and replacement: If online repair is required, bypass the equipment first and establish a compliant bypass process; Maintenance/replacement personnel need to have sufficient skills. If maintenance is required, please contact the Yokogawa sales office.
Firmware update: Only executed by the factory, users do not need to operate on their own, and after the update, they need to fulfill relevant responsibilities according to the replacement process.
(5) Reliability, Environment, and Application Limitations
Reliability data
Detailed Failure Mode, Effects, and Diagnostic Analysis (FMEDA) report (No. YEC 20-02-160 R002 V3R1) can be obtained from Yokogawa, including all failure rates and failure modes.
The device is suitable for "Low Demand Mode" (long average interval between hazardous conditions).
SIL certification: The highest certification under a single (1oo1) configuration is SIL2 (calculated based on the average failure probability (PFDavg) of the entire SIF); The highest certification for device development process is SIL3. When configuring redundancy (hardware fault tolerance level 1), the PFDavg calculation results of the entire SIF can be used for SIL3 scenarios. It is recommended to use a 2% common factor coefficient (β - factor) for redundant configuration.
Environmental and application limitations: The environmental and application limitations of the device must comply with the General Specification (GS) of ROTAMASS Total Insight; If the application limit is exceeded, the reliability data will be invalidated.
Definition and Abbreviations
Core definition: Clearly define terms such as "Safety", "Functional safety", "Basic safety", "Verification", "Validation", "Safety assessment", etc., in accordance with the relevant interpretations of IEC 61508-4 standard.
Key abbreviations:
|Abbreviation | Full name and description|
|DU | Dangerous Undetected|
|FMEDA | Failure Mode, Effects and Diagnostic Analysis|
|IS | Intrinsically safe explosion proof|
|PFDavg | Average Probability of Failure on Demand|
|PLC/DCS | Programmable Logic Controller/Distributed Control System|
|PRM | Plant Resource Manager|
|SIF | Safety Instrumented Function|
|SIL | Safety Integrity Level|
|SIS | Safety Instrumented System|

- ABB
- General Electric
- EMERSON
- Honeywell
- HIMA
- ALSTOM
- Rolls-Royce
- MOTOROLA
- Rockwell
- Siemens
- Woodward
- YOKOGAWA
- FOXBORO
- KOLLMORGEN
- MOOG
- KB
- YAMAHA
- BENDER
- TEKTRONIX
- Westinghouse
- AMAT
- AB
- XYCOM
- Yaskawa
- B&R
- Schneider
- Kongsberg
- NI
- WATLOW
- ProSoft
- SEW
- ADVANCED
- Reliance
- TRICONEX
- METSO
- MAN
- Advantest
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bently
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- Beijer
- Moxa
- Rexroth
- Johnson
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- Application field
- XP POWER
- CTI
- TRICON
- STOBER
- Thinklogical
- Horner Automation
- Meggitt
- Fanuc
- Baldor
- SHINKAWA
- Other Brands




































































































































