SEW MOVITRAC ® B frequency converter
SEW MOVITRAC ® B frequency converter
Product Overview and Safety Foundation
MOVITRAC ® The B frequency converter provides various power levels from 0.25kW to 75kW, covering multiple specifications from 0XS to 5, and can adapt to AC 230V single-phase/three-phase or AC 400/500V three-phase power inputs, meeting diverse market demands. Its standard configuration complies with multiple international certifications such as CE, UL, CSA, etc., especially in terms of electromagnetic compatibility (EMC). With the correct installation method, it can achieve the C1 or C2 interference radiation limit level in EN 61800-3 standard.
Safety is the primary prerequisite for all industrial operations. The design and use of this frequency converter must strictly comply with relevant international electrical standards (such as IEC 60364, IEC 60664). The operation manual categorizes safety prompts into different levels such as "danger", "warning", "caution", etc., clearly indicating the consequences that may result from non-compliance. The core security principles include:
Clear objective: All transportation, installation, commissioning, and maintenance work must be carried out by qualified electrical professionals.
According to regulations: The frequency converter should be integrated into electrical equipment or machines that comply with the EU Machinery Directive (98/37/EC) and comply with the requirements of the EMC Directive. It should be noted that without a higher-level security system, MOVITRAC ® B itself does not have security functions, and for dangerous applications involving lifting, an independent security monitoring system must be additionally configured.
Power outage and protection: Before operating live equipment, it is necessary to cut off the power and wait for the capacitor to discharge. The LED turning off after a power outage does not mean there is no power at all, additional protective measures must be taken. All power terminals must be equipped with contact protection devices that comply with regulations before they can operate.
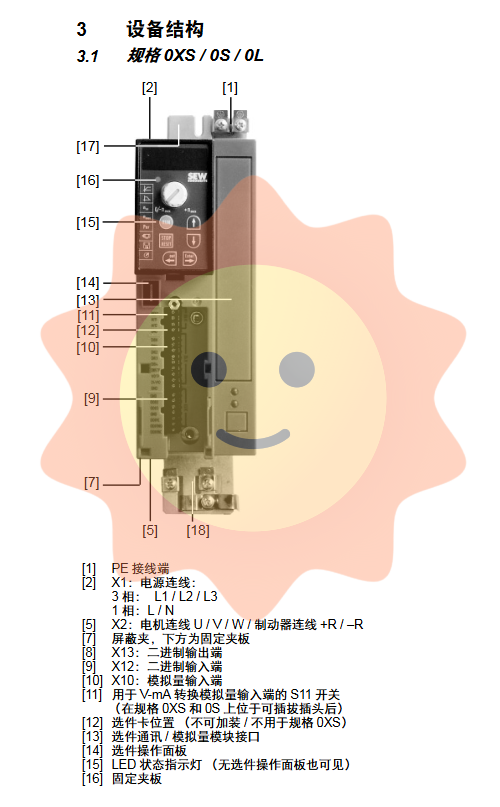
Rigorous installation and electrical connection
The installation quality of a frequency converter directly affects its heat dissipation, electromagnetic compatibility, and long-term stability. The manual has detailed regulations on this.
Installation environment and spacing: It must be installed vertically to facilitate heat dissipation. To ensure effective cooling, a gap of at least 100mm should be left above and below the equipment, and the side can be installed tightly. The installation surface should be flat to ensure good contact. When installing on a cooling plate to adapt to narrow spaces, there are strict requirements for the flatness of the contact surface and installation torque.
EMC (Electromagnetic Compatibility) installation: This is the core difficulty of installation. The key measures include:
Shield all outgoing cables (excluding power cords).
Use shielded motor cables or install output chokes (HD) to limit radiated interference.
Reliable grounding of the frequency converter and all high-frequency equipment through the conductive parts of the installation surface.
Strong current cables and control cables should be laid in separate slots and isolated from each other.
For ungrounded IT networks, it is recommended to turn off the EMC capacitors of specification 0 devices and consider using pulse code measurement for insulation monitoring.
Wiring specifications:
Power supply and motor: According to the equipment specifications, connect the power supply through terminal X1, and connect the motor and brake through X2 (or X3). The cross-sectional area of the wire should be selected according to the rated current.
Braking resistor: When connected to the braking terminal, the wire should be as short and shielded as possible. Overheating protection must be configured, and for the BW... - T series, its internal temperature switch can be used; For the regular BW series, an external bimetallic relay is required. When braking, there is high DC voltage and extremely high surface temperature, so special attention should be paid to the installation position and protection.
Control circuit: Terminal X10 is an analog input, X12 is a binary input, and X13 is a binary output. A screwdriver with a width of 2.5mm should be used for wiring. For switch signals, it is recommended to use dual core shielded copper cables.
Safety function: Equipment with safety stop (S0) model, connected through X17 terminal, but it must be emphasized that its safety function relies entirely on the correct design and implementation of the higher-level safety system, and the frequency converter itself is not a safety component.
Systematic debugging process
MOVITRAC ® B supports debugging through various methods, including option operation panel FBG11B/DBG60B, computer software MOVITOOLS ® MotionStudio and external potentiometers or communication interfaces. Before debugging, it is necessary to complete the mechanical and electrical connections, and ensure that the drive device is in a prohibited state, taking measures to prevent accidental start-up.
1. Debugging through the FBG11B operation panel:
FBG11B provides intuitive 7-segment digital display and button operation. Debugging menu guides users to complete step by step:
Choose motor type: Supports SEW standard motors (DT/DV series) and non SEW motors. For SEW motors, their characteristic data has been pre-set; For non SEW motors, manual input of nameplate data such as rated voltage, current, power, speed, and power factor is required.
Select operating mode: Common modes include standard V/f control (suitable for situations with low dynamic requirements) and VFC control (with slip compensation, good dynamic performance, suitable for high torque, precise control or lifting applications). In VFC mode, DC braking or elevator specific functions can also be added.
Input power data: Set the actual power supply voltage.
Confirmation and Calculation: The system will automatically calculate internal parameters based on input data. For non SEW motors, a brief motor self-test may be required.
2. Parameter adjustment for special applications:
For secondary loads such as pumps, fans, or non SEW motors, the manual recommends specific parameter optimization, such as turning off automatic compensation and IxR compensation, and appropriately extending acceleration/deceleration time to avoid unstable operation or overcurrent protection.
3. Communication and networking debugging:
Bus communication such as RS-485, CANopen (SBus), or Profibus can be achieved through the optional communication module FSC11B or analog module FIO11B. During debugging, it is necessary to set the correct station address and baud rate, and configure the content of the process data word (PO/PI) reasonably, such as the set value (PO2), actual speed (PI1), etc. There are also corresponding debugging strategies for multi motor drive (mechanical coupling) and group drive (mechanical independence but parameter sharing).
Operation, Display, and Fault Diagnosis
Daily operations:
The frequency converter can be controlled through panel buttons or external terminals (such as clockwise/stop, counterclockwise/stop, enable). The set value can be provided through panel analog potentiometer, external analog input, fixed digital set value, or bus communication. The panel supports the "manual rated value adjustment" mode for easy on-site testing.
Status display:
The front-end LED of the device provides quick status indication. Green light indicates enable, red flash indicates overload, and yellow light indicates no enable or disable. The display screen of the operation panel (FBG11B/DBG60B) can provide more detailed information such as status, speed, current, fault codes, etc. Status word 1 can be read through the interface and includes status codes such as 0x0 (not ready), 0x1 (controller disabled), 0x2 (not enabled), 0x3 (DC brake not enabled), 0x4 (enabled), etc.
Fault handling:
Fault codes F-00 to F-113 cover various situations such as overcurrent, overvoltage, overheating, grounding, and communication timeout. When a fault occurs, the frequency converter will execute different responses such as "immediate shutdown", "stop", or "timeout warning" according to the type of fault. The fault information is stored in the memory. Resetting faults can be done through the STOP/RESET button on the panel, external terminals (fault reset), or software. After resetting, the driving device is usually in a locked state and needs to be reconfirmed before it can be started. The manual provides clear explanations of the possible causes and troubleshooting measures for each fault, such as the F-07 intermediate circuit overvoltage, which is usually related to excessive regenerative energy, brake circuit faults, or grid voltage fluctuations.
Overview of Key Technical Parameters
For the convenience of engineers in selecting and designing, MOVITRAC ® B provided detailed technical parameters. Key information includes:
Environmental adaptability: The standard operating temperature range can reach -10 ° C to+50 ° C (depending on specifications and load), and cooling methods include natural cooling and fan forced cooling. The basic protection level is IP20, and in certain cases, adding accessories can reach IP10.
Electrical performance: Input voltage allows for a deviation of ± 10%. The output frequency and voltage are adjustable, and the PWM frequency can be selected as 4/8/12/16 kHz. Built in current limiting function (usually 150% rated current, lasting for 60 seconds).
Control terminal: Analog input compatible with 0-10V or 0 (4) -20mA. The binary input is PLC compatible level, and the output is relay contact or transistor open circuit output.
Braking capability: For models that operate in four quadrants (with brake chopper), an external braking resistor is required, with clear minimum requirements for the resistance value.
Energy consumption: The power loss of different specifications ranges from 30W to 2300W, and heat dissipation needs to be considered when designing the cabinet.
- ABB
- General Electric
- EMERSON
- Honeywell
- HIMA
- ALSTOM
- Rolls-Royce
- MOTOROLA
- Rockwell
- Siemens
- Woodward
- YOKOGAWA
- FOXBORO
- KOLLMORGEN
- MOOG
- KB
- YAMAHA
- BENDER
- TEKTRONIX
- Westinghouse
- AMAT
- AB
- XYCOM
- Yaskawa
- B&R
- Schneider
- Kongsberg
- NI
- WATLOW
- ProSoft
- SEW
- ADVANCED
- Reliance
- TRICONEX
- METSO
- MAN
- Advantest
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bently
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- Beijer
- Moxa
- Rexroth
- Johnson
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- Application field
- XP POWER
- CTI
- TRICON
- STOBER
- Thinklogical
- Horner Automation
- Meggitt
- Fanuc
- Baldor
- SHINKAWA
- Other Brands