ABB MicroFlex servo drive characteristics and installation guide
ABB MicroFlex servo drive characteristics and installation guide
The ABB MicroFlex MN1919WEN series is a high-performance single axis brushless AC servo drive designed specifically for industrial automation. With its compact design and powerful control capabilities, this product line can accurately drive various types of rotary and linear motors. This article will be based on the official manual, providing a detailed analysis of MicroFlex's core features, installation points, configuration process, and troubleshooting methods, aiming to provide engineers with a comprehensive practical guide.
Product Overview and Core Features
The MicroFlex series offers a diverse range of current rating options, including three models: 3A (FMH2A03), 6A (FMH2A06), and 9A (FMH2A09), to meet the application requirements of different power levels. All models support direct connection to 115V or 230V AC power sources (single-phase or three-phase), and are equipped with built-in rectification, smoothing, and input surge protection circuits. The driver is designed to be installed in industrial environments that comply with EN60204 standards, providing a reliable motion control solution for fixed ground applications.
In terms of technical features, MicroFlex integrates Mint WorkBench configuration software, which not only provides an intuitive auto tuning wizard, but also includes software oscilloscope functionality and fine-tuning tools, greatly simplifying the motor matching process. On the communication interface, the driver comes standard with RS232 interface and can choose RS485/RS422 interface according to the model, supporting multi host communication network. In addition, MicroFlex is compatible with various feedback devices such as incremental encoders, absolute value encoders (SSI interfaces), and rotary transformers, ensuring perfect compatibility with different motors and system architectures.
Detailed installation guide
Mechanical installation and heat dissipation
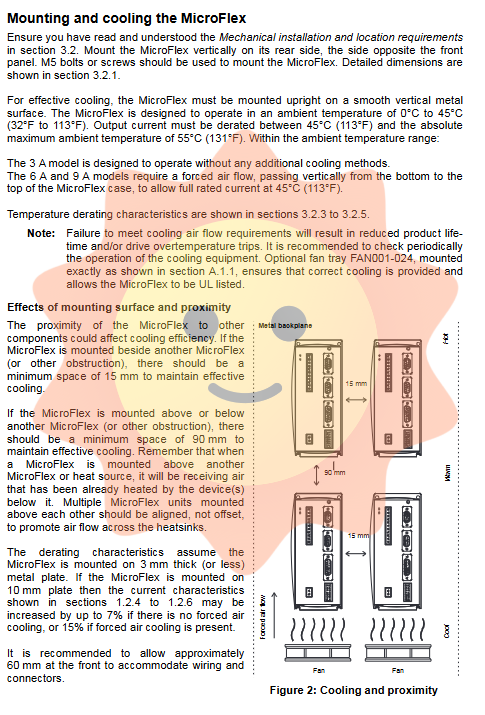
Proper mechanical installation is a prerequisite for ensuring long-term stable operation of the drive. MicroFlex should be installed vertically on the back of the drive and fixed on a smooth vertical metal surface. The manual emphasizes the importance of cooling airflow. Although the 3A model can operate under natural cooling, the 6A and 9A models must be equipped with forced air cooling in ambient temperatures above 45 ° C. The cooling airflow must pass vertically through the drive housing, flowing from the bottom to the top to prevent local hotspots. In addition, the spacing between devices should also be considered during installation. If multiple drivers are installed side by side, the upper and lower spacing should meet specific requirements (such as 90mm above and 15mm on the side) to avoid thermal effects.
Electrical Connection and Protection
Electrical connections involve the connection of the main power supply, control power supply, and motor. The input side of the main power supply must be equipped with fuses or circuit breakers that meet the specifications to provide overcurrent and short-circuit protection. The manual clearly states that it is not recommended to use residual current devices (RCD) as protective devices. For single-phase or three-phase power supplies, the connection must strictly follow the terminal definitions (L1, L2, L3). Grounding (PE) is crucial for safety and must be connected to a dedicated protective grounding terminal on the heat sink. The cross-sectional area of the grounding conductor must meet the EN61800-5-1 standard (e.g. copper wire not less than 10mm ²). In addition, an independent 24V DC control power supply needs to be connected, which should be double insulated or reinforced with insulation isolation from the AC power supply and equipped with fuses. To comply with the CE directive, appropriate EMC filters must be installed.
Feedback and brake resistor wiring
The wiring of the feedback device is crucial for system accuracy. The document provides detailed wiring guidelines for different types of feedback. For incremental encoders, shielded twisted pair cables should be used and connected to specific pins of the X8 terminal (such as CHA+, CHB -, and Hall signals). Rotary transformer signals (SIN+, SIN -, etc.) also require shielded twisted pair cables. If using SSI absolute value encoder, specific clock and data signal definitions must be followed. The shielding layer of all feedback cables must be connected at the outer shell of the D-type connector to maximize anti-interference capability.
In applications that require deceleration or energy dissipation, selecting the appropriate external braking resistor is crucial. The resistance of the braking resistor must be at least 39 ohms to prevent the regenerative switch current from exceeding the maximum limit of the driver. The manual provides calculation formulas based on braking energy (E), cycle time (D), and duty cycle to help users estimate the rated power (Pav) of the required resistance. The safety margin recommended by ABB is 1.25 times, which means the required resistance power rating is 1.25 x Pav. Users can choose standard resistors such as RGJ139 (100W), RGJ160 (100W), or RGJ260 (200W), and are equipped with a heat sink, but derating needs to be considered for use in high ambient temperatures.
- ABB
- General Electric
- EMERSON
- Honeywell
- HIMA
- ALSTOM
- Rolls-Royce
- MOTOROLA
- Rockwell
- Siemens
- Woodward
- YOKOGAWA
- FOXBORO
- KOLLMORGEN
- MOOG
- KB
- YAMAHA
- BENDER
- TEKTRONIX
- Westinghouse
- AMAT
- AB
- XYCOM
- Yaskawa
- B&R
- Schneider
- Kongsberg
- NI
- WATLOW
- ProSoft
- SEW
- ADVANCED
- Reliance
- TRICONEX
- METSO
- MAN
- Advantest
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bently
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- Beijer
- Moxa
- Rexroth
- Johnson
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- Application field
- XP POWER
- CTI
- TRICON
- STOBER
- Thinklogical
- Horner Automation
- Meggitt
- Fanuc
- Baldor
- SHINKAWA
- Other Brands