How to troubleshoot the YOKOGAWA CA500/CA550 multifunctional process calibrator?
YOKOGAWA CA500/CA550 Multi functional Process Calibration Instrument
Instrument positioning and core use
CA500/CA550 is a portable multifunctional process calibrator, whose core function is to provide standard signal generation and parameter measurement for field instruments such as transmitters, sensors, and controllers. It supports synchronous operation of "generation measurement" and achieves high efficiency and accuracy in instrument calibration. The core difference between the two lies in the addition of HART/BRAN communication function in CA550, which can directly interact with smart meters, read device information, perform loop testing, and output adjustment.
Core functions and technical parameters
1. Overview of core functions
CA500/CA550 supports 6 types of signal generation and 6 types of parameter measurement, covering mainstream calibration requirements in industrial sites. The specific functional comparison is as follows:
Function type supports signal (CA500/CA550 universal) CA550 additional functions
Signal generation includes DC voltage (100mV~30V), DC current (20mA/4-20mA), resistance (400 Ω/4000 Ω), thermocouple electromotive force, RTD simulation, frequency/pulse (1Hz~50kHz/CPM), HART/BRAN communication signal superposition, program scanning (20 calibration points), and automatic data grading (Pass/Tail)
Parameter measurement: DC voltage (100mV~50V), DC current (50mA), resistance (400 Ω/4000 Ω), thermocouple temperature, RTD temperature, frequency/pulse counting. HART device information reading (label, range, diagnostic data), BRAIN device model/serial number reading, calibration data CSV export
Scanning function includes linear scanning (0%~100% linear variation), step scanning (equidistant step output), program scanning (CA500 supports 10 points), program scanning supports 20 points, can associate calibration object information (model, serial number, label), automatically save scanning data and grading results
Data management manually saves 100 pieces of data, scanned data is automatically saved (in CA500 dedicated format), data is saved in CSV format (supporting comma/semicolon/tab separation), USB storage is exported, and folders are automatically classified by "year/month/day"
2. Key technical parameters
Accuracy level: DC voltage ± 0.01% FS, DC current ± 0.01% FS, resistance ± 0.01% FS, temperature (thermocouple) ± 0.1 ℃ (K-type, 0~1000 ℃).
Resolution: DC voltage of 100mV with a range of 1 μ V, DC current of 20mA with a range of 1 μ A, resistance of 400 Ω with a range of 0.01 Ω, and frequency of 500Hz with a range of 0.01Hz.
Output capability: DC current output with a maximum load of 20V (4-20mA range), resistance output with a permissible measured current of 0.1-3mA (400 Ω range).
Communication interface: USB Type B (supports remote control and CA550 data export), HART/BRAN communication port (CA550 specific, stacked on 4-20mA loop).

Operation process and core scenarios
1. Basic operations: Signal generation and measurement
Taking "4-20mA current generation+measurement" as an example, explain the standard operating procedure:
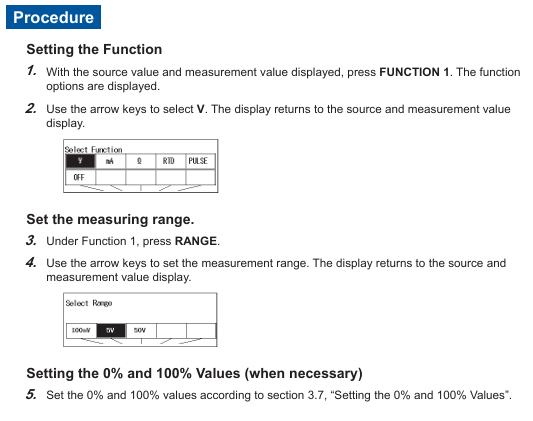
(1) Signal occurrence setting (Function 2)
Function selection: Press the Function 2 key, use the directional keys to select mA (current), and press ENTER to confirm.
Range setting: Press the RANGE key, select 4-20mA (default 0%=4mA, 100%=20mA), and press ENTER to confirm.
Parameter adjustment: Set the output value (such as 8mA) through the numeric keys or UP/DOWN keys, press the OUTPUT ON/OFF key to start the output, and the screen will display "OUTPUT: ON".
Scanning function (optional): If step output is required, enter SETUP → Sweep Setup → Step Sweep, set the interval time (such as 10 seconds) and repeat mode (ON/OFF), press the SWEEP key to start step scanning.
(2) Parameter measurement settings (Function 1)
Function selection: Press the Function 1 key, use the directional keys to select mA (current), and press ENTER to confirm.
Range setting: Press the RANGE button, select 50mA (covering 4-20mA measurement requirements), and press ENTER to confirm.
Loop power supply (optional): If measuring a two-wire transmitter, press the LOOP POWER button, and the instrument will output 24VDC loop power while measuring the transmitter output current.
Data reading: The screen displays the measured values in real-time, and pressing the AVERAGE key can view the 5 times moving average, maximum value, and minimum value.
2. Advanced scenario 1: Temperature calibration (thermocouple/RTD)
(1) Thermocouple temperature occurrence (simulating K-type thermocouple)
Function selection: Function 2 → TC SRC (thermocouple occurrence), select K type with the RANGE key, press ENTER to confirm.
Terminal settings: Go to SETUP → Temperature Setup → TC Terminal, select TC-B (banana plug, supports external reference compensation), set TC-B RJC to ON (enables reference compensation).
Temperature setting: Enter the target temperature (such as 200 ℃) through the numerical keys, press OUTPUT ON/OFF to start the output, and the screen will synchronously display the corresponding thermoelectric potential (such as 8.137mV, in accordance with ITS-90 standard).
(2) RTD temperature measurement (PT100)
Function selection: Function 1 → RTD, select PT100 (IEC 60751 standard, -200~800 ℃) with the RANGE key.
Wiring settings: Go to SETUP → Connection Method, select 3W (three wire system, eliminate lead resistance error).
Measurement execution: Connect the PT100 sensor (three wire system), the screen displays the measured temperature, and press the PLAY button to switch the displayed resistance value (e.g. 273.15 Ω corresponds to 0 ℃).
3. CA550 exclusive scenario: HART instrument calibration
Taking the "HART transmitter loop test" as an example, the operation process is as follows:
Communication settings: Press the COM key to enter on-site communication mode, select HART for the HART/BRAN soft key, and set 250 Ω ON/OFF to ON (providing HART communication impedance).
Device connection: Press the CONNECT Device button, and the instrument will automatically connect to the HART device with address 0. After successful connection, the device label and PV value will be displayed.
Loop test: Press the LOOP TEST button to set the target output current (such as 8mA), and the instrument controls the transmitter output through HART commands. At the same time, measure the actual output current and compare the deviation.
Data saving: Enter SETUP → Program Sweep, set calibration points (such as 4/8/12/16/20mA) and tolerances (such as 0.5%), perform scanning, and automatically save data (including device model, serial number, error, and grading results).

Data Management and Remote Control
1. Data storage and export
(1) CA500 Data Management
Manual save: During the measurement/occurrence process, press the SAVE button to automatically save the current time, function, range, measurement value/occurrence value, up to 100 records (memory numbers 001~100).
Data reading: Press the LOAD key, select the memory number, and press ENTER to view and save the data. CA500 only supports local viewing of the instrument and needs to be exported to the PC through USB commands.
(2) CA550 Data Management
Auto Save: Enable Data Save=ON during program scanning, and save data in CSV format to internal memory. The folder structure is Root → CalibrationData/WeekData/SaveData (manual save).
USB export: Connect to a PC via a USB cable, and the instrument is recognized as a USB storage device. Copy the CSV file directly to the PC and open it for analysis in Excel (supporting comma/semicolon/tab separation).
2. Remote control (USB communication)
Connect to PC through USB interface and use dedicated instructions to achieve remote control. The core instructions are as follows:
Signal generation: SD20.000 (set current generation value of 20.000mA), SO1 (start output).
Parameter measurement: OD0? (Query Function 1 measurement values), OS? (Query current instrument settings).
Data saving: TS (perform manual saving) OM1? (Read the saved data of memory number 1).
Equipment settings: IO1 (enable 250 Ω communication resistor), VO1 (start 24V circuit power supply).
Communication protocol: Following USB CDC (Communication Device Class), Yokogawa YKCDC USB Driver driver needs to be installed. The PC end sends commands through a serial port tool (such as PuTTY), with a default baud rate of 9600bps.
Precautions and Maintenance
1. Operational safety and accuracy assurance
Output protection: Avoid short circuits when outputting DC voltage in the 30V range, and avoid open circuits when outputting DC current. The instrument has built-in overvoltage/overcurrent protection, and the output needs to be restarted after triggering the protection.
Temperature effect: Preheat for 1 hour before temperature calibration to avoid the internal temperature rise of the instrument affecting the compensation accuracy of the reference end; The fluctuation of environmental temperature should be controlled within ± 1 ℃ (especially for IL measurement).
Wiring specifications: Three wire or four wire system should be preferred for resistance/RT D measurement to reduce lead resistance errors; Thermocouple wiring needs to distinguish between positive and negative poles (TC-B terminal: red positive, black negative).
2. Instrument maintenance
Battery management: The instrument supports dual power supply of battery and USB, and Power Select can set power priority; When the battery is low, the screen prompts that it needs to be charged in a timely manner (charging time is about 4 hours, full battery life is about 8 hours).
Memory cleaning: When CA550 data is full (250 CSV files), it is necessary to manually delete useless files or format the internal memory (MENU → File Format → QUICK, note: formatting will clear all data).
Calibration cycle: It is recommended to calibrate the instrument once a year. You can contact the authorized service center of Yokogawa or refer to the "User Calibration Manual" downloaded from the official website for self calibration (standard calibration source is required).
Common problems and troubleshooting
Possible causes and solutions for the fault phenomenon
After starting the output, there is no signal. The output terminal is not connected to the load, and the range setting is incorrect. Confirm that the load is within the allowable range (such as 4-20mA range load ≤ 20V), and select the correct range again
The temperature measurement deviation is large, and the reference compensation is not enabled. If the thermocouple type is selected incorrectly, enter the Temperature Setup and enable TC-B RJC. Confirm that the thermocouple type is consistent with the actual one (such as K type)
HART communication connection failure: 250 Ω resistor not enabled, device address non-zero. Press the COM key to enable 250 Ω. Confirm that the HART device address is 0 (default) and check the circuit wiring
USB cannot recognize that the driver is not installed and the USB cable has poor contact. Install YKCDC USB Driver, replace the USB cable and reconnect it
Data cannot be saved. Memory is full, file format is incorrect. Delete useless data or format memory. Confirm that the save format is CSV (CA550) or dedicated format (CA500)

- ABB
- General Electric
- EMERSON
- Honeywell
- HIMA
- ALSTOM
- Rolls-Royce
- MOTOROLA
- Rockwell
- Siemens
- Woodward
- YOKOGAWA
- FOXBORO
- KOLLMORGEN
- MOOG
- KB
- YAMAHA
- BENDER
- TEKTRONIX
- Westinghouse
- AMAT
- AB
- XYCOM
- Yaskawa
- B&R
- Schneider
- Kongsberg
- NI
- WATLOW
- ProSoft
- SEW
- ADVANCED
- Reliance
- TRICONEX
- METSO
- MAN
- Advantest
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bently
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- Beijer
- Moxa
- Rexroth
- Johnson
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- Application field
- XP POWER
- CTI
- TRICON
- STOBER
- Thinklogical
- Horner Automation
- Meggitt
- Fanuc
- Baldor
- SHINKAWA
- Other Brands




































































































































