Allen Bradley 1747-DCM Direct Communication Module
Allen Bradley 1747-DCM Direct Communication Module
Core framework and scope of application
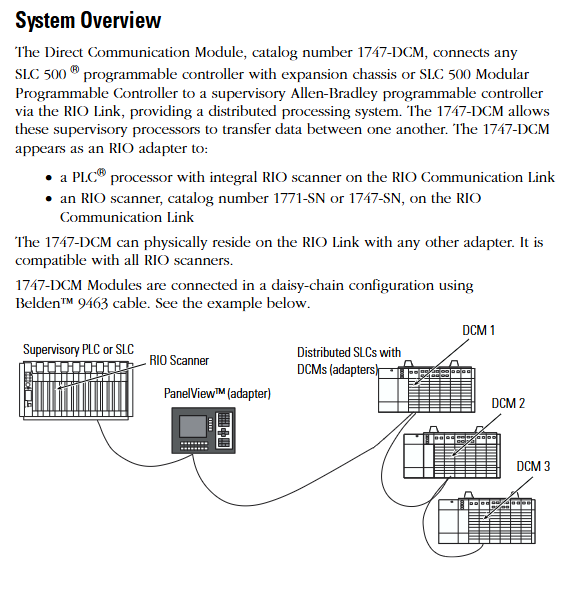
The document follows the logical mainline of "safety specifications → system positioning → hardware configuration → installation and operation → fault handling", covering the entire process of module configuration from early stage to later stage maintenance. The applicable product is the 1747-DCM direct communication module, which serves as the communication interface module for SLC 500 series controllers (including extended chassis or modular controllers). It is connected to higher-level Allen Bradley controllers (such as PLC-2/3/5, SLC with RIO scanner) through RIO (Remote I/O) links to achieve data transmission between distributed processors, and is suitable for multi controller collaboration scenarios in industrial automation (such as multi area data exchange in production lines and remote device monitoring).
Core content sorting
(1) System positioning and hardware characteristics
Module core functions
Communication bridge function: manifested as an RIO adapter on the RIO link, it supports communication with PLC processors (such as PLC-5/250) or independent RIO scanners (1771-SN, 1747-SN) with integrated RIO scanners, enabling bidirectional data transmission between the upper level controller and the distributed SLC 500 controller.
Expansion node capability: Supports expansion node functionality. If all scanners and adapters on the RIO link have this capability, up to 32 adapters can be connected. At full baud rate, 82 Ω terminal resistors (1/2W) need to be connected at both ends of the link to ensure signal integrity.
Hardware structure and key components
Physical components: including self-locking buckle (fixing module to chassis), 2 sets of DIP switches (configuration parameters), 2 status LEDs (red FAULT light, green COMM light), RIO link connector (front end), cable fixing slot, side label (module information), door label (parameter identification). The module is a full-size circuit board and needs to be installed in the non-zero slot of SLC 500 chassis (slot 0 reserved for CPU).
Status LED function:
FAULT light (red): Always on indicates an internal fault, flashing indicates a configuration error, and off indicates normal operation.
COMM light (green): Always on indicates normal communication, flashing indicates that the upper level processor is in programming/testing/fault mode, and off indicates communication interruption (such as scanner not connected or link failure).
(2) Module configuration: DIP switch parameter setting
The 1747-DCM contains 2 sets of 8-bit DIP switches (SW1, SW2), which need to be configured before installation. The key parameters are as follows:
1. SW1 (chassis address and starting I/O group)
Rules for configuring switch position functions
SW1-1~SW1-6 logical chassis addresses correspond to the chassis number (octal) of the higher-level scanner. The switch status needs to be selected according to the scanner type (PLC-2/3/5, 1747-SN). For example, chassis address 1 of PLC-5/250 corresponds to SW1-1~5 being ON and SW1-6 being OFF
The starting I/O group numbers for SW1-7~SW1-8 only support even numbers (0/2/4/6) and need to match the chassis size:
-0 (ON+ON): Suitable for all sizes
-2 (ON+OFF): Suitable for 3/4, 1/2, and 1/4 sizes
-4 (OFF+ON): Suitable for 1/2 and 1/4 sizes
-6 (OFF+OFF): Only compatible with 1/4 size
2. SW2 (data rate, fault handling, chassis attributes)
Rules for configuring switch position functions
SW2-1~SW2-2 data rates support three baud rates, which need to be consistent with the RIO link:
-57.6K baud (ON+ON): Maximum cable length 3048m (Belden 9463)
-115.2K baud (ON+OFF): Maximum 1524m
-230.4K baud (OFF+ON): maximum 762m
-Disable (OFF+OFF): Do not enable communication
When SW2-3 fault occurs, clear all data bits in the input image table (status bits are retained) - OFF: When there is a communication fault with RIO or when the upper level processor enters fault mode, clear all data bits in the input image table
-ON: Maintain the last state of the data bit in case of malfunction (confirm that there is no safety risk)
SW2-4 Last chassis identifier - OFF: The module shares logical chassis with other adapters and is the device with the highest I/O group number in the chassis
-ON: Not the last chassis device
SW2-5~SW2-6 logical chassis size allocation allocates the image space of modules in the scanner, determining the number of data transmission words:
-1/4 size (ON+ON): 1 status word+1 data word (2 words in total)
-1/2 size (ON+OFF): 1 status word+3 data words (4 words in total)
-3/4 size (OFF+ON): 1 status word+5 data words (a total of 6 words)
-Full size (OFF+OFF): 1 status word+7 data words (a total of 8 words)
Key note: Module images cannot cross logical chassis boundaries. For example, selecting the starting I/O group 6 while configuring as 1/2 size will trigger a configuration error.

(3) Installation and wiring: practical operation specifications
Pre-installation preparation
Power requirements: Power is obtained through the SLC 500 chassis backplane, requiring a current of+5V DC/360mA. Before installation, the remaining capacity of the chassis power supply needs to be confirmed; The fixed SLC 500 controller's 2-slot expansion chassis only supports one 1747-DCM and requires reference to the 1746-2.35 manual to confirm compatibility with other I/O modules.
Electrostatic protection: The module contains sensitive electronic components, and before installation/disassembly, it is necessary to touch a grounded object to discharge electricity and avoid electrostatic damage.
Switch pre configuration: DIP switch settings (chassis address, data rate, chassis size, etc.) must be completed before installing the module to avoid repeated disassembly after installation.
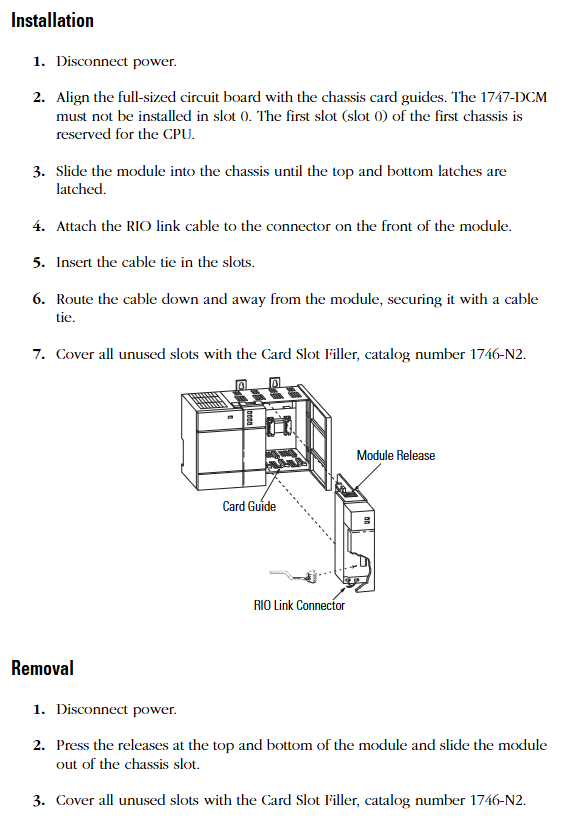
Module installation steps
Power off operation: Disconnect the chassis power supply to ensure safe installation.
Align the guide rail: Align the full-size circuit board with the upper and lower guide rails of the chassis, and confirm that the module is not installed in slot 0 (slot 0 is reserved for the CPU).
Fixed module: Slide the module to the self-locking buckle to ensure reliable contact between the module and the backplane connector.
Connect RIO cable: Connect the RIO link cable to the front-end connector of the module, use cable fixing slots and zip ties to secure the cable and prevent it from loosening.
Covering empty slots: Cover unused slots with 1746-N2 slot fillers to prevent dust from entering or electric shock risks.
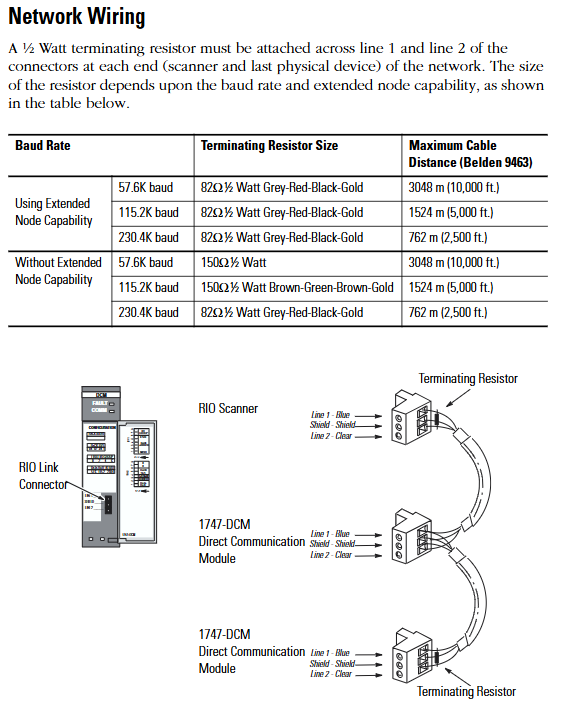
RIO Link Wiring Specification
Cable selection: It is recommended to use Belden 9463 cable, which supports differential signal transmission and has strong anti-interference ability.
Terminal resistance: A 1/2W terminal resistance should be connected at both ends of the link (scanner and the last physical device), and the resistance value should be selected based on whether the expansion node function is enabled
Enable extended node: Use 82 Ω for full baud rate (color ring: gray red black gold).
Extension node not enabled: 150 Ω (brown green brown gold) for 57.6K/115.2K baud, 82 Ω for 230.4K baud.
Wiring definition: The link includes Line 1 (blue), Line 2 (transparent), and a shielding layer. The shielding layer needs to be grounded at one end to avoid interference signals from ground current.
(4) Troubleshooting: LED Status and Handling
Fault interpretation of FAULT light (red)
|LED status | Reason for malfunction | Solution|
|Always on | Internal module faults (such as circuit and memory errors) | Restart I/O chassis containing 1747-DCM; If it still lights up after restarting, replace the module|
|Flashing | Configuration error (such as mismatch between I/O group and chassis size, chassis address error) | Check DIP switch settings to ensure compatibility between the starting I/O group and chassis size, and confirm that the chassis address matches the scanner|
|Extinguish | Normal state | No operation required|
COMM light (green) fault interpretation
|LED status | Reason for malfunction | Solution|
|Always on | Communication is normal | No operation required|
|Blinking | The upper level RIO scanner processor is in programming/testing/fault mode | Investigate the scanner processor fault and restart 1747-DCM after restoring normal mode|
|Extinguish | 1 The scanner is not connected to the processor
2. Scanner chassis disabled
3. No communication between 1747-DCM and scanner (baud rate mismatch, loose cable, connector not installed) | 1 Confirm that the scanner is correctly installed in chassis
2. Check the integrity of the scanner chassis and restart the module after repairing it
3. Verify the baud rate between 1747-DCM and scanner, check cable connections and connector installation|
(5) Technical specifications and safety standards
Core technical parameters
|Category | Specification|
|Power consumption | Backboard power supply,+5V DC/360mA|
|Working temperature | 0 ° C~+60 ° C (32 ° F~+140 ° F)|
|Storage temperature | -40 ° C~+85 ° C (-40 ° F~+185 ° F)|
|Humidity | 5%~95% (no condensation)|
|Certification | UL certification, CSA certification, Class I Division 2 (A/B/C/D groups) hazardous environment certification, CE compliance, C-Tick labeling|
|Physical dimensions | Full size SLC 500 module, compatible with standard SLC chassis slots|
Safety regulations for hazardous environments
The module is only applicable to Class I Division 2 (A/B/C/D groups) hazardous or non hazardous environments and is prohibited from being used in higher-level hazardous areas.
Taboos for operating in hazardous environments: Do not replace components or disconnect equipment (unless power is cut off), do not connect/disconnect components with electricity, all wiring must comply with NEC 501-4 (b) specifications, and do not replace components that may affect the applicability of hazardous environments.
Key considerations and supplementary resources
Compatibility check: The expansion of node functionality requires support from all devices (scanners, adapters) on the RIO link; When installing the 2-plot expansion chassis, it is necessary to confirm compatibility with other I/O modules (refer to manual 1746-2.35).
Configuration consistency: The DIP switch settings need to match the higher-level scanner, especially the chassis address, data rate, and chassis size, to avoid communication failures caused by parameter mismatches.
Wiring specifications: RIO cables should be kept away from power lines (to avoid electromagnetic interference), the shielding layer should be grounded at one end, terminal resistors should only be installed at both ends of the link, and intermediate equipment does not need to be installed.
- ABB
- General Electric
- EMERSON
- Honeywell
- HIMA
- ALSTOM
- Rolls-Royce
- MOTOROLA
- Rockwell
- Siemens
- Woodward
- YOKOGAWA
- FOXBORO
- KOLLMORGEN
- MOOG
- KB
- YAMAHA
- BENDER
- TEKTRONIX
- Westinghouse
- AMAT
- AB
- XYCOM
- Yaskawa
- B&R
- Schneider
- Kongsberg
- NI
- WATLOW
- ProSoft
- SEW
- ADVANCED
- Reliance
- TRICONEX
- METSO
- MAN
- Advantest
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bently
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- Beijer
- Moxa
- Rexroth
- Johnson
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- Application field
- XP POWER
- CTI
- TRICON
- STOBER
- Thinklogical
- Horner Automation
- Meggitt
- Fanuc
- Baldor
- SHINKAWA
- Other Brands




































































































































