YOKOGAWA FA-M3 positioning module (with analog voltage output)
Document identification: Document number IM 34M6H58-01E, document model code DOCIM. This number must be referenced for communication and additional manual purchases; The media number is the same as the document number (CD version), and the copyright belongs to Yokogawa Electric in 1998.
Origin search parameters: including origin search mode (contact detection action), search direction, Z-phase edge selection, Z-phase pulse count, Z-phase search range, origin offset value, no initial value.
Extended instruction parameters: including extended instruction type (servo ON/OFF, brake ON/OFF, driver reset, etc.), static deviation adjustment, manual pulse generator proportional value, without initial value.
Arc interpolation parameters: including center position, radius, starting angle, angle movement, angle target velocity, acceleration and deceleration time, target position, correction pulse range, without initial values.
3. Example of parameter settings
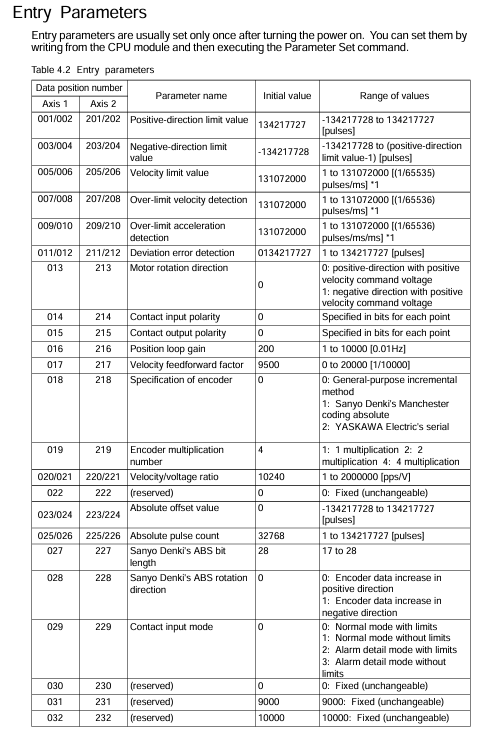
Taking "motor rated speed 3000rpm, rated voltage 6V, encoder 8192 pulses/rev (4x), ball screw pitch 5mm/rev, operating range -500~1000mm" as an example, the key inlet parameters are calculated as follows:
Positive limit value: 1000mm ÷ 5mm/rev x 8192 pulses/rev=1638400 pulses;
Negative limit value: -500mm ÷ 5mm/rev x 8192 pulses/rev=-819200 pulses;
Speed limit value: (100mm/s ÷ 5mm/rev × 8192 pulses/rev) ÷ 1000 × 65536=10737418 (1/65536) pulses/ms;
Speed/voltage ratio: (3000rpm × 8192 pulses/rev ÷ 60s/min) ÷ 6V=68267 pps/V.
Status and I/O Relay
1. Status monitoring
The module status needs to be read through the CPU module, and the core status items are as follows (2-digit data needs to be read as "low word+high word", some of which are fixed-point data):
Status Name Axis 1 Data Position Axis 2 Data Position Description
Error status 101 301: Store error code when an error occurs, meaningless when there are no errors
Contact input status 103 303 stores the external contact input (including emergency stop) status, with 1 bit corresponding to 1 input and polarity defined by parameters
The current status of the instruction position is the path position generated by module 104/105 304/305, which is not the actual position of the motor and is measured in unit pulses
Encoder Position Current Status 108/109 308/309 Encoder Feedback Motor Actual Position, Unit Pulse
Target position status 112/113 312/313: The target position of the positioning operation (calculated according to the target position mode)
Extended state 114 314 stores operational states (acceleration/constant speed/deceleration, mode waiting, control mode, etc.), parsed bit by bit
Remaining deceleration time 115 315 Remaining deceleration time from positioning to target position, 0=path generation stop, -1=acceleration/uniform speed
2. I/O relay (interface CPU module)
Output relays (32 per axis, F3NC51-0N's 2-axis relay is invalid): The core includes start operation instructions (Y Ⅲ 33/49), extension instructions (Y Ⅲ 34/50), deceleration stop requests (Y Ⅲ 35/51), immediate stop requests (Y Ⅲ 36/52), origin search start (Y Ⅲ 37/53), etc., where III is the FA-M3 slot number where the module is located.
Input relays (32 per axis, F3NC51-0N 2-axis relays are meaningless): The core includes confirmation of start operation instructions (X Ⅲ 01/17), confirmation of extension instructions (X Ⅲ 02/18), confirmation of deceleration stop (X Ⅲ 03/19), end of origin search (X Ⅲ 05/21), end of positioning (X Ⅲ 14/30), error notification (X Ⅲ 12/28), etc.
Module access (CPU module interaction)
Supports accessing modules from both sequential CPUs and BASIC CPUs, with core operations including parameter read/write, state read, instruction triggering, etc., requiring adherence to specific instruction formats and operating procedures.
1. Sequential CPU access (ladder program)
Instruction types: Read for dedicated module, Write for dedicated module, Read for High Speed (HRD), Write for High Speed (HWR), INTP/IRET for interrupt handling.
Core operating procedures:
Parameter setting: Write parameters with the WRITE command → trigger the "parameter setting" relay → confirm the "parameter setting confirmation" relay → reset the relay (if the parameter is incorrect, it needs to be rewritten with the correct value);
Error reset: trigger the "error reset" relay → confirm the "error notification" relay reset → reset the relay (when the driver alarm error reset occurs, the driver reset signal is ON for 500ms and then OFF);
Positioning operation: Write the WRITE command to the start parameters → trigger the "start operation command" relay → confirm the "start confirmation" relay → reset the relay → wait for the "positioning end" relay to act;
Other operations: The processes of jog stepping, origin search, speed control, mode switching, etc. are similar, all of which require writing parameters (if necessary), triggering corresponding relays, confirming feedback, and resetting, and must meet the operating prerequisites (such as no errors, servo ON, etc.).
2. BASIC CPU Access (BASIC Program)
Instruction types: Module Usage Declaration (ASSIGN), Parameter/Status Read (ENTER), Parameter Write (OUTPUT), I/O Relay Read (STATUS), I/O Relay Write (CON), Interrupt Declaration (ON INT/GOSUB), Interrupt Reset (OFF INT).
Data processing: Two character data needs to be converted to a long integer (when read, it is a combination of "high character+low character", and when written, it is split into "high character+low character"); The core operations (parameter setting, error reset, positioning, etc.) logic is consistent with the sequence CPU, and process control is achieved through program loop detection of relay status.
- EMERSON
- Honeywell
- CTI
- Rolls-Royce
- General Electric
- Woodward
- Yaskawa
- xYCOM
- Motorola
- Siemens
- Rockwell
- ABB
- B&R
- HIMA
- Construction site
- electricity
- Automobile market
- PLC
- DCS
- Motor drivers
- VSD
- Implications
- cement
- CO2
- CEM
- methane
- Artificial intelligence
- Titanic
- Solar energy
- Hydrogen fuel cell
- Hydrogen and fuel cells
- Hydrogen and oxygen fuel cells
- tyre
- Chemical fiber
- dynamo
- corpuscle
- Pulp and paper
- printing
- fossil
- FANUC
- Food and beverage
- Life science
- Sewage treatment
- Personal care
- electricity
- boats
- infrastructure
- Automobile industry
- metallurgy
- Nuclear power generation
- Geothermal power generation
- Water and wastewater
- Infrastructure construction
- Mine hazard
- steel
- papermaking
- Natural gas industry
- Infrastructure construction
- Power and energy
- Rubber and plastic
- Renewable energy
- pharmacy
- mining
- Plastic industry
- Schneider
- Kongsberg
- NI
- Wind energy
- International petroleum
- International new energy network
- gas
- WATLOW
- ProSoft
- SEW
- wind
- ADVANCED
- Reliance
- YOKOGAWA
- TRICONEX
- FOXBORO
- METSO
- MAN
- Advantest
- ADVANCED
- ALSTOM
- Control Wave
- AB
- AMAT
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- MOTOROLA
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bently
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- Triconex
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- KOLLMORGEN
- Beijer
- Endress+Hauser
- MOOG
- KB
- Moxa
- Rexroth
- YAMAHA
- Johnson
- Westinghouse
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- TEKTRONIX


Email:wang@kongjiangauto.com