ABB NPSI03 Power Supply Module
Basic Information
Module Overview: The ABB NPSI03 Power Supply Module is a key module used to provide power in industrial automation. It is part of ABB's family of automation devices and its main function is to convert the incoming power supply into a stable DC output to provide a reliable power supply to other automation devices such as controllers, I/O modules, sensors and actuators.
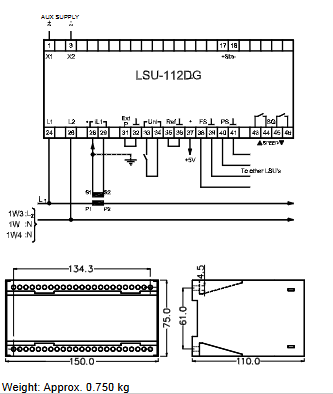
Physical Characteristics: The module usually has a compact design to fit into the limited installation space in industrial control cabinets. The enclosure material generally has good heat dissipation and a certain degree of protection against dust, moisture and other external factors on the internal circuitry. The appearance may have a variety of indicator lights, used to display the working status of the power supply (such as input power is normal, whether the output is normal, etc.), to facilitate the user to carry out a quick check at the scene.
Mounting: Supports a variety of mounting methods, commonly rail mounting (e.g. DIN rail mounting) and screwing directly to the mounting plate. This flexibility allows it to be easily integrated into the control cabinet layout of different industrial automation systems, saving installation time and space.
Input characteristics
Voltage range: The wide input voltage range is designed to accommodate different regional grid standards and voltage fluctuations that may occur in industrial sites. For example, it can accept AC input voltages from 100V AC to 240V AC with a frequency range of typically 50Hz or 60Hz (some models may be compatible with 47 - 63Hz). This design allows it to operate in most global grid environments, reducing power supply problems caused by voltage differences or fluctuations.
Current Characteristics: At rated input voltage, the amount of input current depends on the output power of the power supply module. When the input voltage is at the lower limit and the output power is fully loaded, the input current will increase accordingly, but it will be controlled within the safe range to ensure that the module works normally and meets the electrical safety standards. In addition, it also has a certain degree of inrush current resistance, can withstand the instantaneous connection of the power grid or load sudden change of large current impact, so as to protect the internal circuitry of the module and the connected equipment.
Output Characteristics
Voltage Output: Provides a stable direct current (DC) output voltage, which is a common type of power supply for industrial automation equipment. Typical output voltage is 24V DC, and the output voltage is highly accurate with an error range of ±1% - ±3%. This high accuracy output is critical for voltage-sensitive equipment such as high-precision sensors and precision controllers to ensure that they operate accurately at their rated voltage. Furthermore, the module is able to effectively maintain a stable output voltage in the event of load variations and input voltage fluctuations through techniques such as internal voltage regulator circuits.
Current and Power Output: The size of the output current determines how many devices or how powerful the module can power, NPSI03 power supply modules have different output current specifications, the common output current can be up to 3A - 6A or so (depending on the product model). According to the power formula P = UI (P is power, U is voltage, and I is current), the output power of the NPSI03 power supply module, for example, is 120W with 24V DC output voltage and 5A output current, which makes it possible to provide enough power for multiple loads at the same time, e.g., powering multiple I/O modules, small controllers, or sensors, etc. The NPSI03 power supply module has a load regulation and linearity adjustment ratio.
Load Adjustment Ratio and Linear Adjustment Ratio: Low Load Adjustment Ratio and Linear Adjustment Ratio. Load regulation ratio is the relative rate of change of output voltage when the load current changes from no load to full load; linear regulation ratio is the relative rate of change of output voltage when the input voltage varies within the allowable range. The lower of these two adjustment rates means that the output voltage can remain relatively stable in the case of input voltage fluctuation or load change, further ensuring the quality of power supply, which is very important to ensure the stable operation of industrial automation systems.
Functional features
Protection Mechanisms
Overcurrent Protection (OCP): When the output current exceeds the rated current, the power module will automatically activate the overcurrent protection mechanism. This may include limiting the output current or temporarily cutting off the output to prevent damage to the module itself and connected equipment due to excessive current. The trigger threshold for overcurrent protection is usually adjustable or automatic based on preset criteria, e.g. triggering protection when the output current reaches 120% - 150% of the rated current.
Overvoltage protection (OVP): The overvoltage protection function is triggered in the event of an abnormally high output voltage. The monitoring circuit inside the module will detect the overvoltage condition and take corresponding measures, such as stabilising the output voltage within the safe range or cutting off the output completely, to protect the connected equipment from damage caused by excessive voltage. The overvoltage protection threshold is generally set at about 110% - 130% of the output voltage rating.
Short Circuit Protection (SCP): If a short circuit condition occurs at the output, the module will not be damaged, but will quickly cut off the output current to avoid the internal components of the module from burning due to the excessive short circuit current. After the short-circuit situation is lifted, some modules can also automatically resume normal output, which greatly improves the reliability of the module in complex industrial environments.
Stability and reliability enhancement measures
Temperature compensation: The internal circuit design takes into account the effect of temperature on the output voltage, and through temperature compensation technology, the output voltage can be kept stable in different operating temperature ranges. For example, in the industrial ambient temperature range of - 20℃ - + 70℃, the variation of output voltage can still be controlled within the permissible accuracy range.
Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC): good electromagnetic compatibility, on the one hand, to resist external electromagnetic interference, such as electromagnetic radiation from other industrial equipment, electrostatic discharge, etc.; on the other hand, the electromagnetic interference generated by itself is also within the prescribed range, will not cause adverse effects on the surrounding electronic equipment. This is achieved through reasonable circuit layout, shielding measures and filtering techniques.
Redundancy design (optional): Some models may support redundancy function, i.e. two or more power supply modules can be configured to work at the same time, so that when one of them fails, the other can seamlessly take over all or part of the load to ensure the continuity of power supply. This is important for critical industrial applications where power outages are not permitted, such as powering critical instrumentation in chemical process control.

- User name Member Level Quantity Specification Purchase Date
- Satisfaction :
-