Deep Analysis of HIMA HIMax Safety Control System: Architecture, Redundancy, and Engineering Application Guidelines
Deep Analysis of HIMA HIMax Safety Control System: Architecture, Redundancy, and Engineering Application Guidelines
1.Introduction: Overview of HIMax System
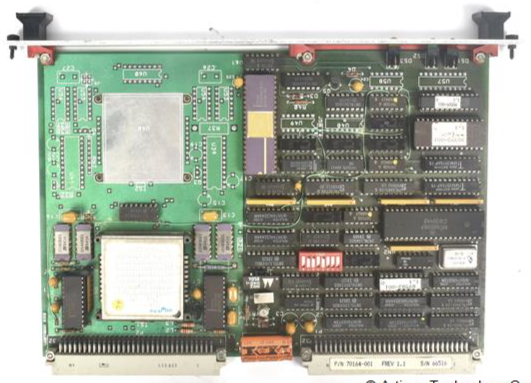
HIMax is a safety related control system designed by HIMA for continuous operation and maximum availability. As a highly modular system, HIMax distributes processing, input/output (I/O), and communication functions in pluggable modules installed on one or more baseboards. By connecting the motherboard through Ethernet cables, the system has strong scalability and can easily adapt to the expansion needs of future process flows.
This system not only complies with the IEC 61508 SIL 3 standard, but also supports multiple configuration modes from single machine non redundant to highly redundant, making it an ideal choice for critical safety tasks in the fields of process automation and factory automation.
2. Hardware architecture and system bus
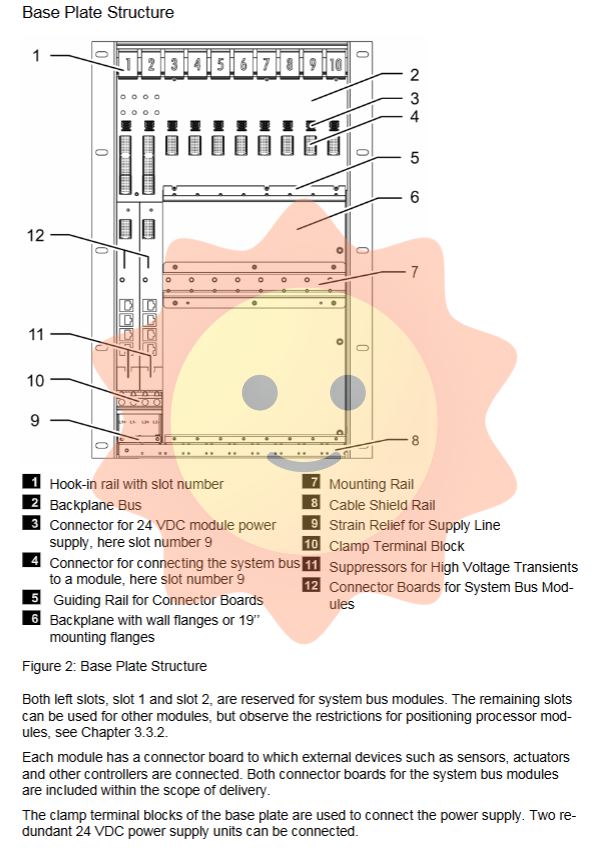
2.1 Modular Base Plate Design
The core physical foundation of HIMax is the baseboard, which provides various types of baseboards according to the number of slots to meet different installation requirements:
10 slots (X-BASE PLATE 10 01): suitable for flat base installation.
15 slots (X-BASE PLATE 15 01/02): suitable for backplane installation or 19 inch cabinet installation.
18 slots (X-BASE PLATE 18 01): Suitable for backplane installation, providing maximum density.
Each slot can accommodate one module and one connection board. The slots 1 and 2 on the left side of the motherboard are reserved for the system bus module, while the remaining slots are used for processors, I/O, or communication modules.
2.2 Redundant System Bus
The HIMax system operates on two redundant system buses: System Bus A and System Bus B.
Communication mechanism: The module is inserted into the motherboard and connected to the system bus. If both buses are running, communication will occur simultaneously on both buses.
Scalability: The system bus is based on Ethernet technology, allowing the system to span vast production lines. When using fiber optic components, the maximum extension distance of the HIMax system can reach 19.6 kilometers.
Isolation: The system bus connection between the module and the motherboard is electrically isolated, ensuring at least 1500 V insulation voltage between the processor module and each I/O module.
3. Safety standards and operating principles
3.1 Safety Integrity Level (SIL)
HIMax safety related controllers are certified for the following high standard applications:
SIL 3 (compliant with IEC 61508)
Category 4 (compliant with EN 954-1)
PL e (compliant with ISO 13849-1)
3.2 Operating Principles
The system design follows the following core security principles:
Loss of excitation trip: The system design conforms to the principle of "loss of excitation trip", which means that no electricity is required to perform safety functions. Once a malfunction occurs, the input and output signals will enter a disabled safe state.
Power on trip: HIMax can also be used for "power on trip" applications (such as fire alarm systems), but it must meet the corresponding application standards (such as line diagnosis).
Fault tolerance time (FTT): When implementing safety related communication, it is necessary to ensure that the overall response time does not exceed the fault tolerance time.
4. High availability: comprehensive redundancy design
The conceptual design of HIMax is centered around high availability. Redundancy is only used to improve availability, not to increase SIL level.
4.1 Redundancy of processor modules
The system can be configured as a standalone system or a highly available system (supporting up to 4 redundant processor modules).
Downgrading and upgrading: Even if a processor module fails or is removed, the system can continue to operate safely. When adding a new processor module during operation, it will automatically synchronize with the existing module without interrupting security related operations.
4.2 I/O module and channel redundancy
Module redundancy: Two or three I/O modules of the same type can be defined as mutually redundant.
Channel redundancy: Channels with the same number can be defined as redundant. For input channels, users can specify how the controller combines signals from two redundant channels (such as 2oo3 voting).
Connection board: In order to save wiring workload, a special connection board allows two redundant modules to be inserted into adjacent slots, while on-site connections only need to be created once.
5. Engineering and Programming: Based on SILworX
The user program is created through a programming system (PADT) consisting of a PC with SILworX tool installed.
5.1 Multi task processing
HIMax supports processing up to 32 user programs simultaneously within the processor module.
Multi tasking mode:
Mode 1: Utilize unused execution time to reduce CPU cycle time (fastest response).
Mode 2: Allocate unused time from low priority programs to high priority programs (high availability mode).
Mode 3: Wait for unused time to expire in order to maintain a fixed CPU cycle time (constant cycle).
5.2 Variables and System Parameters
Variable types: Supports local variables (VAR) and global variables (VAR_GLOBAL). Global variables allow data exchange between program organizational units (POUs).
- ABB
- General Electric
- EMERSON
- Honeywell
- HIMA
- ALSTOM
- Rolls-Royce
- MOTOROLA
- Rockwell
- Siemens
- Woodward
- YOKOGAWA
- FOXBORO
- KOLLMORGEN
- MOOG
- KB
- YAMAHA
- BENDER
- TEKTRONIX
- Westinghouse
- AMAT
- AB
- XYCOM
- Yaskawa
- B&R
- Schneider
- Kongsberg
- NI
- WATLOW
- ProSoft
- SEW
- ADVANCED
- Reliance
- TRICONEX
- METSO
- MAN
- Advantest
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bently
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- Triconex
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- Beijer
- Moxa
- Rexroth
- Johnson
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- Application field
- XP POWER
- CTI
- TRICON
- STOBER
- Thinklogical
- Horner Automation
- Meggitt
- Fanuc