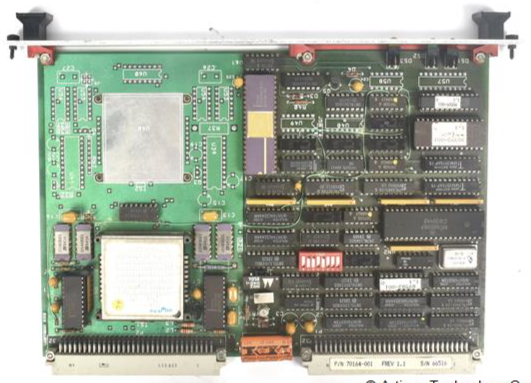
ABB SPAU 341 C Voltage Regulator
Core value: Supports independent voltage regulation of a single transformer and parallel operation of multiple transformers, with functions such as line voltage drop compensation, overcurrent/undervoltage lockout, overvoltage detection, etc., to meet the stability requirements of industrial power supply;
Module composition: It consists of an automatic voltage regulation module (SPCU 1D50), a manual voltage regulation module (SPCN 1D56), a power module (SPGU 240 A1/SPGU 48 B2), an I/O module (SPTR 6B32), and a motherboard. It supports fiber optic serial bus communication (requires SPA-ZC series bus modules).
ABB SPAU 341 C Voltage Regulator
Product basic positioning and core functions
1. Product positioning
Application scenario: Designed specifically for on load tap changers in distribution substations, the secondary voltage of the transformer is regulated by controlling tap changers to ensure stable load voltage and adapt to 50/60Hz power grids;
Core value: Supports independent voltage regulation of a single transformer and parallel operation of multiple transformers, with functions such as line voltage drop compensation, overcurrent/undervoltage lockout, overvoltage detection, etc., to meet the stability requirements of industrial power supply;
Module composition: It consists of an automatic voltage regulation module (SPCU 1D50), a manual voltage regulation module (SPCN 1D56), a power module (SPGU 240 A1/SPGU 48 B2), an I/O module (SPTR 6B32), and a motherboard. It supports fiber optic serial bus communication (requires SPA-ZC series bus modules).
2. Core Function List
Functional categories, specific abilities, and application value
Voltage control with automatic/manual dual-mode voltage regulation, adjusting the voltage to adapt to load changes through the "Raise/Lower" signal of the tap changer, and maintaining stable secondary voltage
Compensation function circuit voltage drop compensation (U ₐ), compensating for voltage loss caused by circuit resistance (R) and reactance (X) to ensure that the voltage at the remote load end meets the standard, avoiding high near end voltage/low far end voltage
Protection lockout overcurrent lockout (I>), undervoltage lockout (U<), overvoltage detection (U>), external lockout input prevents the tap changer from operating in fault states (such as short circuit, abnormal voltage), extending equipment life
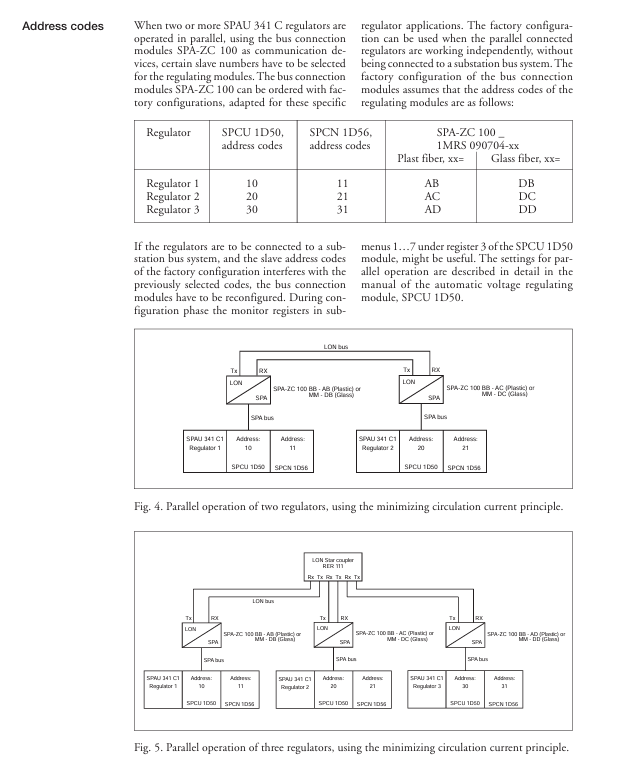
Parallel operation supports three parallel control principles: Master/Slave, Negative Reaction, and Minimizing Circulating Current. When multiple transformers supply power to the same bus, they balance the load and circulating current to avoid equipment overload
Real time self inspection of self-monitoring hardware/software, triggering IRF (Internal Relay Fault) alarm in case of failure, blocking output to improve system reliability, and reducing the risk of fault expansion
Data exchange with digital display of set/measured values, RS485 serial interface, fiber optic bus communication for convenient on-site debugging and remote monitoring, compatible with substation automation systems
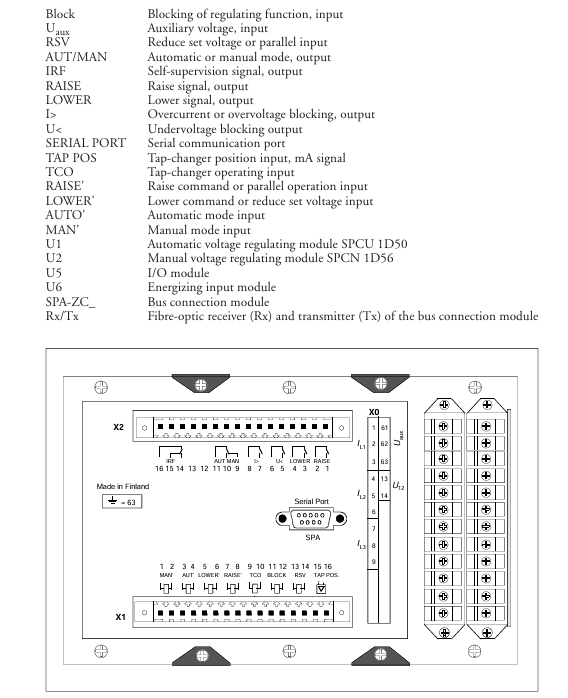
Core working principle and key parameters
1. Voltage regulation core logic
Control voltage calculation: The controller calculates the target control voltage (U ₚ) through "reference voltage (U ₛ) ± line voltage drop compensation (U_z) ± circulating current compensation (U_ci) - set voltage drop (U_rsv)", and the formula is:
Uₚ = Uₛ ± U_z ± U_ci - U_rsv
Adjustment trigger mechanism:
Compare the measured voltage (U ₘ) with the control voltage (U ₚ). If U ₘ exceeds the "bandwidth (∆ U ₛ)" range (default ± 1.5% U ₙ), initiate the first delay (T1, default 60s);
If U ₘ still exceeds the hysteresis range (∆ U ₕ, default 90% ∆ U ₛ) during the delay period, the tap changer will be triggered;
If a single action does not cause U ₘ to return to bandwidth, initiate the second delay (T2, default 30s) and repeat the adjustment until the voltage meets the standard;
The delay feature supports both "definite time limit" and "inverse time limit" (the delay is inversely proportional to the voltage deviation, and the larger the deviation, the shorter the delay).
2. Key technical parameters (core indicators)
Specific specifications for parameter categories
Voltage input rated voltage U ₙ: 100V/110V/120V (line voltage), continuous withstand voltage 2U ₙ, power consumption<0.5VA, suitable for different regional power grid rated voltages
Current input rated current I ₙ: 1A/5A (optional), 1A model can withstand 4A and 25A continuously for 10 seconds; 5A model can withstand 20A and 100A continuously for 10 seconds, compatible with current transformers (CT) of different transformation ratios
Output contact adjustment contact (Raise/Power): 250V AC/DC, continuous 5A, 0.5s on-off 30A; signal contact (lockout/alarm): 250V AC/DC, continuous 5A, compatible with tap changer drive circuit and alarm circuit
Power module SPGU 240 A1: 80~265V AC/DC (compatible with 110/230V mainstream voltage); SPGU 48 B2: 18~80V DC (compatible with low-voltage DC system) to meet different substation power configurations
Environmental adaptability: working temperature -10~+55 ℃, storage temperature -40~+70 ℃, humidity 5%~95%, non condensing, protection level IP54 (embedded installation), suitable for industrial harsh environment, dustproof and splash proof
Communication capability: Fiber optic serial bus, ASCII encoding, speed 4800/9600 Bd, supports SPA-ZC series modules (SPA-ZC 17/21 for plastic fiber optic and SPA-ZC 17 MM/21 MM for glass fiber optic) to achieve data exchange among multiple regulators, supports parallel operation and remote monitoring
Core configuration and operation process
1. Key configurations before installation (mandatory steps)
(1) Hardware wiring specifications
Core input/output wiring:
Voltage input: X0/13-14 terminals are connected to the secondary side line voltage of the transformer (U ₁₂, 100/110/120V);
Current input: Connect the X0 terminal to three-phase current (1A to 1-3/4-6/7-9, 5A to 1-2/4-5/7-8), and a single transformer can only measure the L1 phase current (selected through SGF2/6/7 software switch);
Control output: X2 terminal outputs Raise/Power signal to the tap changer, X1 terminal connects external control signal (automatic/manual switching, external locking);
Grounding requirement: Connect the protective ground through the X0/63 terminal to ensure reliable grounding between the module and chassis, avoiding electromagnetic interference.
(2) Core parameter setting (configured through panel buttons or serial port)
Parameter Name Setting Range Default Values Key Role
Reference voltage U ₛ 0.85~1.15U ₙ 1.00U ₙ Set target secondary voltage
Bandwidth ∆ U ₛ 0.60~9.00% U ₙ 1.50% U ₙ Voltage fluctuation tolerance range, avoiding frequent adjustments
Delay T1/T2 0.0~300s 60s/30s to prevent momentary voltage fluctuations from triggering misoperations
Overcurrent lockout I>1.00~2.00I ₙ 2.00I ₙ When overcurrent occurs, voltage regulation is prohibited to protect the tap changer
Line compensation U ᵣ/U ₓ 0.0~25.0% U ₙ 0.0% U ₙ Compensation line impedance voltage drop, U ᵣ=√ 3I ₗₒₐ𝒹 R × 100/U ₙ, U ₓ=√ 3I ₗₒₐ𝒹 X × 100/U ₙ
2. Operation mode and process
(1) Automatic voltage regulation mode (default, SPCU 1D50 dominant)
Trigger condition: If U ₘ exceeds the range of ∆ U ₛ and lasts for T1 time, the controller outputs Raise/Power signal to drive the tap changer;
Compensation logic: Based on the load current (I ₗₒₐ𝒹) and the line parameters (R/X), U_z is automatically calculated to increase the remote voltage (such as a line voltage drop of 2V, U_ is automatically increased by 2V).
(2) Manual voltage regulation mode (dominated by SPCN 1D56)
Activation method: Switch through the panel "MAN" button or external "MAN '" input, and the MAN indicator light will turn on;
Operation steps: Press the "Raise"/"Lower" button, the corresponding indicator light flashes → Confirm that there is no lock (I>/U<light is not on) → Press the corresponding button again to trigger the tap changer action, and the TCO light is on to indicate that the tap changer is running.
(3) Multiple transformers running in parallel (three modes)
Parallel mode is suitable for key configurations in applicable scenarios
Master/Slave mode: The main regulator of a transformer with the same capacity and tap voltage measures voltage/current and controls it. The slave regulator follows the action of the main regulator and needs to be directly wired to connect the master slave "up/down" output and input
Negative Reaction mode: Transformers with different capacities and tap voltages do not require physical connections. The "load phase shift" parameter is set, and the controller compensates for the voltage deviation between the measured phase shift and the set value, adapting to the parallel connection of dispersed substations
In scenarios where there are large differences in transformation ratio/capacity and large fluctuations in reactive load, the Minimum Circulating Current mode needs to be paired with the SPA-ZC 100 bus module. Multiple regulators exchange current/phase shift data, calculate and minimize circulating current, and support up to 3 parallel regulators

Fault handling and maintenance
1. Interpretation of status indicator lights (core fault diagnosis basis)
Suggestions for handling the meaning of indicator light status
Module status (MS): red, constantly on, unrecoverable fault (such as hardware damage). Power off and restart, if ineffective, check the connection between the I/O module and the motherboard, and contact after-sales service
Overcurrent lockout (I>), red constant light. If the current exceeds the set value, check if the load is overloaded and if the CT wiring is normal. After troubleshooting, reset
Under voltage lockout (U<), red constant light, voltage lower than U<set value (default 0.7U ₙ), check the grid voltage. If the grid is normal, adjust U<set value
Overvoltage detection (U>): The red constant light indicates that the voltage is higher than the set value (default is 1.25U ₙ), triggering "rapid voltage reduction" without manual intervention. After the voltage is restored, it will automatically exit
Self check fault (IRF): The hardware/software fault record of the red module is constantly on, and the display screen shows the fault code (such as 1-030=program memory fault). Contact after-sales maintenance for assistance
2. Common fault codes and their solutions
Fault code, fault type, handling measures
1-004 voltage regulation control circuit fault check tap changer "up/down" coil wiring, confirm power module output voltage
1-030 Program Memory (ROM) malfunction module internal failure, SPCU 1D50 module needs to be replaced
1-050 working memory (RAM) failure, power off and restart. If the failure persists, replace the motherboard
1-051 Parameter Memory (EEPROM) Failure: Format EEPROM with V167 parameters and reconfigure parameters
3. Key points of daily maintenance
Regular inspection: Check the terminal wiring for looseness and proper heat dissipation every month, and clean the module dust screen (if any) every quarter;
Parameter backup: Backup parameters (such as U ₛ, ∆ U ₛ, U ᵣ/U ₓ) through serial software to avoid module failure causing parameter loss;
Spare parts preparation: It is recommended to reserve key spare parts such as power module (SPGU 240 A1) and I/O module (SPTR 6B32) to shorten the time for fault repair.
Installation and selection suggestions
1. Installation requirements
Environmental conditions: Avoid high temperature heat sources (such as the transformer body), installation location temperature ≤ 55 ℃, humidity ≤ 95% non condensing, protection level IP54 (requires compatible casing);
Wiring specifications: Voltage/current signal lines and power lines should be laid separately. The length of the fiber optic bus cable should be ≤ 100m (plastic fiber)/2km (glass fiber), and the bending radius should be ≥ 10 times the cable diameter;
Size and fixation: Adopting embedded installation, the panel opening size needs to match (214 × 139mm ± 1mm), and the installation depth can be adjusted through the SPA-ZX series height increasing frame (3 specifications).
2. Selection and matching
Power module selection: Select SPGU 240 A1 (80~265V AC/DC) for conventional scenarios, and SPGU 48 B2 (18~80V DC) for low-voltage DC systems;
Bus module selection: SPA-ZC 17 BB/21 BB for plastic fiber optic, SPA-ZC 17 MM/21 MM for glass fiber optic, and SPA-ZC 100 BB/MM for parallel minimum circulating current;
Cable selection: 100V shielded wire is used for voltage signals, CT dedicated shielded wire is used for current signals, and ABB recommends plastic/glass fiber optic cables (such as SPA-ZP 25A05) for optical fibers.
- ABB
- General Electric
- EMERSON
- Honeywell
- HIMA
- ALSTOM
- Rolls-Royce
- MOTOROLA
- Rockwell
- Siemens
- Woodward
- YOKOGAWA
- FOXBORO
- KOLLMORGEN
- MOOG
- KB
- YAMAHA
- BENDER
- TEKTRONIX
- Westinghouse
- AMAT
- AB
- XYCOM
- Yaskawa
- B&R
- Schneider
- Kongsberg
- NI
- WATLOW
- ProSoft
- SEW
- ADVANCED
- Reliance
- TRICONEX
- METSO
- MAN
- Advantest
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bently
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- Triconex
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- Beijer
- Moxa
- Rexroth
- Johnson
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- Application field
- XP POWER
- CTI
- TRICON
- STOBER
- Thinklogical
- Horner Automation
- Meggitt
- Fanuc
- Baldor