Honeywell Experion PKS Series C I/O
Series C I/O Definition: It is a series of traditional and special function input/output signal interface devices that support local software configuration, share the same external specifications with the C300 controller, and use the same installation system.
Series C I/O Mark II: It is an enhancement of the existing Series C platform in terms of IO modules, related IOTA, IO links, power supply, distribution, and cabinet infrastructure, making it more cost-effective. The design style remains unchanged, but it does not support any PM I/O.
Series C Pulse Input Module (SCPIM): capable of high-precision pulse counting, with 8 input channels, some of which can be configured as dual inputs, and the last 2 channels can also be configured as fast cut-off outputs. It has multiple functions and is different from Series A PIM in terms of external specifications, redundancy support, and other aspects.
Honeywell Experion PKS Series C I/O
Series C I/O Usage
Comparison with Process Manager I/O: There are differences in non-volatile memory, IOL speed, HART support, master-slave module separation, installation environment, and configuration of memory backup.
Series C I/O Definition: It is a series of traditional and special function input/output signal interface devices that support local software configuration, share the same external specifications with the C300 controller, and use the same installation system.
Series C I/O Mark II: It is an enhancement of the existing Series C platform in terms of IO modules, related IOTA, IO links, power supply, distribution, and cabinet infrastructure, making it more cost-effective. The design style remains unchanged, but it does not support any PM I/O.
Series C Pulse Input Module (SCPIM): capable of high-precision pulse counting, with 8 input channels, some of which can be configured as dual inputs, and the last 2 channels can also be configured as fast cut-off outputs. It has multiple functions and is different from Series A PIM in terms of external specifications, redundancy support, and other aspects.
Universal Input/Output (UIO) module: 32 channels can be independently configured into multiple types, supporting multiple functions. There are differences in temperature range and channel configuration compared to existing Series C AI, AO, DI, DO modules.
Low level analog input (LLAI) module: used for low-voltage devices, supports 16 channels, accepts millivolt level temperature input, has many characteristics, and differs from AI-LLMUX modules in terms of channel quantity and other aspects.
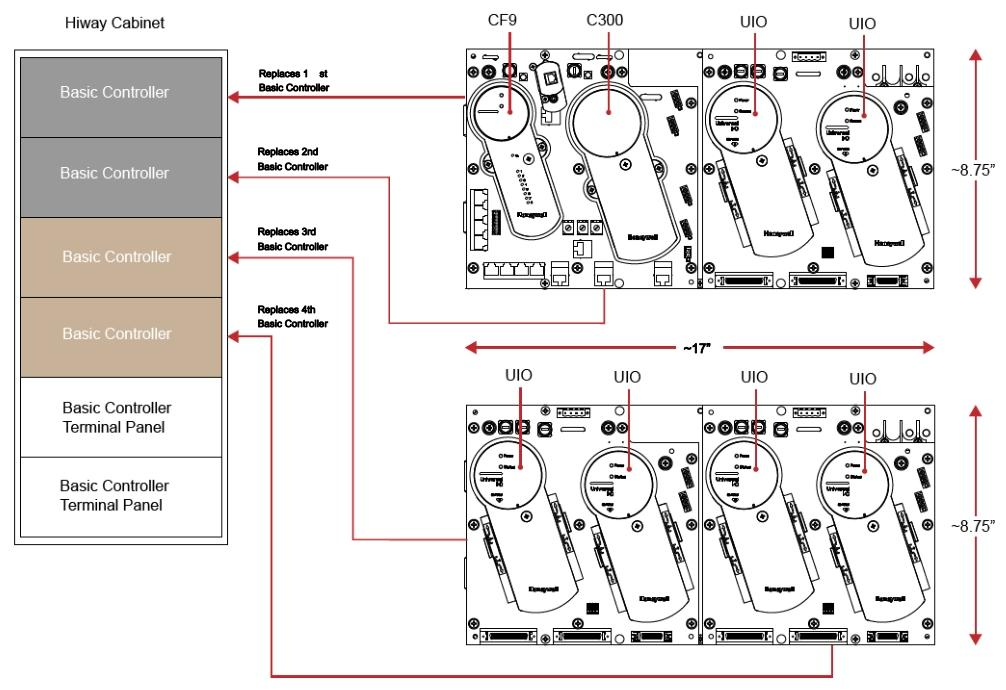
Overview of Universal Horizontal Input/Output (UHIO): It can replace the TDC 2000 basic controller and expansion controller, and introduces the mapping, functions, hardware, differences from Series C IOTA, and certification related content with CB/EC rack.
Series C I/O Planning and Design
General planning reference: Referring to relevant planning documents, introduce the appearance of Series C I/O and the functional characteristics of various modules.
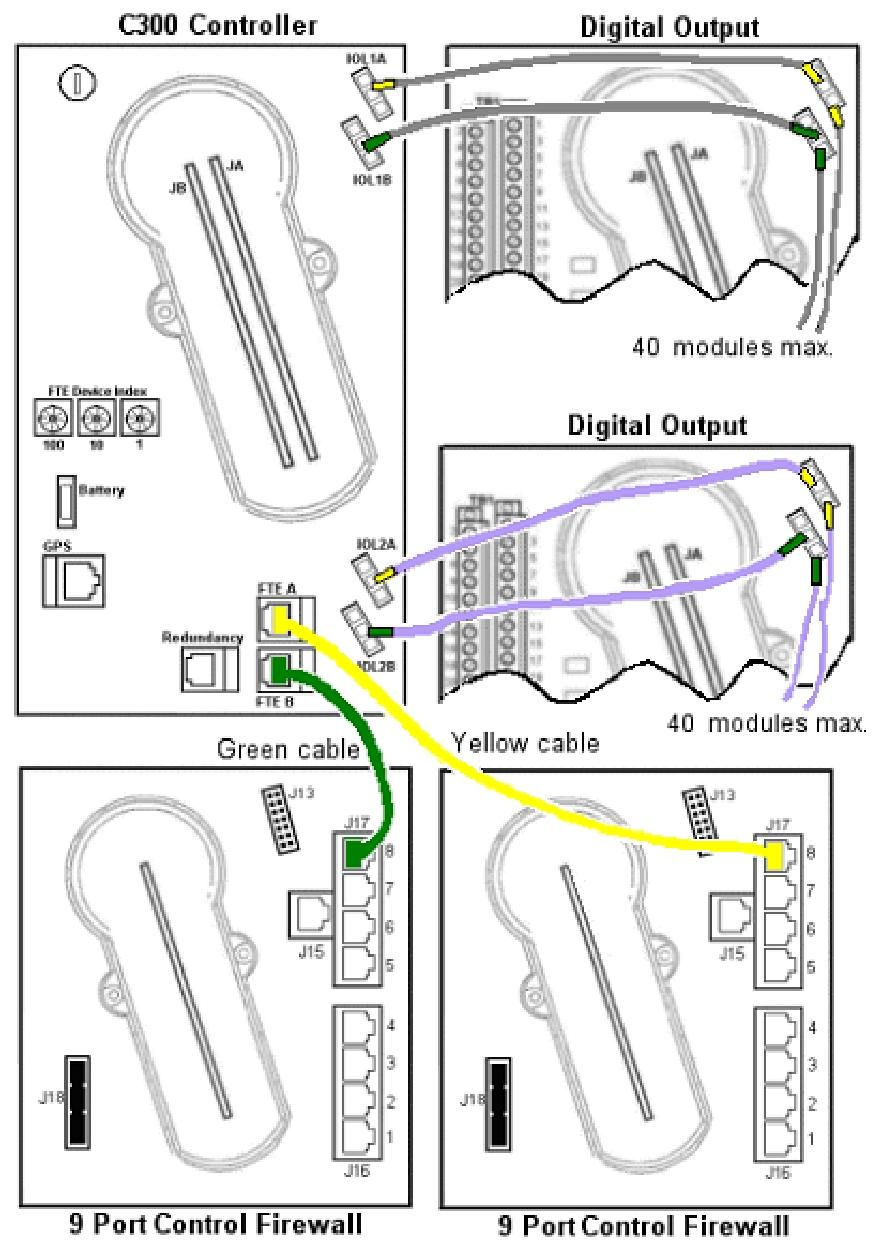
Compared to the C300/CN100 topology structure, it follows certain topology rules, involving redundancy, switching, initialization, number of I/O links, performance, capacity, and other aspects.
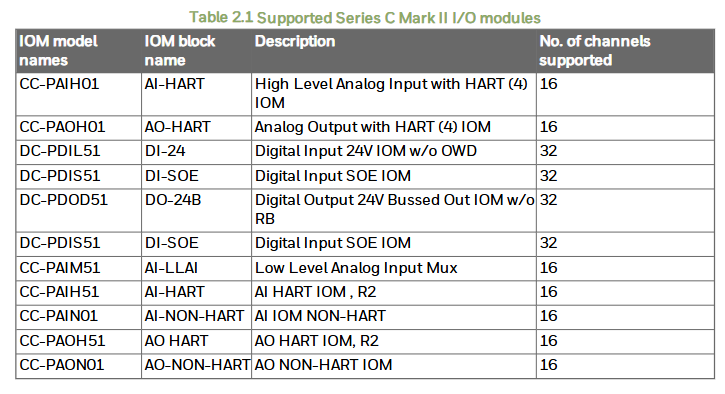
Supported Series C I/O modules: List various module models, names, descriptions, and compatibility matrices, differences between different module models, identification methods, redundant configuration considerations, and lifecycle changes.
Supported Series C I/O options: including multiple options, as well as checking I/O libraries, IOM function blocks, channel function blocks, defining module inclusion relationships, and calculating UIO temperature derating and internal dissipation.
I/O link performance specifications: Introduces the concept of link units, transmission rates, as well as link unit utilization, reducing I/O link traffic, event collection, PV, and reverse calculation scanning.
Universal Input/Output Module 2 (UIO-2): In addition to all the functions of UIO, it also has enhanced features, which differ from UIO-1 in multiple aspects.
Series C I/O installation and upgrade
Installation statement: Emphasize that equipment installation must comply with relevant electrical specifications, pay attention to electrostatic discharge protection, and ensure safe operation in hazardous areas.
Installing Series C IOTA onto the carrier: Certain prerequisites must be met and specific steps must be followed for installation.
Installing the I/O module to IOTA: There are corresponding prerequisites and installation steps, and attention should be paid to the use of screws during installation.
Grounding and power considerations for IOTA board: Introduces the connection and power testing methods and precautions for IOTA board.
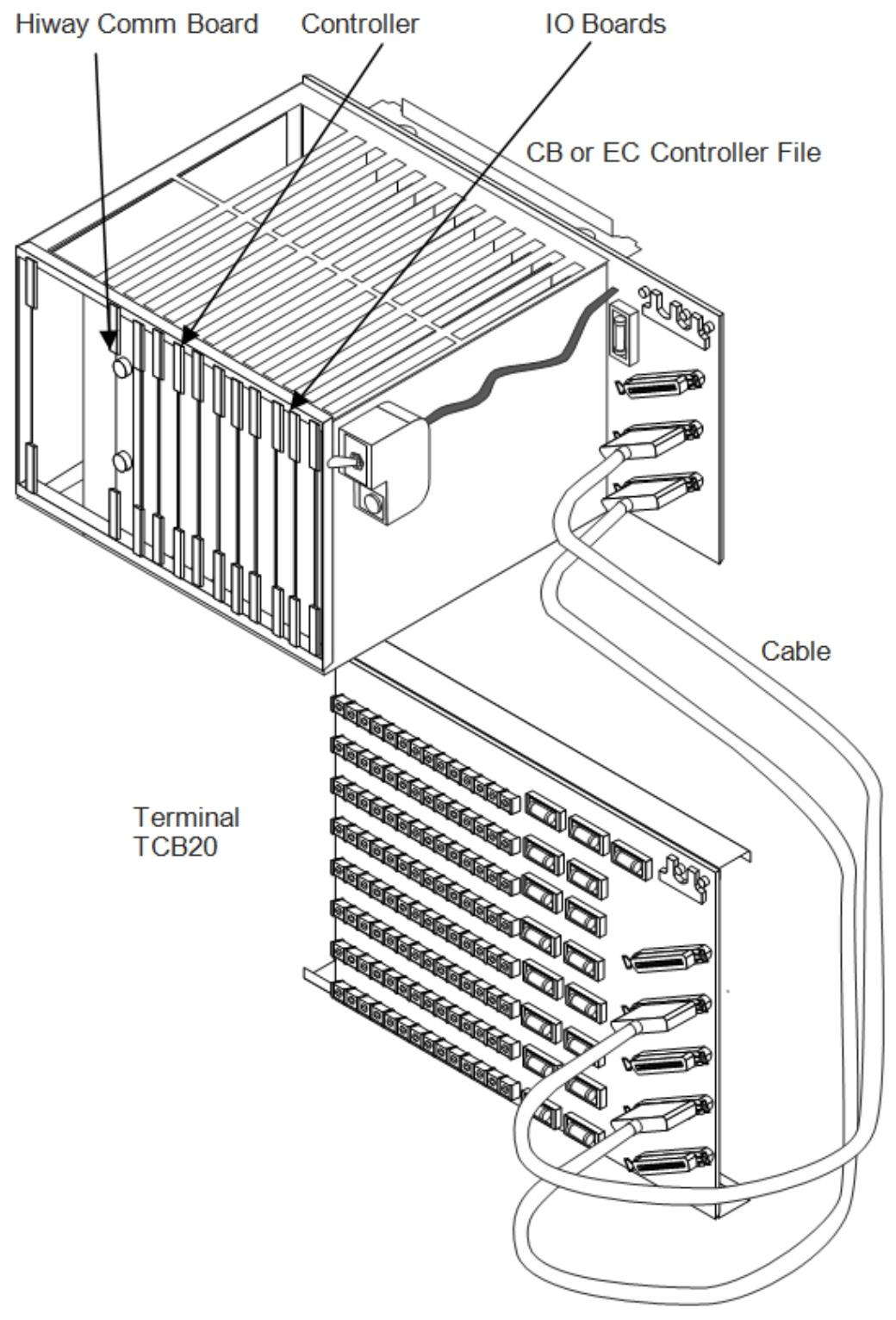
Connecting IOM and field devices through I/O terminal components: illustrates the relationship between IOM types and auxiliary hardware, and related tables.
Power supply for Series C system: The power system provides multiple functions, similar to the Process Manager power system.
Series C IOTA board fuse: All IOTAs must contain at least one fuse, and the relevant properties are described.
Series C IOTA Pin Allocation
Detailed introduction of various IOTA models, including analog input, output, digital input, output, low-level analog input multiplexer, speed protection module, servo valve locator module, universal input/output, etc., involving terminal block wiring, field wiring, module protection, allowed wiring resistance, board connection, and other contents.
Series C PIM Connection
Connection diagram: shows the various components and signal processing flow of PIM connection.
On site device output stage types: Introduces various output stage types and their compatibility with PIM.
PIM resistor bias terminal block: used for installing appropriate bias resistors, introduces related operations.
Definition and allocation of pins for each terminal block: including signal definition and pin allocation for TB1, TB2, TB3, and TB4.
Pulse verification enabled: Select the flow to be verified in Control Builder.
Connection with other devices: Introduces the connection methods with ST500 dual pulse simulator, dual current devices, other sensor types, as well as input threshold selection and recommended cable types.

Series C Universal Horizontal Input/Output (UHIO) Components
Introduced the system and grounding audit checklist for horizontal C300/CF9 IOTA, horizontal UHIO IOTA, I/O connectors, TDC 2000 system, UHIO components, installation, general regulatory compliance, COTS AC-DC power supply, protective grounding, and environmental characteristics.
Universal Input/Output (UIO) module for rail installation
Advantages: Low space consumption, high cost-effectiveness, and simple component relocation.
Physical description: Introduces the composition of the components and the model, size, weight, and other information of some components.
Input/Output Link (IOL) Management: Supports specific UIO IOTA versions and DIN rail installations, and introduces relevant cables.
Single mode FOE: It is a necessary component for installing UIO on rails, and its component options, installation positions, etc. are introduced.
System wiring: It demonstrates the end-to-end connection of UIO modules installed on rails in a single cabinet and adjacent cabinets.
Power requirements: Powered by a+24VDC remote industrial grade power supply, including voltage range, power consumption, related protection, wiring, fuse terminal blocks, and circuit breakers.
Institutional certification: Possessing certifications such as CE, CTick, HAZLOC, etc.
Environmental conditions: Clearly defined environmental parameters such as temperature and humidity for work and storage.
Module assembly, installation, connection, disassembly: Detailed introduction of relevant steps and precautions.
Replaceable spare parts: lists the models and names of some replaceable spare parts.
Reference for Series C I/O Configuration Form
Determine redundancy: IOM blocks represent hardware instances of I/O modules, configurable redundancy, and generate system events and alerts.
Switching and secondary readiness: Switching is the process of a secondary module becoming a primary state, and the readiness state of the secondary module determines whether it can take over control functions.
Fault conditions and switching: Some faults may cause switching, such as primary module power failure, while others may not.
Configuration tool: Creating control policies using the Expert Control Builder requires multiple operations, and the IOM must be present during configuration loading.
Each tag configuration: detailed introduction Main、Server History、Server Displays、Control Confirmation、Identification、QVCS、Calibration、HART Status The parameter configuration method and content of the waiting tab.
- ABB
- General Electric
- EMERSON
- Honeywell
- HIMA
- ALSTOM
- Rolls-Royce
- MOTOROLA
- Rockwell
- Siemens
- Woodward
- YOKOGAWA
- FOXBORO
- KOLLMORGEN
- MOOG
- KB
- YAMAHA
- BENDER
- TEKTRONIX
- Westinghouse
- AMAT
- AB
- XYCOM
- Yaskawa
- B&R
- Schneider
- Kongsberg
- NI
- WATLOW
- ProSoft
- SEW
- ADVANCED
- Reliance
- TRICONEX
- METSO
- MAN
- Advantest
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bently
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- Triconex
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- Beijer
- Moxa
- Rexroth
- Johnson
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- Application field
- XP POWER
- CTI
- TRICON
- STOBER
- Thinklogical
- Horner Automation
- Meggitt
- Fanuc
- Baldor