Toshiba Discrete IGBT Product Technology Analysis and Application Guide
A Comprehensive Analysis of Toshiba's Discrete IGBT Products: Technological Evolution, Product Line, and Core Applications
1. Overview of IGBT Technology and Toshiba Product Features
1.1 Basic principles and advantages of IGBT
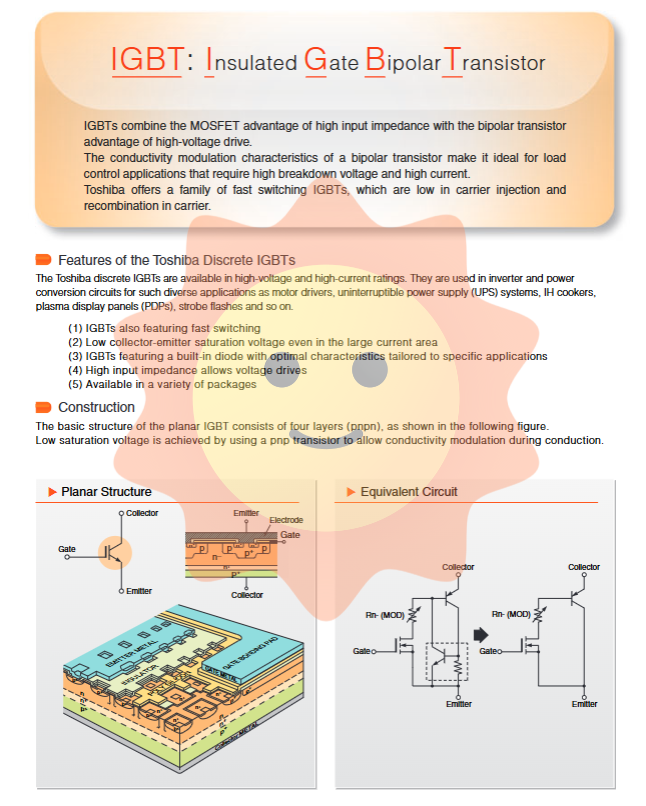
IGBT is a composite power semiconductor device with a four layer (PNPN) structure. Its basic structure (planar type) is shown in the figure, which achieves carrier modulation effect during conduction period through PNP bipolar transistor, thereby obtaining lower conduction voltage drop (VCE (sat)) under high voltage. Its equivalent circuit can be regarded as a MOSFET driving a PNP bipolar transistor.
The core advantage lies in:
High input impedance: voltage driven, simple driving circuit.
Low conduction voltage drop: Thanks to the conductivity modulation effect of bipolar structure, especially in high voltage and high current regions, it has obvious advantages.
High voltage withstand and high current capability: suitable for high-voltage power conversion applications.
1.2 Core characteristics of Toshiba discrete IGBT
Toshiba's discrete IGBT product line aims to meet diverse industrial and consumer electronics needs, with key features including:
High speed switch performance: Through optimized carrier lifetime control technology, fast switching is achieved and switch losses are reduced.
Excellent saturation voltage drop characteristics: Even under high current conditions, it can maintain a low VCE (sat), which helps reduce conduction losses.
Built in optimized diodes: Many models integrate feature optimized anti parallel fast recovery diodes (FRD) or freewheeling diodes (FWD) to simplify peripheral circuits and improve system reliability.
Rich packaging options: Provides a variety of packaging options from compact TSON-8, SOP-8 to high-power TO-220 series, TO-3P series, etc., to adapt to different power levels and installation requirements.
High robustness: Designed for harsh industrial environments, it has good impact resistance and durability.
2. Technological development trends and intergenerational evolution
Toshiba IGBT technology continues to iterate and has launched multiple generations of products for different voltage levels and application requirements. Its development trend is mainly reflected in reducing VCE (sat), improving switching speed, enhancing robustness, and adopting new structures such as trench gate and RC-IGBT.
The following table summarizes Toshiba's technological development path on IGBTs of different voltage levels:
Generation and main characteristics of voltage level development
1200 V (1) 3rd generation (high robustness): Optimized carrier injection and thinner wafers to achieve low VCEsat and high robustness.
(2) 5th generation (soft switch): adopts trench gate structure to reduce VCEsat.
(3) Generation 6.5: Adopting RC (reverse conduction) structure.
900-1500 V (1) 4th generation (soft switch): trench gate structure achieves low VCEsat.
(2) 5th generation (soft switch): optimized carrier injection combined with trench gate.
(3) 6th generation (soft switch): thinner wafers and finer processes.
(4) Generation 6.5: RC structure.
600 V (1) 3rd generation (high robustness): Optimized carrier injection and thin wafers to achieve low VCEsat and high robustness.
(2) 4th generation (high-speed switch): Optimize carrier injection to improve switch speed.
(3) 4th generation (soft switch): trench gate reduces VCEsat.
(4) 6th generation (low VCEsat): thin wafers and fine craftsmanship.
(5) 5th generation (soft switch): thin wafer.
(6) 6th generation (soft switch): thin wafers and fine craftsmanship.
400 V (1) 5th generation (flash): Trench gate structure achieves low VCEsat.
(2) 6th generation (flash): Trench gate and optimized wafer achieve high current.
(3) 7th generation (flash): Optimized wafer and fine process to achieve high current.
300-400 V (1) 4th generation (plasma display): Trench gate and lifetime control achieve low VCEsat and high IC.
(2) 5th generation (plasma display): Fine craftsmanship reduces turn-on losses.
(3) 6th generation (plasma display): Optimizing wafers and fine processes to reduce turn-on losses.
(4) 7th generation (plasma display): thinner wafers and finer processes.
Taking the VCE (sat) characteristic curve of IGBT with 900V soft switching as an example, Toshiba continuously lowers the saturation voltage drop and improves energy efficiency through continuous carrier injection optimization and process improvement.
3. Overview of Product Lines and Model Naming Rules
3.1 Product Line Matrix
Toshiba discrete IGBTs are classified by application and characteristics to form a complete product matrix, covering a wide range of voltages from 600V to 1200V and even higher, and currents from a few amperes to hundreds of amperes. There are various packaging forms, including TSON-8, SOP-8, TO-220SIS, TO-220SM (MX6), TO-3PN, TO-3P (LH), etc.
The main application series include:
Universal frequency converter/motor drive: high robustness series, high-speed switch (FS) series.
Soft switch application: a series of soft switches designed specifically for resonant transformations, such as induction cookers and microwave ovens.
Power factor correction (PFC).
Flash application: Low gate driving voltage series.
Plasma Display Panel (PDP) driver.
3.2 Model Naming Rules
Using Toshiba model GT 60 M 3 03 A as an example for decoding:
GT: Product prefix, representing discrete IGBT.
60: Rated collector current (DC), in amperes (A).
M: Rated voltage code. Refer to the voltage code table (e.g. M represents 900V).
3: Channel type and structural code. 1=N-channel, 2=P-channel, 3=N-channel with built-in freewheeling diode, R=RC-IGBT with built-in freewheeling diode.
03: Serial number.
A: Version number.
Example of voltage code representation: C=150V, D=200V,... J=600V, M=900V, Q=1200V, etc.
4. Key application scenarios and selection guidelines
4.1 General frequency conversion and motor drive
This is the most traditional core market for IGBT. Toshiba offers a complete solution from the 3rd generation high robustness series to the 4th generation high-speed switch (FS) series.
High robustness series (such as GTxQ101/301, GTxJ101/301): For industrial motor drives and general purpose frequency converters, the switching frequency can usually reach 20kHz, emphasizing reliability and durability.
High speed switch series (FS series, such as GT30J121): The switching frequency can reach 50kHz, and the switching loss is reduced through optimization, making it suitable for occasions with higher efficiency and frequency requirements.
Technical advantages: Low and flat temperature characteristic VCE (sat), as well as built-in optimized fast recovery diode (FRD), bring low conduction loss and excellent reverse recovery characteristics.
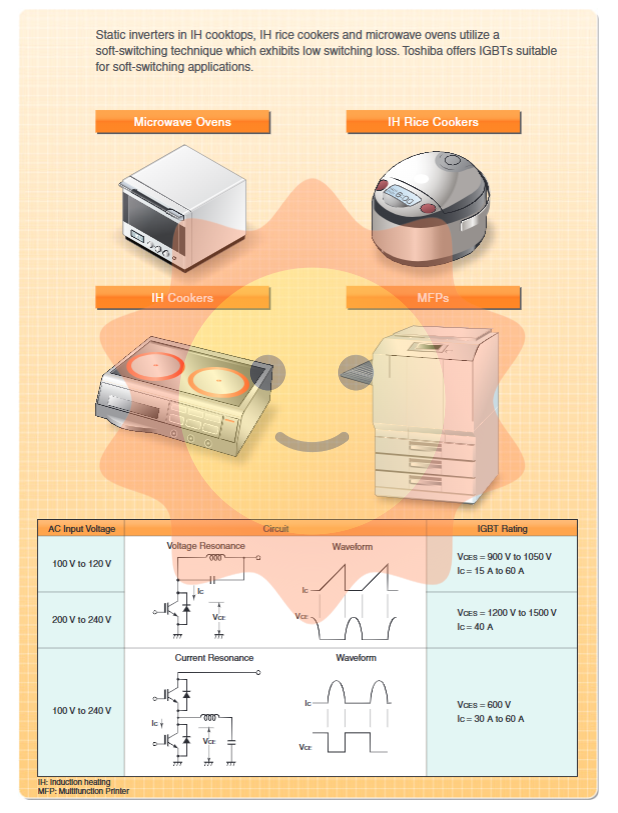
4.2 Soft switch applications (electromagnetic heating, microwave ovens, etc.)
In situations where voltage or current resonant soft switching technology is used in IH cookware, microwave ovens, etc., switching losses are significantly reduced. Toshiba offers an IGBT series optimized for soft switching.
Voltage range: Depending on the input voltage (AC 100V/200V), specifications such as 600V, 900V, 1200V, etc. are mainly selected.
Product series: covering 4th to 6.5th generation technologies, such as GTxJ32x (600V), GTxM32x (900V), GTxN32x (1000V) and other models, many of which have built-in FRD/FWD.
Latest technology -6.5th generation RC-IGBT: such as GTxxMR21/GTxxNR21 series. RC-IGBT integrates IGBT and FWD on a single chip, eliminating the necessity of discrete diodes and reducing thermal resistance through reverse conduction structure, making it more environmentally friendly and compact. It allows the junction temperature (Tj) to increase to 175 ° C, improving power density and reliability.
4.3 Flash application
With the miniaturization of digital cameras, there is a demand for small size and low driving voltage of switch devices in flash circuits.
Low gate driving voltage: Toshiba offers a 2.5V-4.0V gate driving series (such as GT5G133, GT8G151), which can directly use the camera's internal 3.3V or 5V power supply to simplify the circuit.
High pulse current capability: Despite its small size (TSON-8, SOP-8 packaging), it can withstand pulse currents of hundreds of amperes (such as 130A-200A).
Integrated protection: Typically, a Zener diode is integrated between the gate and emitter to provide ESD protection.
4.4 Plasma display panel driver
In high current PDP sustain driving circuits, IGBT gradually replaces parallel MOSFET due to its excellent current conduction capability.
Voltage level: mainly providing 300V, 400V, and 600V products.
Packaging: TO-220SIS, TO-220SM and other surface mount packaging are commonly used for compact layout.
Features: Emphasize low VCE (sat) to reduce conduction losses, as well as good pulse current handling capability.
5. Packaging and Product Lifecycle Management
Toshiba offers a wide range of packaging options to meet the needs of different heat dissipation, power, and installation methods. The document provides detailed dimension drawings of key packages such as TO-220SM (MXN) and TSON-8 for PCB design and heat dissipation design reference.
In addition, Toshiba implements transparent management of the product lifecycle. The document clearly lists old models that are in the final stage or have been discontinued, and provides recommended alternative new products to help customers smoothly complete design migration and ensure supply chain continuity.
- ABB
- General Electric
- EMERSON
- Honeywell
- HIMA
- ALSTOM
- Rolls-Royce
- MOTOROLA
- Rockwell
- Siemens
- Woodward
- YOKOGAWA
- FOXBORO
- KOLLMORGEN
- MOOG
- KB
- YAMAHA
- BENDER
- TEKTRONIX
- Westinghouse
- AMAT
- AB
- XYCOM
- Yaskawa
- B&R
- Schneider
- Kongsberg
- NI
- WATLOW
- ProSoft
- SEW
- ADVANCED
- Reliance
- TRICONEX
- METSO
- MAN
- Advantest
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bently
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- Triconex
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- Beijer
- Moxa
- Rexroth
- Johnson
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- Application field
- XP POWER
- CTI
- TRICON
- STOBER
- Thinklogical
- Horner Automation
- Meggitt
- Fanuc
- Baldor