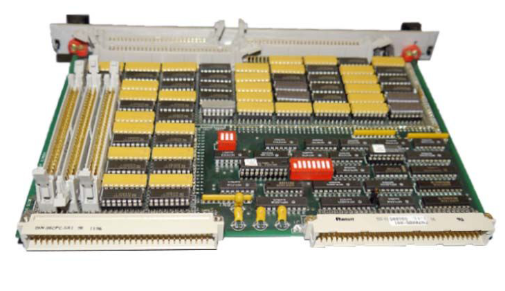
Toshiba T1-16S Programmable Controller I/O Module Detailed Explanation
TOSHIBA T1-16S Programmable Controller I/O Module System
In industrial automation control systems, the scalability and modular design of programmable logic controllers (PLCs) are key to achieving flexible control. The T1-16S programmable controller launched by Toshiba is widely used in small and medium-sized control scenarios due to its compact structure, rich I/O module options, and reliable network communication capabilities. This article will be based on the "T1-16S User Manual - I/O Module" to deeply analyze the configuration, functions, installation, and communication integration of its I/O module system, providing a comprehensive technical reference for automation engineers.
T1-16S System Architecture and Modular Scalability
The T1-16S body has basic digital input and output functions, and supports up to 8 I/O module connections through the right-hand expansion interface. If all 16 point modules are used, the system can be expanded to 144 I/O points, fully meeting the control needs of most small and medium-sized devices. The system adopts 5VDC internal power supply, with a maximum output current of 1.5A. However, the actual available current needs to deduct the power consumption of the 24Vdc auxiliary power supply, handheld programmer HP911A, and RS-485 port. Therefore, power capacity verification must be performed when configuring the module.
Rich types of I/O modules and their technical specifications
T1-16S offers up to 10 types of I/O modules, covering digital, analog, and specialized functional requirements:
Digital quantity module:
DI116M: 16 point DC input (24Vdc, 5mA), supports source/drain wiring, and has an ON/OFF delay of 10ms.
DO116M: 16 point transistor output (24Vdc, 100mA/point), supports current sink output, fast response speed (ON delay 1ms, OFF delay 2ms).
DD116M: A combination module with 8-point DC input and 8-point DC output, saving installation space.
RO108M: 8-point relay output, supports AC/DC loads (240Vac/24Vdc, 1A/point), suitable for driving contactors, low-power motors, etc.
Analog module:
The input modules AD121M (0-5V/0-20mA) and AD131M (± 10V) both have a 12 bit resolution, a conversion period of 2ms, and an overall accuracy of ± 0.5% FS at 25 ℃.
The output modules DA121M (0-20mA) and DA131M (± 10V), both with 12 bit resolution, can accurately convert the digital quantities in the controller into on-site signals.
Specialized functional module:
TC111M: Thermocouple input module, supporting K, J, E type thermocouples and mV signals, with a resolution of up to 0.3 ℃, suitable for precise temperature monitoring.
FR112M: TOSLINE-F10 remote station module, used for high-speed data connection with the upper level T series PLC, with a transmission speed of up to 750kbps.
DN111M: DeviceNet slave module, compliant with ODVA standards, supports up to 16 word input/output data exchange, and achieves integration with mainstream device networks.
Deep integration of network communication module
TOSLINE-F10 remote communication:
The FR112M module enables T1-16S to be connected as a slave to the Toshiba high-speed bus network. Its data is exchanged through fixed allocation of special registers SW34 (send) and SW35 (receive). The system has a comprehensive RAS (reliability, availability, maintainability) information management system. In case of communication failure, the special relay S00D will be turned on to ensure that the system is known and controllable.
DeviceNet fieldbus integration:
The DN111M module seamlessly integrates T1-16S into a wider device layer network. The module configures the node address (0-63), network speed (125/250/500kbps), and data size (4 to 16 words) through DIP switches. Its status is clearly indicated by dual color LEDs and interacts with T1-16S through RW registers (status/command) and D registers (I/O data), following the allocation rules of "OPT" type modules.
I/O allocation and register mapping rules
T1-16S identifies physical modules through the 'I/O allocation table'. The allocation method can be automatically scanned or manually edited. Register allocation follows strict rules:
The main station occupies a fixed X+Y 4W (XW00, XW01, YW02, YW03).
Ordinary I/O modules allocate consecutive XW or YW registers in sequence.
FR112M (TL-F type) is fixed with SW34/SW35.
The OPT type modules such as DN111M do not use XW/YW, but are mapped to RW240-RW255 (status/command) and D4000-D4095 (data area). Please note that the total data volume of all OPT modules must not exceed 96 words, otherwise it may cause system errors.
Practical Guide for Installation, Configuration, and Diagnosis
Safety first: The installation and disassembly of all modules must be carried out under power-off conditions to prevent electric shock or equipment damage.
Installation steps: Remove the right expansion port cover plate, insert the module along the guide rail and lock it. When disassembling, it is necessary to simultaneously press the upper and lower locking buckles.
Status visualization: The 16 point LED on the T1-16S body can flexibly display the I/O status of modules on the body or any slot by setting the value of the special register SW54, greatly facilitating on-site debugging and diagnosis.
Configuration tool: For DeviceNet networks, the "DeviceNet Wizard" configuration tool provided by Toshiba can be used, or the DN111M EDS file can be downloaded from the ODVA official website and used in other mainstream configuration software.
Key points of system design and application
Power planning: It is necessary to calculate the total current of 5VDC for all modules (especially analog and communication modules with high power consumption) to ensure that it does not exceed the power supply capacity of the main unit under specific operating conditions.
Module layout: FR112M must be installed at the far right end; There is no limit to the location of DN111M, but only one is allowed in a system.
Environment and Compliance: When DN111M is used in systems that comply with CE certification, it is necessary to strictly follow the manual requirements to install magnetic rings on the cables, implement shielding layer grounding, and lay the cables in metal conduit slots.
Programming precautions: Avoid directly dividing SW54 to avoid accidentally changing the value of adjacent register SW55.
- ABB
- General Electric
- EMERSON
- Honeywell
- HIMA
- ALSTOM
- Rolls-Royce
- MOTOROLA
- Rockwell
- Siemens
- Woodward
- YOKOGAWA
- FOXBORO
- KOLLMORGEN
- MOOG
- KB
- YAMAHA
- BENDER
- TEKTRONIX
- Westinghouse
- AMAT
- AB
- XYCOM
- Yaskawa
- B&R
- Schneider
- Kongsberg
- NI
- WATLOW
- ProSoft
- SEW
- ADVANCED
- Reliance
- TRICONEX
- METSO
- MAN
- Advantest
- STUDER
- KONGSBERG
- DANAHER MOTION
- Bently
- Galil
- EATON
- MOLEX
- Triconex
- DEIF
- B&W
- ZYGO
- Aerotech
- DANFOSS
- Beijer
- Moxa
- Rexroth
- Johnson
- WAGO
- TOSHIBA
- BMCM
- SMC
- HITACHI
- HIRSCHMANN
- Application field
- XP POWER
- CTI
- TRICON
- STOBER
- Thinklogical
- Horner Automation
- Meggitt
- Fanuc
- Baldor