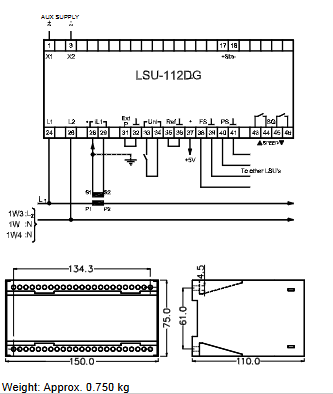
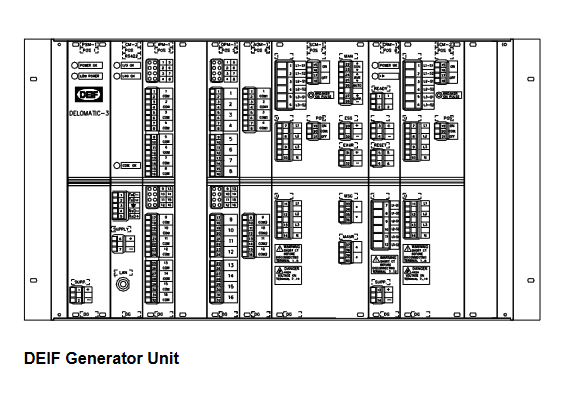
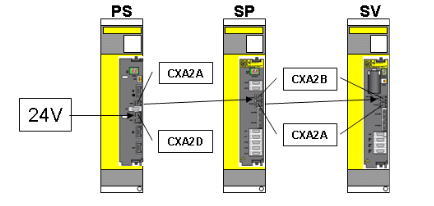
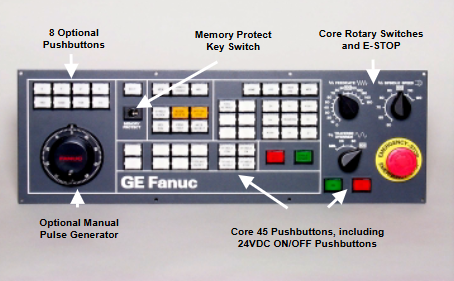
The core positioning of the APBU-44C 64669982 controller module is an "industrial grade high-precision control center", designed around the three core requirements of "high reliability, high real-time performance, and high scalability".
ABB APBU-44C 64669982 High Performance Controller Module
Core positioning and technological advantages
The core positioning of the APBU-44C 64669982 controller module is an "industrial grade high-precision control center", designed around the three core requirements of "high reliability, high real-time performance, and high scalability". Compared with ordinary controller modules, it has the following significant technical advantages:
1. Super powerful computing performance: Equipped with a high-performance 32-bit embedded processor, the computing frequency can reach hundreds of MHz, supporting multitasking parallel processing, and can simultaneously process dozens of analog and digital signals. The response time to complex control algorithms (such as PID closed-loop control and fuzzy control) is only milliseconds, ensuring the accuracy and real-time performance of industrial process control.
2. Industrial grade stability: Adopting a wide temperature design and anti-interference circuit, it can operate stably in extreme temperature environments ranging from -40 ℃ to+70 ℃, with electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) performance according to IEC standards, and can resist strong electromagnetic interference, voltage fluctuations and other interference factors in industrial sites. The average time between failures (MTBF) exceeds 100000 hours.
3. Flexible expansion capability: Supports ABB standard modular expansion interfaces, which can be flexibly matched with digital input/output modules, analog acquisition modules, communication modules, etc. according to actual needs. It can expand up to dozens of I/O points and adapt to various scenarios from small and medium-sized equipment control to large-scale system integration.
4. Multi protocol compatibility feature: Built in multiple industrial communication protocols, including mainstream Ethernet protocols such as PROFINET, Modbus TCP, EtherNet/IP, as well as serial communication protocols such as RS485 and CANopen, can seamlessly interface with PLC, HMI, SCADA systems, and various intelligent sensors to achieve efficient data exchange and centralized control.
Core functions and application value
The APBU-44C 64669982 module covers the entire process of industrial control, forming a complete closed loop from data acquisition, operation processing to instruction output. The specific core functions and application value are as follows:
1. High precision data acquisition and processing
The module has multiple high-precision signal acquisition channels, supporting standard analog signal inputs such as 0-10V and 4-20mA, as well as digital signal inputs such as dry contacts and PNP/NPN. The signal acquisition accuracy can reach 0.1% FS, and can accurately capture key process parameters such as temperature, pressure, flow rate, and liquid level in industrial sites. Meanwhile, the built-in signal filtering algorithm can effectively eliminate noise interference in the signal, ensuring the authenticity and reliability of the data, and providing accurate basis for control decisions. For example, in chemical production, real-time temperature and pressure data of reaction vessels can be collected to provide data support for subsequent heating or pressure control.
2. Execution of complex control algorithms
Pre integrated with various industrial control algorithm libraries, including conventional PID control, adaptive PID control, cascade control, ratio control, etc., supporting user-defined control logic (through ABB dedicated programming software). The module can quickly calculate and output precise control instructions (such as 4-20mA analog output or relay contact output) based on real-time data collected and preset control objectives, achieving closed-loop control of actuators (such as regulating valves, frequency converters, motors). In the power system, it can be used for speed regulation of generators or voltage stability control of transformers to ensure that equipment operating parameters are stable within the target range.
3. Multi dimensional system communication and linkage
With the help of rich communication interfaces and protocol compatibility capabilities, modules can achieve full level data interaction of "device module upper system". On the one hand, it can communicate bidirectionally with on-site intelligent devices (such as smart meters and sensors) to obtain device status information and issue control instructions; On the other hand, it can be connected to the factory SCADA system or MES system to upload real-time process data and equipment operation status, while receiving control instructions from the upper system, achieving centralized monitoring and remote control. In intelligent manufacturing production lines, multiple devices can be linked to form collaborative control, improving the automation level of the production process.
4. Fault diagnosis and safety protection
Built in comprehensive fault diagnosis mechanism, which can monitor the real-time operation status of the module itself (such as power supply, communication, I/O interface) and the working status of connected devices. When power supply abnormalities, communication interruptions, signal overtravel and other faults occur, local alarms will be immediately triggered (through alarm indicator lights) and fault information will be uploaded to the upper system. At the same time, preset safety protection logic (such as emergency shutdown, valve reset) will be executed to avoid the expansion of faults. For example, in metallurgical production, if the module detects abnormal temperature signals in the heating furnace, it can quickly cut off the heating power and issue an alarm to ensure production safety.
5. Data storage and log management
Equipped with built-in memory, it can locally store key process data, equipment operation logs, and fault records. The storage capacity supports expansion, and the data retention time can reach several years (maintained by backup batteries after power failure). These data can be used for subsequent process optimization analysis, equipment maintenance plan formulation, and fault tracing, providing data support for refined management of industrial production.
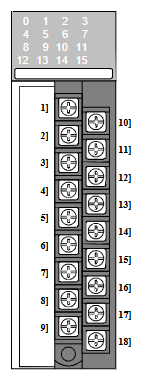
Structural composition and key interfaces
The APBU-44C 64669982 module adopts a standardized industrial packaging design, with a compact structure and easy installation. It is mainly composed of a core computing unit, an I/O interface unit, a communication interface unit, a power supply unit, and an indicator unit. The various parts work together to achieve the complete function of the controller:
component
core component
Key interfaces/features
function and role
Core computing unit
32-bit embedded processor, cache, program memory
Built in algorithm library, supports online programming
Perform control logic operations, data processing, and task scheduling
I/O interface unit
Analog input/output module, digital input/output module
8-way AI (4-20mA), 4-channel AO (4-20mA), 16 way DI, 8-way DO (relay)
Realize signal interaction with on-site sensors and actuators
Communication interface unit
Ethernet controller, serial communication chip
2 RJ45 Ethernet ports, 2 RS485 ports, 1 CANopen port
Support multi protocol communication and achieve linkage with upper level systems and devices
Power supply unit
Wide range power adapter, backup battery interface
Input: DC 24V ± 20%, supports backup battery power supply
Provide stable power supply for each unit of the module to ensure that data is not lost after power failure
Indicating unit
LED indicator light
Power light (PWR), Running light (RUN), Alarm light (ALM), Communication light (COMM)
Intuitive feedback on module operation status, facilitating on-site maintenance and troubleshooting
Typical application scenarios
The APBU-44C 64669982 module, with its high performance and reliability, is widely used in various industrial automation scenarios, especially in fields that require strict control accuracy, real-time performance, and stability. Typical applications include:
1. Power system control
In thermal power generation, hydropower generation, and new energy power stations, it is used for key links such as generator excitation control, turbine speed regulation, and transformer voltage regulation. The module can accurately collect parameters such as voltage, current, and speed of the generator, and adjust the excitation current or steam inlet of the turbine through PID algorithm to ensure stable operation of the power generation system. At the same time, the operating data is uploaded to the power station monitoring system to achieve centralized control.
2. Chemical process control
Applied to process control of chemical reaction vessels, distillation towers and other equipment, real-time collection of reaction temperature, pressure, material flow rate and other parameters, precise control of heating devices, cooling systems and feed valves based on preset process curves, ensuring stable process conditions for chemical reactions, improving product quality and production safety, and avoiding production accidents caused by parameter fluctuations.
3. Metallurgical industry control
In the process of steel and non-ferrous metal smelting, it is used for temperature control of blast furnace hot blast stove, oxygen supply flow control of converter, speed regulation of rolling mill and other scenarios. The module can resist the high temperature, high dust and strong electromagnetic interference environment in the metallurgical workshop, stably collect various process parameters and execute control instructions, ensure the continuity and stability of the smelting process, and improve the qualification rate of metallurgical products.
4. Intelligent manufacturing production line
In automated production lines such as automobile manufacturing and electronic component production, as the core of equipment collaborative control, robots, conveyor belts, detection equipment, etc. are linked to achieve automated connection of production processes. The module can issue control instructions to various devices according to the production plan, while collecting equipment operation status and product detection data, achieving full traceability and precise control of the production process, and improving production efficiency.
5. Municipal public works
Used for dissolved oxygen control in aeration tanks of sewage treatment plants, control of dosing systems in water plants, temperature regulation of urban heating pipelines, and other scenarios. The module can automatically adjust the operating status of aeration equipment, dosing pumps, and heating valves based on parameters such as water quality, water pressure, and temperature, achieving energy-saving operation and refined management of municipal engineering.
Key points for installation, debugging, usage, and maintenance
To fully leverage the performance advantages of the APBU-44C 64669982 module and ensure long-term stable operation of the system, it is necessary to strictly follow the following installation, debugging, and maintenance specifications:
1. Installation specifications
-The module needs to be installed on a standard DIN rail, and the installation position should be far away from high-temperature heat sources (such as heaters, frequency converters), strong electromagnetic radiation sources (such as high-power motors), and areas that are prone to dust and corrosive gases, ensuring good ventilation and environmental temperature and humidity that meet the working requirements of the module (-40 ℃~+70 ℃, humidity 5%~95% without condensation).
-When wiring, it is necessary to strictly distinguish between power supply, I/O signals, and communication lines. Power supply lines should be separately wired and equipped with fuses (recommended 1A). Analog signal lines should use shielded wires, and the shielding layer should be grounded at one end to avoid parallel laying with strong current lines and prevent signal interference.
-The module installation and fixation should be firm to prevent loose wiring or module displacement caused by equipment vibration. After installation, it is necessary to check whether the interface connections are reliable.
2. Key debugging points
-Before debugging, control logic programming and parameter configuration need to be completed through ABB's dedicated programming software (such as Control Builder M). After programming is completed, offline simulation testing is required to verify the correctness of the control logic.
-When powering on for debugging, first check if the power indicator light (PWR) is lit up properly, then connect the module through software to confirm the communication status (COMM light is constantly on or flashing), and then perform I/O signal calibration to ensure that the analog acquisition accuracy and output accuracy meet the requirements.
-During the system integration phase, it is necessary to simulate various process scenarios, verify the control response speed and accuracy of the module, and test the fault diagnosis function to ensure that the module can correctly trigger alarms and protection logic when faults occur.
3. Daily maintenance
-During daily inspections, focus on observing the status of module indicator lights (RUN light constantly on indicates normal operation, ALM light on indicates a fault), checking for dust accumulation on the surface of the module, and whether the ambient temperature and humidity are within the allowable range.
-Regularly check module operation logs through the upper system every month, analyze fluctuations in key process parameters, check the stability of communication links, and promptly address potential communication anomalies.
-Perform comprehensive maintenance on the module once every quarter, including cleaning the surface dust of the module, checking the tightness of the wiring terminals, testing the voltage of the backup battery (to ensure that the power-off data storage function is normal), and replacing aging wiring or shielding layers.
-Perform software and firmware upgrades once a year, obtain the latest versions of firmware and programming software through ABB's official channels, improve module performance and compatibility, and fix potential software vulnerabilities.
4. Common fault handling
-The power light is not on: Check if the power input is normal, if the fuse is blown, and if the wiring terminals are loose. If the power input is normal, it may be a module power unit failure and ABB after-sales maintenance should be contacted.
-Communication interruption (COMM light not on): Check whether the Ethernet or RS485 line connection is reliable, whether the communication parameters (IP address, port number, baud rate) match the upper system, and troubleshoot whether the network switch or communication bus is faulty.
-Decreased control accuracy: Check if there is interference in the analog acquisition circuit and recalibrate the I/O signal. If the problem persists, it may be a sensor malfunction or an abnormal module computing unit, which needs to be investigated one by one.
-Alarm light on: Query the fault log through the upper system or programming software, locate the fault type based on the log information (such as signal over range, equipment offline), and perform a fault reset operation after targeted processing.
- User name Member Level Quantity Specification Purchase Date
- Satisfaction :
-