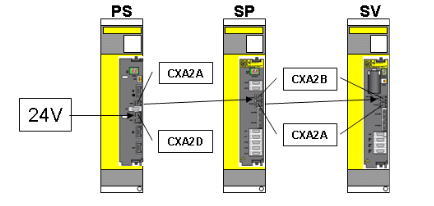
The product analyzed in this document is the 500PSM02 digital power module under the ABB brand, with the complete model identification being 1MRB150015R1 AD-272.100.20-01 AZ: C. The model coding system has clear directionality: 1MRB150015R1 is the core product code officially set by ABB, used to accurately define module models and basic configurations; AD-272.100.20-01 usually represents the hardware version, design code, or supporting parameters of the module; AZ: C is mostly used for production sequence identification, regional adaptation marking, or quality level code, providing key basis for the full lifecycle management (traceability, maintenance, upgrade) of products.
ABB 500PSM02 1MRB150015R1 AD-272.100.20-01 AZ: C digital power module
Basic information of module
The product analyzed in this document is the 500PSM02 digital power module under the ABB brand, with the complete model identification being 1MRB150015R1 AD-272.100.20-01 AZ: C. The model coding system has clear directionality: 1MRB150015R1 is the core product code officially set by ABB, used to accurately define module models and basic configurations; AD-272.100.20-01 usually represents the hardware version, design code, or supporting parameters of the module; AZ: C is mostly used for production sequence identification, regional adaptation marking, or quality level code, providing key basis for the full lifecycle management (traceability, maintenance, upgrade) of products.
As a core component in industrial automation power supply systems, the 500PSM02 digital power module is mainly responsible for efficiently converting input electrical energy, stabilizing output, and realizing digital monitoring and protection functions. It is the "power core" that ensures the reliable operation of automation equipment such as PLCs, controllers, and sensors, and is widely used in various industrial control scenarios.
Core technical characteristics
1. Efficient energy conversion and stable output
-High conversion efficiency: Adopting advanced switching power supply topology and digital control algorithms, the energy conversion efficiency can reach over 90% (specific values need to be combined with actual input and output conditions), effectively reducing energy loss, meeting industrial energy-saving needs, while reducing module self heating and improving operational stability.
-Accurate output adjustment: Supports a wide range of input voltages (commonly compatible with AC 85-264V or DC 110-375V, subject to official parameters), and can stably output preset DC voltages (such as 24V, 48V, and other industrial standard voltages). The output voltage accuracy is usually controlled within ± 1%, with extremely low ripple and noise, providing clean power for sensitive electronic devices.
-Overload and fault protection: Built in comprehensive protection mechanisms, including overcurrent protection, overvoltage protection, undervoltage protection, over temperature protection, and short circuit protection. When abnormal operating conditions occur, the module can respond quickly (usually in microseconds), protect itself and backend load devices by limiting current, shutting down output, and other methods to avoid the expansion of faults.
2. Digital monitoring and intelligent management
-Real time status monitoring: Equipped with digital communication interfaces (such as RS485, CAN or Ethernet interfaces, configured according to the model), the module operating parameters (input voltage, output voltage, output current, module temperature, working status, etc.) can be uploaded to the PLC or monitoring system through the communication bus to achieve remote real-time monitoring.
-Parameter Configurability: Supports configuring module core parameters through upper computer software or local debugging interfaces, such as output voltage fine-tuning, protection threshold setting, communication address configuration, etc., to adapt to power supply needs in different scenarios and enhance module flexibility.
-Fault diagnosis and alarm: When a module malfunctions or is abnormal, in addition to automatically activating the protection mechanism, it can also output fault codes (such as overcurrent codes, overtemperature codes, etc.) through the communication interface. At the same time, some models support local indicator light alarms, making it easy for operation and maintenance personnel to quickly locate the cause of the fault.
3. Industrial grade reliability design
-Wide temperature working range: Industrial grade components are used to support a wide temperature working environment of -25 ℃~70 ℃, which can adapt to extreme industrial sites such as high and low temperatures, and avoid module performance degradation or failure caused by temperature fluctuations.
-Strong anti-interference ability: Through EMC (electromagnetic compatibility) certification, it has strong anti-interference ability and can resist electromagnetic interference generated by motor start stop and frequency converter operation in industrial sites, ensuring stable operation of the module in complex electromagnetic environments.
-High protection and durability: The module casing is made of flame-retardant and impact resistant materials, and some models support protection levels of IP20 and above, effectively preventing dust and accidental contact; The internal circuit adopts anti vibration design, adapted to the vibration environment of industrial sites, and extends the service life of the module.
Typical application scenarios
With its high efficiency, stability, and intelligence, the 500PSM02 digital power module is widely used in various industrial automation fields, mainly including:
1. Power supply for PLC and control system: As a dedicated or compatible power supply for ABB AC 500 series PLC and other brands of PLC, it provides stable DC power supply for core control equipment such as PLC host, I/O module, and controller module (such as 500AIM02), ensuring the normal operation of the control system.
2. Intelligent manufacturing production line: In automated production lines such as automobile manufacturing, electronic assembly, and food processing, power is supplied to sensors, actuators (such as cylinders and motors), human-machine interfaces (HMI), robots, and other equipment to ensure the coordinated and stable operation of various devices in the production line, avoiding production interruptions caused by abnormal power supply.
3. Process control and monitoring system: In process control scenarios in industries such as chemical, petroleum, and power, it supplies power to monitoring instruments such as temperature, pressure, and flow, online analytical instruments, and data acquisition modules (DAQ) to ensure real-time acquisition and control of process parameters and improve production process stability.
4. Energy and power industry: In substations, new energy generation (photovoltaic, wind power), and energy storage systems, power is supplied to monitoring terminals, protection devices, communication equipment, etc. to ensure the normal monitoring, control, and communication functions of the energy system, and to enhance the reliability and safety of the energy system.
5. Rail Transit and Infrastructure: In infrastructure projects such as subways, light rails, water treatment plants, and sewage treatment stations, power is supplied to on-site control equipment, security monitoring equipment, emergency systems, etc., to adapt to the complex environment of the infrastructure site and ensure the stable operation of the project.
Selection and usage precautions
1. Key points of selection
-Matching load requirements: Clearly define the total power, rated voltage, and maximum current of the backend load devices, ensuring that the output power of the power module (rated output current x output voltage) is greater than 1.2-1.5 times the total load power (with redundancy reserved to avoid overload), and that the output voltage is consistent with the rated load voltage.
-Adapt to input conditions: Based on the on-site power supply conditions (such as AC mains power, DC bus voltage), select the module model corresponding to the input voltage range to avoid module damage caused by input voltage exceeding the module adaptation range.
-Confirm communication and control requirements: If remote monitoring, parameter configuration, and other functions need to be implemented, it is necessary to confirm that the communication interface type of the module (such as RS485 Modbus, Profinet, etc.) is compatible with the communication protocol of the existing control system.
-Evaluate the on-site environment: Based on parameters such as temperature, humidity, electromagnetic interference intensity, and protection requirements, confirm that the environmental adaptability of the module (such as wide temperature range, protection level, EMC performance) meets the on-site requirements.
2. Installation and maintenance specifications
-Correct installation of wiring: Strictly follow the ABB official installation manual, distinguish between input terminals (L, N, PE) and output terminals (+, -), ensure that the wiring is firm and the polarity is correct; Sufficient heat dissipation space should be reserved for module installation (usually it is recommended to reserve more than 5cm of space on both sides and the top of the module), avoiding installation in close proximity to devices with high heat generation.
-Check before powering on: Before powering on, use a multimeter to check if the input voltage is normal and if the output terminal is short circuited. After confirming that everything is correct, turn on the power supply; After the first power on, it is necessary to monitor whether the output voltage meets the preset value to avoid damage to the load caused by abnormal voltage.
-Regular maintenance: Clean the module regularly (recommended every 3-6 months) to remove surface dust (can be wiped with compressed air or a dry cloth); Check if the wiring terminals are loose and if the module indicator lights are functioning properly; For modules that operate for a long time, parameters such as output voltage and ripple can be regularly monitored to evaluate the performance status of the module.
-Fault handling principle: When a module experiences a fault alarm, the input power should be disconnected first, and then the cause of the fault should be investigated (which can be combined with fault codes, detection of input and output parameters, etc.); Troubleshooting should be carried out by professional electricians or automation engineers to avoid disassembling modules without authorization. If necessary, contact ABB's official after-sales service for repair or replacement.

- User name Member Level Quantity Specification Purchase Date
- Satisfaction :
-