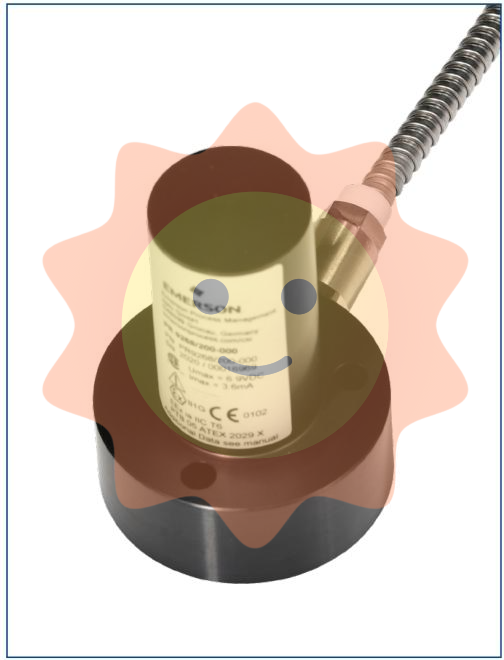
XMTC-62-21 anametrics XMTC Thermal Conductivity Transmitter, Precision Measurement for Industrial Control Applications
Thermal Conductivity Range:0.1 10 W/mK Operating Temperature Range:-40"C to +85"C Accuracy:+/- 2% of full scale Response Time:Less than 0.1 seconds Power Consumption:2.5V @ 50mA Sensor Type:Resistance Temperature Detector (RTD) Communication Protocol:MODBUS RTU This high-performance GE XMTC-62-21 anametrics XMTC Thermal Conductivity Transmitter is a cornerstone of industrial automation systems, providing unparalleled accuracy and reliability in measuring thermal conductivity. Ideal for applications in chemical processing, HVAC systems, and power generation, this transmitter ensures precise temperature management and process control.
Crafted with precision engineering, the transmitter features a compact design that seamlessly integrates into existing industrial control setups. Its robust construction withstands harsh environments, guaranteeing long-lasting performance without maintenance interruptions. Equipped with advanced signal processing capabilities, the XMTC-62-21 can adapt to varying operational conditions, delivering consistent readings even under fluctuating temperatures. This makes it an indispensable tool for maintaining optimal efficiency in thermal management systems. Installation is straightforward, thanks to its plug-and-play compatibility with most industrial control protocols.
Our detailed user manuals and technical support ensure a smooth setup process, minimizing downtime and maximizing productivity. Backed by GE commitment to quality and innovation, the XMTC-62-21 anametrics XMTC Thermal Conductivity Transmitter comes with a comprehensive warranty and ongoing technical assistance. Trust us to deliver the precision you need for your most critical applications. The GE XMTC-62-21 anametrics XMTC Thermal Conductivity Transmitter is designed for precise measurement of thermal conductivity in industrial control applications, ensuring reliable data acquisition for process optimization.
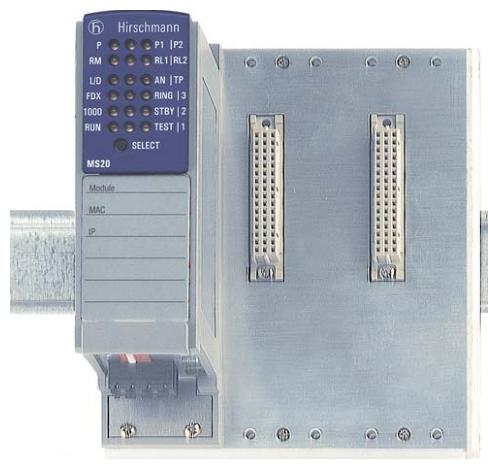
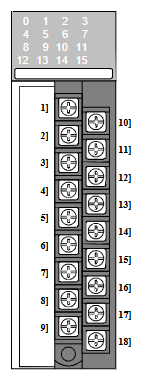
The IO module has the following main functions
Input Function
The IO module can receive input signals sent by external devices and convert them into digital or analogue signals for use by the computer system or control system. These input signals can come from a variety of sensors, such as temperature sensors, pressure sensors, photosensitive sensors and so on. By receiving and parsing these input signals, the system can monitor and control the external environment in real time.
Output Functions
The IO module is capable of converting the output signals generated by a computer system or control system into the form required by an external device. These output signals are typically used to control actuators such as motors, valves, lights, etc. By sending appropriate output signals to external devices, the system enables control and operation of the external environment.
Data Acquisition and Processing
The IO module is capable of acquiring data from external devices and transferring it to a computer system or control system for further processing. This enables the system to acquire environmental data, status information and user inputs in real time and make appropriate decisions or perform specific tasks based on these data.
Communication Interfaces
IO modules are usually equipped with different types of communication interfaces, such as serial interfaces (RS232, RS485), Ethernet interfaces, CAN bus interfaces, and so on. These interfaces enable IO modules to exchange data and communicate efficiently with computer systems or other external devices.

- User name Member Level Quantity Specification Purchase Date
- Satisfaction :
-