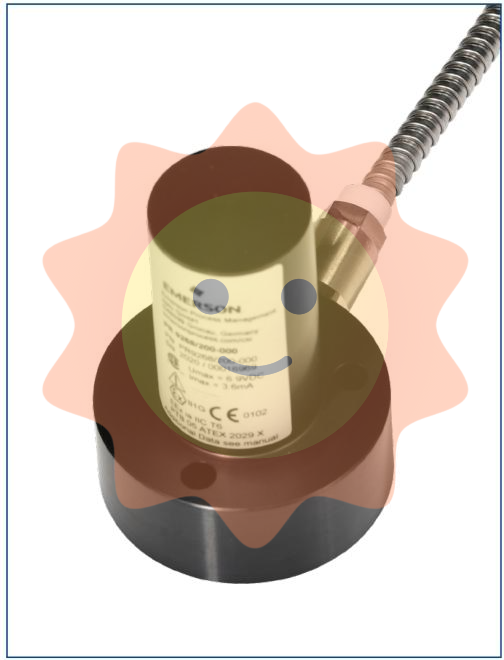
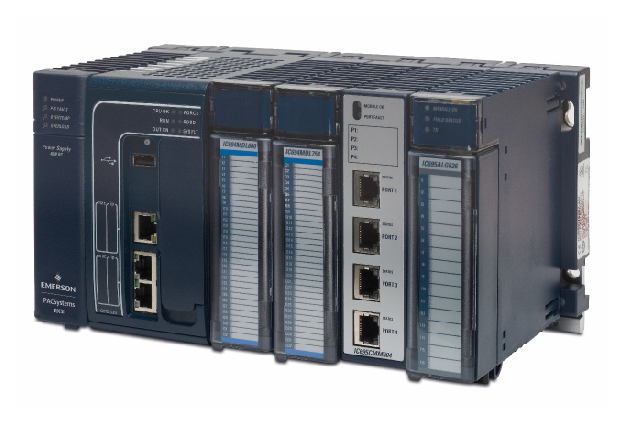
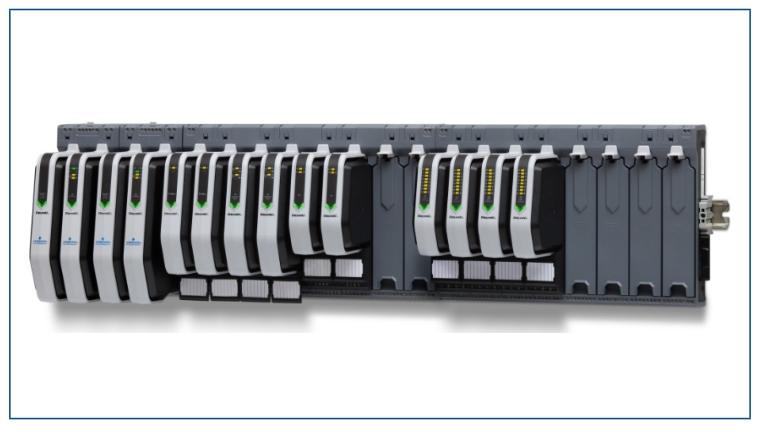
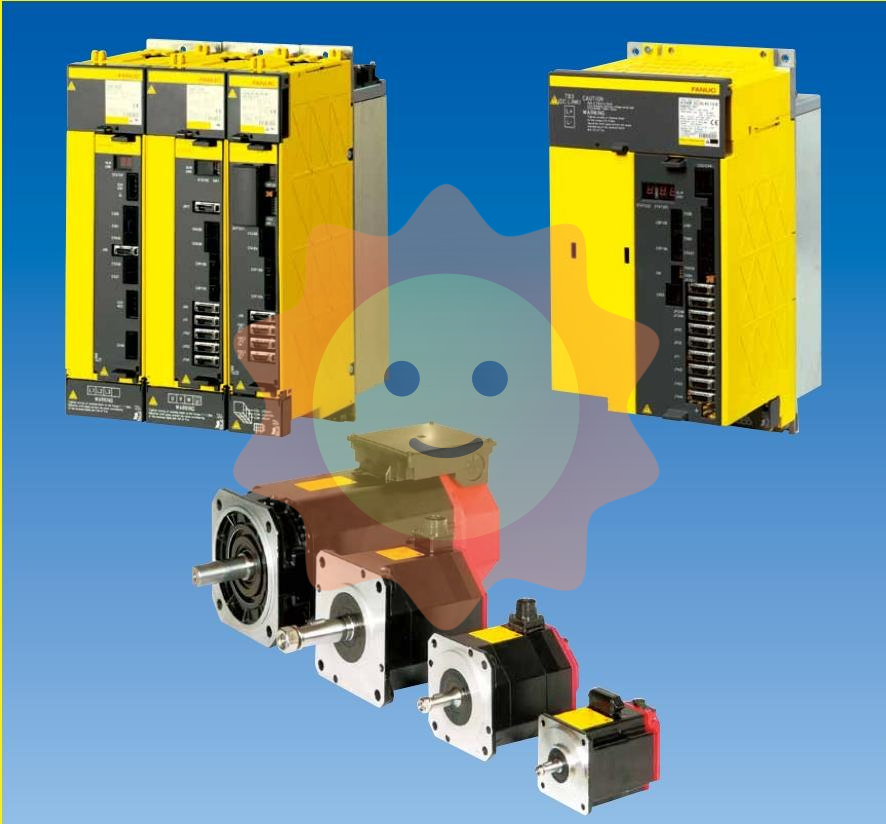
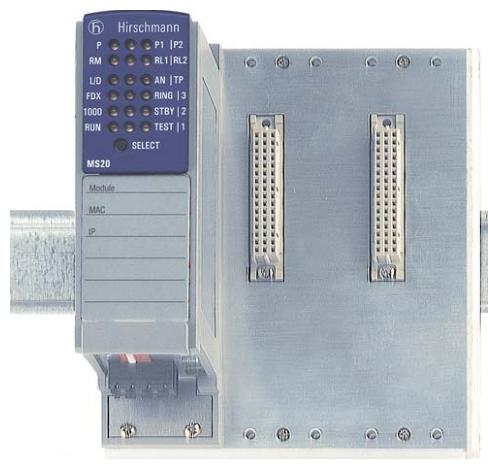
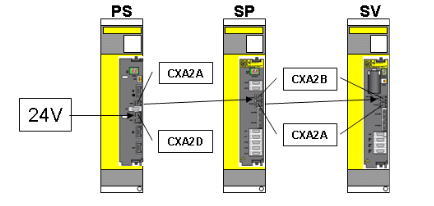
The Dummy Unit of ABB robot servo drive unit, also known as the empty slot cover plate, is not a traditional signal control interface module. Its core value lies in ensuring the integrity and maintainability of the drive system, commonly found in the drive unit array of controllers such as ABB M2000 series.
ABB 3HAB9271-1/01B Robotic Control Interface Module
Product core positioning
Official definition: The Dummy Unit of ABB robot servo drive unit, also known as the empty slot cover plate, is not a traditional signal control interface module. Its core value lies in ensuring the integrity and maintainability of the drive system, commonly found in the drive unit array of controllers such as ABB M2000 series.
Three core functions
Occupancy adaptation
When the robot system does not require the activation of all drive channels, this module can fill the vacant slots to ensure the mechanical integrity of the drive unit frame and avoid installation position displacement caused by slot vacancies.
Protective isolation
As a physical barrier, it can effectively prevent dust, oil stains, and metal debris from entering the empty slots in the production environment, reducing the risks of circuit board short circuits, component corrosion, etc., especially suitable for dusty working conditions such as automotive welding and mechanical processing.
Test diagnosis
During the system debugging or troubleshooting phase, it can replace the real servo drive unit to connect to the slot, and work with ABB robot diagnostic software to simulate the status of the drive channel, quickly locate "module faults" or "system bus problems".
Key technical characteristics
Model identification
3HAB9271-1/01B
The end "01B" represents hardware version iteration
Product type
Virtual servo drive unit
No actual power output and signal processing function
Applicable system
ABB Robot Drive System
Compatible with mainstream industrial robot controllers
Core material
Flame retardant engineering plastic+metal interface
Meet the requirements of industrial grade protection level
Main functions
Occupation, protection, testing
Non functional module, no electrical parameters
Installation and maintenance specifications
1. Installation process
Preparation work: Turn off the main power of the drive system, wear an anti-static wristband, and clean up the debris in the slot;
Installation operation: Align with the slot guide rail and gently push in until the buckle is locked (no need to connect power and signal wires);
Verification check: After installation, confirm that there is no gap between the module and adjacent units, and that the frame panel is flat.
2. Maintenance points
Daily cleaning: Blow the surface of the module with dry compressed air every month to avoid dust accumulation affecting heat dissipation;
Replacement scenario: When the corresponding slot requires the installation of a real driver unit, simply unlock the buckle and remove it without any special disassembly process;
Fault diagnosis: If the module is physically damaged (such as buckle breakage or shell cracking), it should be replaced immediately to prevent loss of protective function.
Common application scenarios
System configuration optimization: When the load demand of the robot decreases, remove the redundant drive unit and use this module to fill the gap;
New machine debugging phase: When all driver units are not yet fully equipped, use virtual modules to complete system initialization and bus testing;
Emergency handling of faults: When there is a suspected drive unit fault, replace the module for testing and quickly distinguish between hardware and software issues.

- User name Member Level Quantity Specification Purchase Date
- Satisfaction :
-