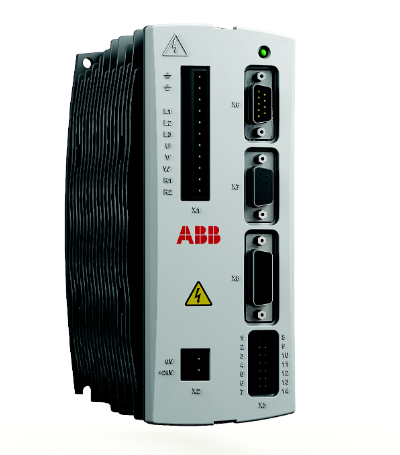
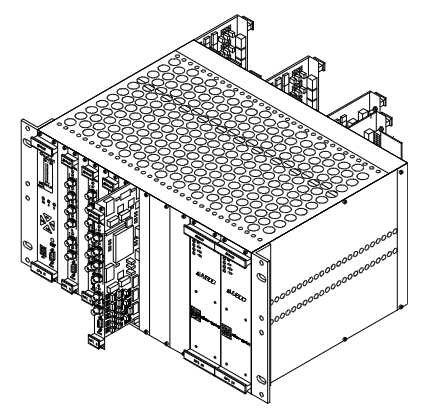
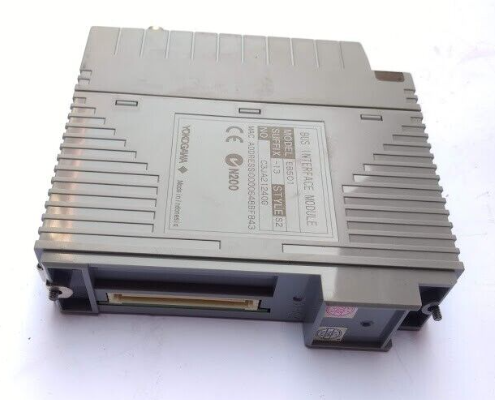
The YOKOGAWA EB501 bus interface module is designed specifically for optical ESB bus communication. Its core positioning is to achieve long-distance data transmission and interaction of various node units in industrial control systems. The upstream optical ESB bus transmission distance can reach 5-50km, and the downstream optical ESB bus transmission distance is 0-5km, which can effectively adapt to the communication needs of large factory areas and cross regional industrial facilities. This module strictly follows multiple international safety and compliance standards such as ATEX and EMC, and has a complete explosion-proof and anti-interference protection design, which can adapt to the complex electromagnetic environment and special working conditions requirements of industrial sites. Its core advantages lie in long communication distance, high transmission stability, flexible node adaptation, and support for standardized installation and safe operation, which can meet the core requirements of long-distance bus communication in industrial automation systems.
YOKOGAWA EB501 Bus Interface Module
The YOKOGAWA EB501 bus interface module is designed specifically for optical ESB bus communication. Its core positioning is to achieve long-distance data transmission and interaction of various node units in industrial control systems. The upstream optical ESB bus transmission distance can reach 5-50km, and the downstream optical ESB bus transmission distance is 0-5km, which can effectively adapt to the communication needs of large factory areas and cross regional industrial facilities. This module strictly follows multiple international safety and compliance standards such as ATEX and EMC, and has a complete explosion-proof and anti-interference protection design, which can adapt to the complex electromagnetic environment and special working conditions requirements of industrial sites. Its core advantages lie in long communication distance, high transmission stability, flexible node adaptation, and support for standardized installation and safe operation, which can meet the core requirements of long-distance bus communication in industrial automation systems.
Core functional characteristics
The YOKOGAWA EB501 bus interface module integrates Yokogawa Electric's dedicated optical ESB bus technology with a high reliability industrial communication design. It has the following core functional characteristics and can adapt to the long-distance and high stability bus communication needs of industrial sites:
1. Dedicated optical ESB bus for long-distance stable transmission
The module adopts dedicated optical ESB bus technology to achieve differentiated long-distance transmission between uplink and downlink: the transmission distance of uplink optical ESB bus can reach 5-50km, and the transmission distance of downlink optical ESB bus is 0-5km (specific transmission distance can be adjusted according to configuration, adapted to A2EN501-S12 ≤ 0 specification), which can effectively solve the distance limitation of cross regional communication in large industrial scenarios. Using fiber optic transmission medium, it has extremely strong anti electromagnetic interference ability, which can effectively avoid the influence of strong electromagnetic interference sources such as industrial field frequency converters and high-power motors on communication signals, ensuring the stability and integrity of data transmission, and the transmission error rate is as low as industrial grade high standards.
2. Flexible node adaptation and seamless system integration
The module has flexible node interface adaptation capability, which can directly connect to specified models of node interface units, such as A2NN30D adapted to A2FV50D and other node devices. It can be flexibly expanded according to the node configuration requirements of industrial control systems, achieving multi node collaborative communication. Adopting standardized interface design, it can be seamlessly integrated into various automation control systems in Yokogawa without the need for additional adaptation and modification, reducing the difficulty and cost of system integration. Simultaneously supporting real-time monitoring of node status to ensure stable connection between each node unit and the bus communication.
3. Strict safety compliance and perfect protection design
The module strictly follows multiple international safety and compliance standards, including ATEX explosion-proof standards, EMC (electromagnetic compatibility) compliance standards, Pressure Equipment Directive (PED), etc., and has reliable explosion-proof protection performance, which can adapt to the installation requirements of potential explosive environments. Adopting reinforced insulation and sealing protection design, it can effectively resist the adverse environmental effects such as dust and humidity in industrial sites. At the same time, it has complete overvoltage and overcurrent protection functions, which can prevent external voltage/current abnormalities from causing damage to modules and bus systems, ensuring the safety of equipment and personnel.
4. Real time status monitoring and fault alarm
The module integrates comprehensive status monitoring and fault alarm functions, capable of real-time monitoring of bus communication status (uplink/downlink connection status, data transmission status), module working status (power status, internal circuit operation status), and node connection status. Equipped with clear LED indicator lights, it can intuitively provide feedback on the status of normal/abnormal power supply, normal/interrupted bus communication, normal/faulty node connection, etc., making it convenient for on-site maintenance personnel to quickly check. When a fault occurs, the module immediately triggers an alarm signal and uploads fault codes (such as link interruption, node abnormality, power failure, etc.) to assist maintenance personnel in quickly locating and solving problems, ensuring the continuity of bus communication.
5. Standardize installation design and adapt to industrial working conditions
The module adopts industrial grade standardized installation design, supports standardized panel or rail installation, and has flexible installation position selection. At the same time, the installation environment and spacing requirements are clearly defined to ensure heat dissipation and operational convenience after installation. In response to explosion-proof installation requirements, we have a dedicated explosion-proof installation adaptation design and can complete the installation and deployment of explosion-proof scenarios according to ATEX documentation requirements. In addition, the wiring terminals of the module are designed to prevent accidental insertion and loosening, and the fiber optic interface has dust-proof and anti pollution protection, further improving the reliability of the module under industrial conditions.
Installation and commissioning specifications
Proper installation and debugging are key to ensuring stable and safe operation of module bus communication. It is necessary to strictly follow the following specifications and international safety standards (ATEX, EMC, etc.), and configure according to on-site communication requirements:
1. Preparation before installation
Before installation, the following checks and preparations need to be completed: ① Verify that the module model (EB501) and specifications are consistent with the order requirements, check that the module surface is free of physical damage, the interface is not deformed, and the fiber optic interface is free of stains or scratches; ② Confirm that the installation environment meets the requirements: the installation location should be far away from high-temperature heat sources and strong electromagnetic interference sources, with an ambient temperature of -10 ℃~60 ℃ and humidity of 10%~95% RH (no condensation); If it is installed in an explosion-proof scenario, it is necessary to confirm that the installation environment meets the ATEX explosion-proof level requirements and is kept away from flammable and explosive media; The installation location should be easy to operate and maintain, with sufficient space reserved for heat dissipation and wiring; ③ Prepare the necessary installation tools (screwdriver, fiber optic cutting tool, optical power meter, electrical testing equipment), compatible fiber optic cables, node interface units, wiring terminals, and power cables that meet specifications; ④ Check the integrity and transmission performance of the fiber optic cable, and confirm the compatibility of the node interface unit model and module (such as the compatibility of A2NN30D and A2FV50D).
2. Installation process
① Basic installation: Fix the module on the installation panel or guide rail according to the size of the module installation hole, use compatible screws to tighten the module, and control the tightening torque of the screws within the specified range (recommended 0.4~0.6N · m) to avoid damaging the module housing due to over tightening; If it is an explosion-proof installation, it is necessary to strictly follow the ATEX documentation requirements to complete explosion-proof sealing and fixing, ensuring that the explosion-proof performance meets the standards after installation; ② Node connection: Connect the adapted node interface unit (such as A2NN30D) to the module's node connection interface, ensuring a secure connection and dust sealing treatment at the interface; ③ Installation confirmation: Ensure that the module is securely installed without any looseness, and that all interfaces are unobstructed, facilitating subsequent wiring and maintenance; Check if the ventilation and heat dissipation conditions of the installation environment meet the requirements.
3. Wiring and fiber optic connection specifications
Before connecting the wiring and fiber optic cables, it is necessary to disconnect the system power supply to avoid electric shock or damage to the module. Strictly follow the module wiring diagram and relevant safety standards for operation: ① Power wiring: Connect the positive pole (L+) of the 24V DC power supply to the module power terminal "+V", and connect the negative pole (GND) to "- V", ensuring that the positive and negative poles are connected correctly and avoiding reverse connection; Install an appropriate circuit breaker (recommended 3A, 24V DC) at the power input end for overcurrent protection at the power supply end; The power cable should maintain a safe distance (≥ 1cm) from the fiber optic cable to avoid interference; ② Fiber optic connection: According to the uplink/downlink requirements, connect the fiber optic cable to the corresponding optical ESB bus interface, ensure that the fiber optic connector is inserted in place, and tighten the fixing nut at the interface; The bending radius of fiber optic cables should meet the requirements (recommended ≥ 30mm) to avoid excessive bending that may lead to a decrease in transmission performance; Dust and pollution prevention measures should be taken at the fiber optic joint. If there are stains, they should be wiped clean with a special cleaning agent; ③ Wiring confirmation: Check whether all wiring and fiber optic connections are firm, the positive and negative poles of the power supply are not reversed, the fiber optic interface is not loose, the laying path of cables and fiber optic cables is reasonable, and there is no compression or tension situation; Wiring must comply with relevant electrical construction standards and NEC (ANSI/NFPA 70) requirements in the installation area.
4. Debugging steps
① Power on self-test: When the system power is connected, the module automatically enters self-test mode. Observe whether the power indicator light (green) lights up normally, and whether the bus communication indicator light and node connection indicator light have no abnormal alarms (the alarm light is red and does not light up normally); If the self-test fails, power off and check the power wiring and module hardware; ② Communication parameter configuration: Enter the configuration interface through the local configuration interface of the upper computer software or module, set bus transmission parameters, node addresses, communication protocols, etc. according to the on-site communication requirements, save and restart the module after configuration is completed; ③ Link testing: Use an optical power meter to test the transmission performance of the fiber optic link and confirm that the optical power of the uplink/downlink meets the requirements; Send test data through the upper computer software to check whether the data transmission between the module and each node unit, as well as between the upper computer, is normal, without packet loss, excessive delay, or other issues; ④ Fault simulation test: Simulate fault scenarios such as fiber breakage, node disconnection, and power supply abnormalities, check whether the module can accurately trigger alarms and output protection signals, whether the fault information can be uploaded to the upper computer normally, and ensure that the fault alarm function is effective.

- User name Member Level Quantity Specification Purchase Date
- Satisfaction :
-