The YOKOGAWA CP451-10 process control module is designed specifically for parameter control in general industrial scenarios. It can accurately collect various process parameter signals on site, output stable control signals through built-in mature control algorithms, and drive the actuator to complete parameter adjustment, forming a closed-loop control circuit. This module strictly complies with multiple international safety standards such as IEC/EN 61010, and has standardized electrical protection design. It is only suitable for indoor control cabinet installation and can effectively adapt to the conventional electromagnetic environment and working conditions requirements of industrial sites. Its core advantages lie in easy installation, simple operation, reliable operation, and support for standardized communication and flexible configuration, which can meet the process control needs of most general industrial scenarios.
YOKOGAWA CP451-10 Process Control Module
The YOKOGAWA CP451-10 process control module is designed specifically for parameter control in general industrial scenarios. It can accurately collect various process parameter signals on site, output stable control signals through built-in mature control algorithms, and drive the actuator to complete parameter adjustment, forming a closed-loop control circuit. This module strictly complies with multiple international safety standards such as IEC/EN 61010, and has standardized electrical protection design. It is only suitable for indoor control cabinet installation and can effectively adapt to the conventional electromagnetic environment and working conditions requirements of industrial sites. Its core advantages lie in easy installation, simple operation, reliable operation, and support for standardized communication and flexible configuration, which can meet the process control needs of most general industrial scenarios.
Key technical parameters
Control the number of channels
Standard 10 channel configuration (CP451-10:10 channel configuration)
Support parameter types
Temperature, pressure, flow rate, etc; Compatible sensor/transmitter types: Pt100, Pt1000, K/J thermocouple, 4-20mA transmitter signal, etc
measurement range
Temperature: -200 ℃~850 ℃ (Pt100), -270 ℃~1372 ℃ (K-type thermocouple); Pressure: 0~10MPa (according to transmitter configuration); Flow rate: 0~100m ³/h (depending on transmitter configuration)
measurement accuracy
Temperature: ± 0.2 ℃ (-50 ℃~200 ℃, Pt100 sensor); Pressure: ± 0.1% FS; Flow rate: ± 0.1% FS
control accuracy
± 0.3 ℃ (temperature steady state), ± 0.2% FS (pressure/flow steady state, no load fluctuation)
control algorithm
Classic PID control, supporting parameter self-tuning
output type
1 relay output per channel (AC250V/3A), 1 4-20mA analog output
Isolation method
Input/power isolation, isolation voltage 1kV rms (1 minute)
Rated power supply voltage
100-240V AC ± 10% or 24V DC ± 10% (dual power supply compatible, subject to configuration)
power consumption
≤ 15W during normal operation, ≤ 2W during standby
Working environment temperature
0 ℃~50 ℃ (no condensation), only suitable for indoor installation
Working environment humidity
20%~90% RH (no condensation)
Protection level
IP20 (panel installation status)
Installation method
Panel installation, compatible with installation panels with a maximum thickness of 8mm
communication interface
Supports RS485 (Modbus RTU) industrial communication protocol
safety standards
IEC/EN 61010-1(CE)、IEC/EN 61010-2-201(CE)、UL 61010-1(UL)、CAN/CSA C22.2 No.61010-1(CSA)
Installation category/pollution level
Installation category II, pollution level 2
Installation and commissioning specifications
Proper installation and debugging are key to ensuring the precise and stable operation of the module. It is necessary to strictly follow the following specifications and international safety standards, and configure parameters based on on-site process requirements:
1. Preparation before installation
Before installation, the following checks and preparations need to be completed: ① Verify that the module model (CP451-10) and specifications are consistent with the order requirements, check that the module surface is free of physical damage, the interface is not deformed, and the pins are not bent; ② Confirm that the installation environment meets the requirements: only suitable for indoor installation, the installation location should be away from high temperature heat sources, strong electromagnetic interference sources (such as frequency converters, high-power motors), corrosive gases and dust, no vibration and impact, ambient temperature of 0 ℃~50 ℃, humidity of 20%~90% RH (no condensation); The installation location should be easy to operate and maintain, and ensure that the terminals are not easily touched accidentally; ③ Prepare the necessary installation tools (screwdriver, crimping tool, multimeter, electrical testing equipment), compatible sensors/transmitters, wiring terminals, and cables that meet specifications (cable temperature level should be ≥ 75 ℃, sensor cables are recommended to use shielded cables with a cross-sectional area of ≥ 0.75mm ²; The power cable must comply with IEC standards or relevant requirements of the installation area; ④ Prepare circuit breakers that meet the requirements (IEC 60947 compatible products, 5A, 100V or 220V AC) for overcurrent protection at the power supply end.
2. Installation process
① Panel installation: Drill holes on the installation panel (maximum thickness 8mm) according to the size of the module installation holes, fit the module to the installation panel, and use compatible screws to fix the module. The tightening torque of the screws should be controlled within the specified range (recommended 0.5~0.8N · m) to avoid damaging the module housing due to over tightening; ② Installation confirmation: Ensure that the module is securely installed without any looseness, and that the terminal area is unobstructed, facilitating subsequent wiring and maintenance; The installation position should ensure that the control cabinet can completely enclose the rear shell, exposed terminals, and back wiring of the module, in compliance with safety protection requirements.
3. Wiring specifications
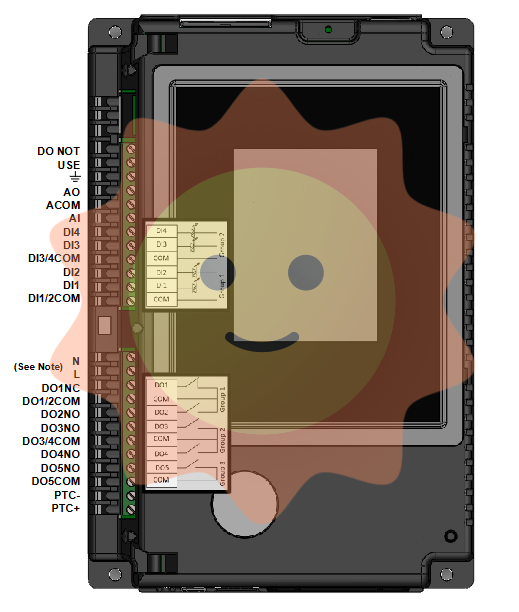
Before wiring, it is necessary to disconnect the system power supply and use electrical testing equipment to confirm that the cable is not powered, in order to avoid electric shock or damage to the module. Strictly follow the module wiring diagram and relevant safety standards for wiring: ① Power wiring: According to the module power type (AC/DC), connect the power supply to the corresponding terminal, ensure that the positive and negative poles/phase neutral wires are connected correctly, and avoid reverse connection; Install a prepared circuit breaker at the power input end, in a convenient location near the module for operation, and label the switch as the module power control switch; The power cable should be kept at a distance of ≥ 1cm from other signal lines to avoid interference; ② Sensor/transmitter wiring: According to the wiring method corresponding to the parameter type, connect the sensor/transmitter cable to the input channel terminal of the module. The temperature sensor adopts a three wire or four wire wiring system (to ensure measurement accuracy), and the 4-20mA transmitter should pay attention to the correct connection of the positive and negative poles. The shielding layer should be grounded at one end (near the module end) to reduce electromagnetic interference; If it involves sensors for pipeline installation, the straight pipe section requirements must be followed (such as upstream straight pipe section ≥ 10D, downstream ≥ 2D, where D is the sensor diameter); ③ Output wiring: Connect the actuator (regulating valve, frequency converter, etc.) to the output terminal of the module. The relay output should pay attention to the load voltage and current not exceeding the rated value. Inductive loads (such as motors) should be connected in parallel with freewheeling diodes; The output terminal of the module relay is functionally insulated, and reinforced insulation should be provided externally according to requirements; Shielded cables should be used for analog output wiring and kept away from power cables; ④ Communication wiring: Connect the communication cable to the RS485 communication interface of the module, confirm that lines A and B are connected correctly, and install terminal resistors (120 Ω) at both ends of the bus to reduce signal reflection; The wiring must comply with NEC (ANSI/NFPA 70) or the wiring construction standards of the installation area.
4. Debugging steps
① Power on self-test: Connect the system power supply, the module automatically enters self-test mode, observe whether the power indicator light (green) is on normally, and whether the status indicator lights of each channel have no abnormal alarms (the alarm light is red and does not light up normally); If the self-test fails, power off and check the power wiring and module hardware; ② Parameter configuration: Enter the configuration interface through the local buttons of the upper computer software or module, and sequentially configure various channel parameter types, measurement ranges, control target values, PID parameters (or enable self-tuning function), alarm upper and lower limits and other parameters. After configuration is completed, save and restart the module; ③ Accuracy calibration: Connect the standard signal source to each channel, compare the measured values of the module with the standard values, and if there is a deviation, perform zero and full-scale calibration through the upper computer software to ensure that the measurement accuracy meets the requirements; ④ Control testing: Simulate on-site process conditions, observe whether the module can output control signals based on the deviation between measured parameters and set values, whether the actuator responds normally, whether the parameters can be stable near the set values, and whether there is no obvious overshoot or oscillation; If the control effect is poor, optimize the PID parameters; ⑤ Fault simulation test: Simulate sensor disconnection, short circuit, parameter exceeding threshold and other fault scenarios, check whether the module can accurately trigger alarms and output protection signals, and whether the fault information can be uploaded to the upper computer normally.
Key points of maintenance and upkeep
To extend the service life of the module and ensure the accuracy and stability of process control, it is necessary to follow the principle of "preventive maintenance" and conduct regular maintenance:
Regular cleaning: Clean the module every 3 months. After disconnecting the power, use compressed air to remove dust from the surface, heat dissipation holes, and interfaces of the module. If there is oil stains, wipe them with anhydrous ethanol to prevent cleaning agents from entering the interior of the module;
Regular inspection: Conduct monthly inspections on the operation status of the module, check whether the power supply voltage is stable, whether the circuit breaker is working properly, whether the wiring terminals are loose or oxidized (after oxidation, they need to be cleaned or replaced in a timely manner), whether the cables are aging and damaged, and whether the temperature level meets the requirements. Check whether the sensors/transmitters are normal (without looseness, disconnection, or corrosion); Observe whether the parameter displays of each channel are consistent with the actual on-site status;
Environmental maintenance: Regularly check the temperature, humidity, and cleanliness of the installation environment to ensure compliance with the module's operating requirements (0 ℃~50 ℃, 20%~90% RH without condensation), and avoid the module from being affected by vibration, impact, and corrosive gases; Check the sealing of the control cabinet to ensure that the rear shell, terminals, and back wiring of the module are completely sealed;
Accuracy calibration: The module is calibrated every 6 months, and the measurement accuracy of each channel is checked using a standard signal source. If the deviation exceeds the allowable range, calibration is carried out in a timely manner, and relevant data is recorded after calibration; The calibration process must strictly follow the operating specifications in the product manual;
Parameter backup: Regularly backup the configuration parameters of the module (recommended once a month) to avoid parameter loss due to module failures or unexpected power outages; Simultaneously record the content of each maintenance (maintenance time, discovered problems, handling measures, calibration data, etc.), establish maintenance files, and provide reference for subsequent maintenance;
Maintenance of power supply and protection components: Check the stability of the output voltage of the power module and the status of the circuit breaker. If there are voltage fluctuations or abnormal circuit breakers, promptly repair or replace them to avoid damage to the internal circuit of the module caused by abnormal voltage or overcurrent.

- User name Member Level Quantity Specification Purchase Date
- Satisfaction :
-