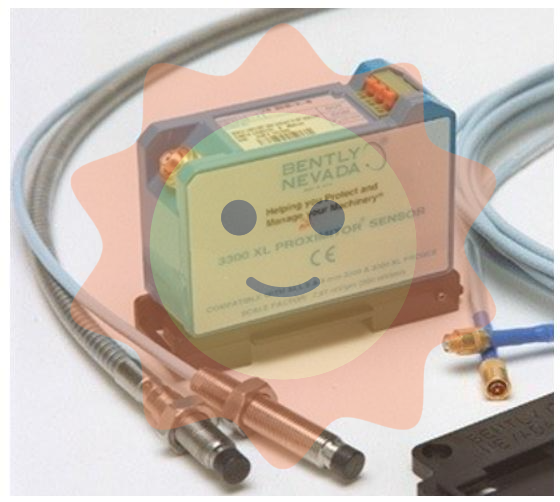
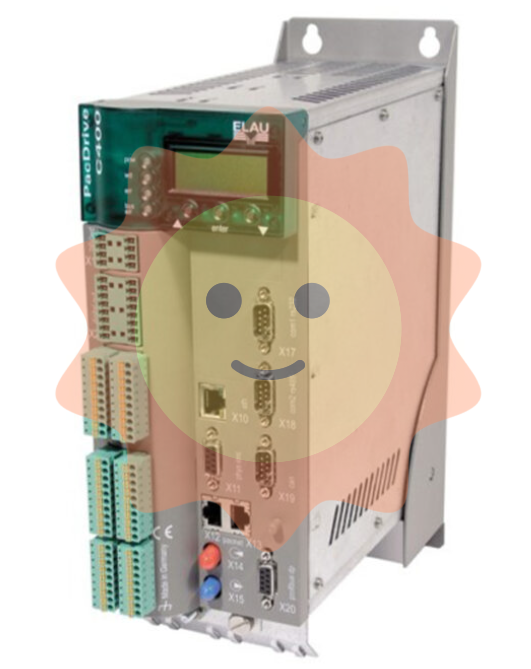
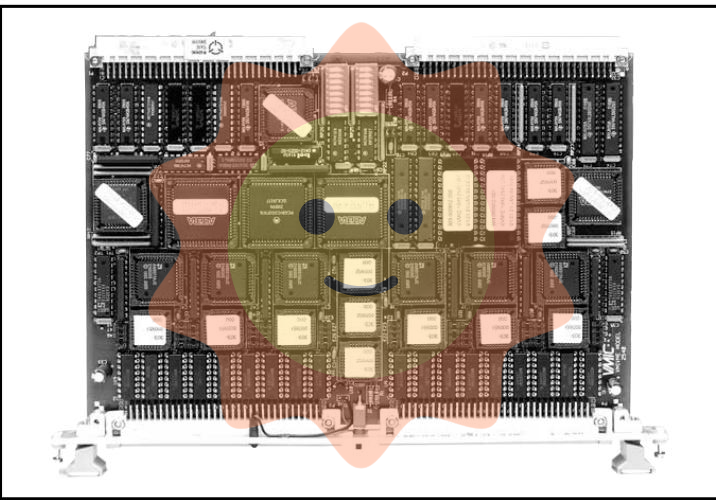
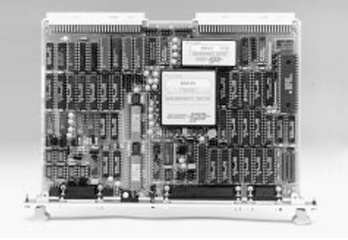
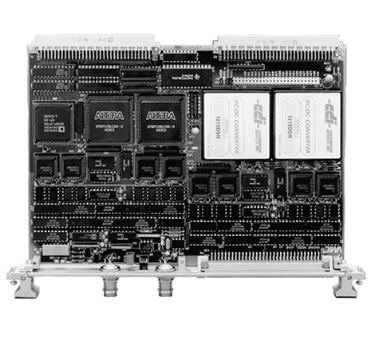
ABB 3HAB3700-1 Measuring board
ABB 3HAB3700-1 Measuring board
Overview
The ABB 3HAB3700 - 1 Measuring Board is a critical component in ABB's equipment, especially in systems that require accurate measurement of various electrical and physical parameters. It is designed to interface with sensors and other devices to collect and process measurement data.
Functionality and Features
Measurement Capabilities
Analog Signal Measurement: The board is capable of measuring a range of analog signals. These can include voltage, current, resistance, and other electrical parameters. For example, it can measure the output voltage of a power supply or the current flowing through a circuit. The measurement range and resolution are carefully designed to provide accurate readings. The resolution might be in the millivolt or milliampere range, depending on the specific design and application requirements.
Physical Quantity Measurement: In addition to electrical parameters, it can also measure physical quantities such as temperature, pressure, and strain. This is achieved through appropriate sensors that convert the physical quantity into an electrical signal, which the measuring board can then process. For example, a thermocouple can convert temperature into a voltage signal that the board can measure and convert back to a temperature value.
Signal Conditioning and Processing
The 3HAB3700 - 1 Measuring Board performs signal - conditioning functions. It can amplify, filter, and convert the input signals to a format suitable for further processing or for transmission to other components. For instance, if the input signal from a sensor is weak or noisy, the board can amplify and filter it to improve the signal - to - noise ratio. It can also perform analog - to - digital conversion (ADC) to convert the analog measurement signals into digital values for more precise processing and storage.
Data Transmission and Communication
The measuring board has the ability to transmit the measured data to other parts of the system. It can communicate with a central - control unit, such as a Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) or a Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) system. The communication interfaces supported can include standard protocols like Modbus, Profibus, or Ethernet/IP. This allows for seamless integration into an industrial - automation or - monitoring system, enabling the measured data to be used for control, analysis, and decision - making.
Calibration and Accuracy
To ensure the accuracy of the measurements, the board can be calibrated. Calibration procedures involve adjusting the measurement parameters to match known reference values. The board may have built - in calibration features or may require external calibration equipment. The accuracy of the measurements is typically specified as a percentage of the full - scale reading or in absolute terms, such as ±0.1% of the measured value.
Technical Specifications
Measurement - Range Specifications
For each measurable parameter, the board has defined measurement ranges. For example, the voltage - measurement range could be from - 10V to +10V, and the current - measurement range from - 5A to +5A. The temperature - measurement range might cover a wide span, such as from - 200°C to +1000°C, depending on the type of temperature - sensor interface. The resistance - measurement range and other physical - quantity - measurement ranges are also precisely specified.
Resolution and Precision
The resolution of the measurements is an important specification. For digital - converted measurements, it is usually specified in bits. For example, an ADC with a 12 - bit resolution can provide more precise measurements than an 8 - bit ADC. The precision of the board also takes into account factors such as the accuracy of the internal components, the stability of the signal - conditioning circuitry, and the noise level. The combined effect of these factors determines the overall precision of the measurements.
Communication - Interface Specifications
The communication interfaces have their own set of technical details. For each supported protocol, the board has details such as the maximum data - transfer rate, the number of supported connections, and the physical - connection requirements (e.g., Ethernet - port type, RS - 485 - termination requirements). These specifications ensure that the measuring board can effectively communicate with other devices in the industrial - network environment.
Applications
Industrial Automation and Control
In industrial - automation systems, the ABB 3HAB3700 - 1 Measuring Board is used to monitor and control various processes. It can measure the power consumption of motors, the temperature of industrial ovens, and the pressure in hydraulic systems. The measured data can then be used to adjust the operation of equipment such as conveyor - belts, robotic - arms, and pumps to optimize the production process and ensure the safety and quality of products.
Power - Generation and - Distribution
In power - generation and - distribution systems, the measuring board is used to monitor the performance of generators, transformers, and transmission lines. It can measure electrical parameters such as voltage, current, and power - factor. The data is used for grid - stability analysis, load - management, and fault - detection. For example, it can detect over - voltage or over - current conditions in a power - substation and send an alarm or take corrective action.
Research and Development Laboratories
In research and development settings, the 3HAB3700 - 1 Measuring Board is a valuable tool for experimental setups. It can be used to measure and record a wide range of physical and electrical phenomena. For example, in a materials - science laboratory, it can measure the strain and temperature of a test - specimen during a mechanical - or - thermal - testing process.
- User name Member Level Quantity Specification Purchase Date
- Satisfaction :
-









Email:wang@kongjiangauto.com