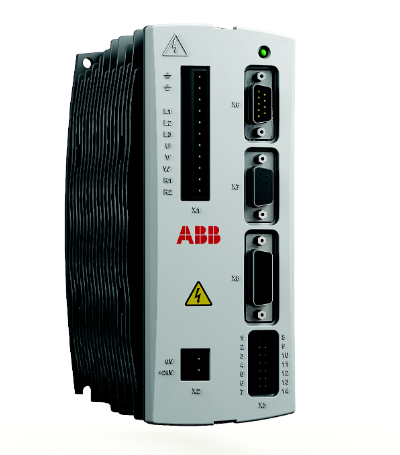
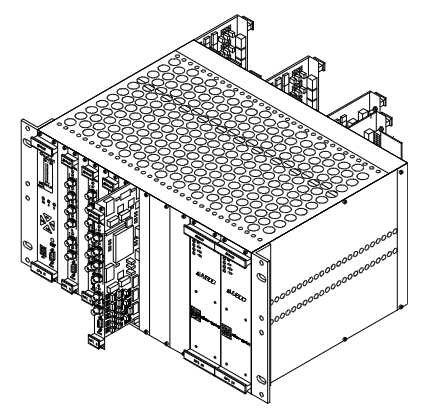
ABB CI627A (order number: 3BSE017457R1) is a high-performance communication interface module designed specifically for industrial automation control systems, belonging to the I/O module family of control systems such as ABB Advant OCS or AC 800M. Its core positioning is to serve as a "data bridge" between the control system and external devices and networks, enabling efficient data exchange under different communication protocols, ensuring accurate transmission of control instructions and real-time feedback of on-site data in industrial production processes, and providing critical support for the stable operation of automation systems.
ABB CI627A 3BSE017457R1 Communication Interface
Product Overview
ABB CI627A (order number: 3BSE017457R1) is a high-performance communication interface module designed specifically for industrial automation control systems, belonging to the I/O module family of control systems such as ABB Advant OCS or AC 800M. Its core positioning is to serve as a "data bridge" between the control system and external devices and networks, enabling efficient data exchange under different communication protocols, ensuring accurate transmission of control instructions and real-time feedback of on-site data in industrial production processes, and providing critical support for the stable operation of automation systems.
This module, with ABB's profound technical accumulation in the field of industrial control, has high reliability, strong anti-interference ability, and flexible configuration characteristics. It can adapt to the harsh operating environment of various complex industrial scenarios such as metallurgy, chemical industry, power, and papermaking, and is one of the core components for improving the scalability and compatibility of control systems.
Core functions and roles
2.1 Multi protocol data conversion and transmission
The core function of the CI627A module is to achieve bidirectional data conversion and transparent transmission between different communication protocols. It can parse and convert proprietary protocols within the control system (such as ABB's Control Network protocol) with external common industrial protocols (such as Modbus, Profibus DP, etc., specific supported protocols need to be confirmed with configuration versions), enabling seamless data exchange between the control system and third-party devices (such as sensors, actuators, smart meters, other brands of PLCs) and upper monitoring systems. For example, the pressure, temperature, and other data collected by on-site instruments can be converted into a format recognizable by the system and uploaded to the controller. At the same time, the control instructions issued by the controller can be converted into a protocol format supported by external devices to ensure the effective execution of control logic.
2.2 Communication link management and redundancy guarantee
The module is equipped with a comprehensive communication link monitoring mechanism, which can monitor the data transmission status in real time. When abnormal situations such as link interruption, data packet loss, or error occur, an alarm signal can be quickly triggered and fed back to the control system, making it easy for operation and maintenance personnel to troubleshoot in a timely manner. For industrial scenarios that require high availability, some configurations of CI627A support communication redundancy function. Through a dual link backup design, when the main communication link fails, it can automatically switch to the backup link to ensure the continuity of data transmission and reduce production risks caused by communication interruptions.
2.3 System Expansion and Compatibility Enhancement
In the architecture of ABB control systems, the CI627A module greatly enhances the system's scalability. Through this module, the control system can easily access different types of external devices and networks without the need for significant modifications to the core control logic, reducing the cost of system upgrades and renovations. At the same time, it is compatible with multiple series of controllers such as ABB Advant OCS and AC 800M, with good downward and upward compatibility, making it easy to integrate and transition between old and new systems.
2.4 Data caching and real-time optimization
To meet the sudden and real-time requirements of data transmission in industrial sites, the CI627A module has a built-in data caching unit with a certain capacity. When external device data is suddenly transmitted or the system load is high, the module can temporarily store data to avoid data loss; At the same time, by optimizing data processing algorithms, the delay of protocol conversion is reduced, ensuring the real-time transmission of key control data and meeting the strict requirements of industrial control for response speed.
Key technical parameters
Order Number
3BSE017457R1
Module Model
CI627A
Communication interface type
RS-485/RS-232 (depending on configuration), Industrial Ethernet (optional)
Supported Protocols
Modbus RTU/TCP, Profibus DP, ABB Control Network, etc
Data transmission rate
RS-485: up to 115.2kbps; Ethernet: up to 100Mbps (adaptive)
Working Voltage
DC 24V ±10%
Working temperature range
-25℃ ~ +60℃
relative humidity
5%~95% (non condensing)
Installation method
DIN rail installation or rack mounted installation
Protection level
IP20 (module itself), requires coordination with the control cabinet to achieve higher protection
Connection method with controller
Through ABB dedicated I/O bus (such as PROFIBUS DP or ABB S800 I/O bus)
Installation and configuration points
4.1 Installation precautions
-The module should be installed in a well ventilated control cabinet away from strong electromagnetic interference sources such as high-power motors and frequency converters, avoiding direct sunlight and liquid erosion.
-When installing with DIN rails, it is necessary to ensure that the rails are firmly fixed, and at least 5mm of heat dissipation space should be reserved between the module and adjacent equipment.
-Before wiring, disconnect the module power supply and strictly follow the definition of the wiring terminals, especially the positive and negative terminals of the power supply and the A/B ends of the communication line, to avoid module damage caused by reverse connection.
4.2 Configuration Process
1. Hardware connection: Complete the wiring between the module and the controller, external devices, and power supply to ensure smooth physical links.
2. Software access: Add the module to the control system project through ABB's dedicated configuration software (such as Control Builder M or 800xA Engineering Studio), and automatically identify the module model and firmware version.
3. Protocol configuration: Based on the communication protocol type of the external device, configure the communication parameters of the module in the software, including protocol type, data transmission rate, parity bit, slave address (such as Modbus slave number), etc.
4. Data Mapping: Define the data exchange area between the module and the controller, map the input/output data of external devices to the I/O variables of the controller, and achieve bidirectional data exchange.
5. Test verification: After the configuration is completed, start the system for communication testing, check the accuracy and real-time performance of data transmission, and troubleshoot issues such as link interruptions and data errors.
Common faults and troubleshooting methods
The module power indicator light is not on
Power supply not connected, abnormal power supply voltage, loose wiring, or module damage
1. Check if the power supply wiring is secure and measure if the power supply voltage is within the range of DC 24V ± 10%; 2. After replacing the power circuit and retesting, if it still does not light up, it may be a module failure and the module needs to be replaced.
Communication indicator light flashing abnormally (normally off or on)
Communication line wiring errors, mismatched communication parameters, external device failures, or link interruptions
1. Check if the A/B terminals of the communication line are wired correctly and if there are any loose connections or short circuits; 2. Verify whether the communication parameters (rate, checksum, address) between the module and external devices are consistent; 3. Test external devices separately and troubleshoot equipment malfunctions.
Data transmission error or loss
Electromagnetic interference, long transmission distance, data cache overflow, or protocol configuration errors
1. Check whether the communication line uses shielded wire and whether the shielding layer is reliably grounded; 2. Shorten communication distance or increase repeaters; 3. Optimize system load and reduce data transmission volume; 4. Recheck the protocol configuration and data mapping relationship.
The module cannot be recognized by the controller
Bus connection failure between module and controller, incompatible firmware version of module
1. Check if the bus cable connection is secure and replace the bus cable for testing; 2. Check the firmware version of the module through software. If it is not compatible with the controller, upgrade the module firmware.
Maintenance and upkeep suggestions
-Regularly (quarterly) inspect the appearance of the module, clean the dust on the surface of the module and the wiring terminals, and check whether the wiring is loose.
-Regularly check the running status and firmware version of modules by configuring software, update firmware in a timely manner to fix known vulnerabilities, and improve module performance.
-Avoid plugging and unplugging wiring or making configuration modifications while the module is live, to prevent static electricity or current shock from damaging the module.
-Establish a module operation file to record the installation time, fault conditions, and maintenance records of the module, providing reference for subsequent operation and maintenance.

- User name Member Level Quantity Specification Purchase Date
- Satisfaction :
-